Organization of external financial relations
Lecture 1
Lecture topic: "The essence of the finance of organizations"
Lecture sections:
1. Financial relations of organizations. Functions of finance.
2. Financial resources of organizations. Principles of organization of finance.
3. Financial mechanism of organizations.

SECTION 1. FINANCIAL RELATIONSHIPS OF ORGANIZATIONS(ENTERPRISES).FUNCTIONS OF FINANCE.
An organization (enterprise) (French organization, from Latin Organiso - I give a slim look) is an independent business entity with the rights legal entity producing products, goods, providing services, performing work, engaged in various types of economic activity, the purpose of which is to meet social needs, make profits and increase capital.
An organization (enterprise) can carry out any of the types entrepreneurial activity or all types at the same time.
In the process of entrepreneurial activity, organizations (enterprises) have certain economic relations with its counterparties: suppliers and buyers; partners in joint activities; unions and associations; financial and credit system, etc., accompanied by the movement of funds.
WHAT IS THE MATERIAL BASIS OF FINANCE?
The material basis of finance is money. However necessary condition the emergence of finance - the real movement of funds: their accumulation, spending and use at all levels of management. It is due to mutual settlements between business entities, with budgetary and credit systems, in the process of which centralized and decentralized funds of funds are created and used.
WHAT IS THE ESSENCE OF FINANCE?
In foreign literature, finance is considered as cash flows (processes associated with the movement of money).
In the works of domestic scientists, the essence of finance is usually expressed as a set of economic relations that arise during the formation, distribution and use of funds of funds. Behind Lately there were other definitions of the content of finance, close to foreign ones. The ambiguous interpretation of the definition indicates the complexity and multilateral nature of finance.
WHAT IS THE OBJECT OF FINANCE?
The object of finance is not only the processes arising from the movement of funds, but also mediating them. economic relations.
WHAT IS ORGANIZATIONAL FINANCE?
The finances of organizations (enterprises) are a set of monetary relations that mediate economic relations related to the organization of production and the sale of products, the performance of work, the provision of services, the formation of financial resources, and the implementation of investment activities.
As an economic category, the finance of organizations (enterprises) is a system of financial or monetary relations that arise in the process of formation of fixed and working capital, cash funds of an organization (enterprise) and their use. They are distributive and redistributive in nature and have a direct impact on the reproductive process.
The finances of organizations (enterprises) are an independent link financial system serving material production and services. It is in this link of the financial system that a significant part of the national income of the country is formed, they are distributed within organizations and partially redistributed through the budget system and the system of extra-budgetary funds.
The sphere of financial relations of organizations (enterprises) is diverse and has significantly expanded and changed with the development of real market relations, the introduction of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.

IN WHAT AREAS CAN FINANCIAL RELATIONS OF ORGANIZATIONS BE GROUPED?
Depending on the economic content, the financial relations of organizations (enterprises) can be grouped into the following areas:
Arising between the founders at the time of the creation of the organization (enterprise) in the formation of the authorized (reserve, share) capital. In turn, the authorized (reserve, share) capital serves as the initial source of formation production assets, acquisition of intangible assets;
Between individual organizations (enterprises) associated with the production and sale of products, the emergence of newly created value. These include financial relations between the supplier and the buyer of raw materials, materials, finished products etc., relations with construction organizations during the period of investment activity, with transport organizations during the transportation of goods, with communications enterprises, customs, foreign firms, etc. These relationships are fundamental to economic activity, since the gross domestic product and national income are created in the sphere of material production. They account for the largest volume of payments; the financial result of enterprises' activities largely depends on their effective organization;
Between organizations (enterprises) and their divisions - branches, workshops, departments, teams - in the process of financing costs, distribution and redistribution of profits, working capital. This group of relations influences the organization and rhythm of production;
Between organizations (enterprises) and their employees in the distribution and use of income, the issuance and placement of shares and bonds of the enterprise, the payment of interest on bonds and dividends on shares, the recovery of fines and compensation for the damage caused material damage, withholding taxes from individuals. Their organization affects the efficiency of the use of labor resources;
Between organizations (enterprises) and higher organizations, within financial and industrial groups, within the holding, with unions and associations, of which the organization (enterprise) is a member. These relations arise in the formation, distribution and use of centralized trust funds and reserves for financing target industry programs, conducting marketing research, research work, organizing exhibitions, providing financial assistance on a repayable basis for the implementation of investment projects and replenishment of working capital, during reorganization. This group of relations, as a rule, is associated with the intra-industry redistribution of funds and is aimed at supporting and developing organizations (enterprises);
Between organizations (enterprises) and the financial system of the state when paying taxes and other obligatory payments to budgets of different levels, forming off-budget funds, providing tax benefits, applying penalties, receiving appropriations from the budget. The organization of this group of relations determines the financial condition of organizations (enterprises) and the formation of the revenue base of budgets of different levels;
Between organizations (enterprises) and banking system in the process of keeping money in commercial banks, organizing cashless payments, obtaining and repaying loans, paying interest on loans, buying and selling foreign currency, and providing other banking services. The financial condition of enterprises also depends on the organization of these relations;
Between organizations (enterprises) and insurance companies and organizations arising from property insurance, certain categories employees, commercial and entrepreneurial risks;
Between organizations (enterprises) and investment institutions in the course of investment placement, privatization and other business entities.
WHAT IS THE MATERIAL BASIS OF FINANCIAL RELATIONS?
Each of the listed groups of financial relations of organizations has its own characteristics and scope, methods of implementation. However, all of them are bilateral in nature and their material basis is the movement of funds, thanks to their use, cash flows are formed, they are accompanied by the formation authorized capital organizations (enterprises), the circulation of funds begins and ends, the formation and use of monetary funds for various purposes, financial reserves and, in general, the financial resources of the organization.
WHAT FUNCTIONS DO FINANCE PERFORM?
The essence of finance is most fully manifested in their functions. There is no consensus among economists about the functions of finance organizations (enterprises). In the economic literature, there is currently a wide variation in the definition of functions, both in terms of their number and content. Unity is noted only in two functions: distributive and control.
Many literary sources indicate the following functions: the formation of capital, income and cash funds; use of income and funds, resource-saving, control, etc.
Obviously, the listed functions in their content have the same nature and purpose - providing the necessary sources of financing for the activities of the organization (enterprise).
Most economists recognize that business finance has three main functions.
1. FUNCTION OF FORMING CAPITAL AND INCOME OF ORGANIZATION (ENTERPRISE);
2. FUNCTION OF DISTRIBUTION AND USE OF INCOME;
3. CONTROL FUNCTION.

All functions closely interact with each other.
1. When finance performs the function of capital formation, the initial capital of the organization (enterprise) is formed, its increment; attraction of funds from various sources in order to form the volume of financial resources necessary for entrepreneurial activity, accompanied by the movement of funds. IN modern conditions Not all funds of the enterprise are stock in nature. The enterprise independently decides the issue of formation of cash funds and reserves.
2. The distribution and use of income at the level of organizations (enterprises) is manifested in the distribution of proceeds from the sale of products and income from other activities in value terms by areas of use, determining the main cost proportions in the process of distributing income and financial resources, ensuring the optimal combination of interests of individual producers, enterprises and organizations and the state as a whole.
3. The objective basis of the control function is the cost accounting for the production and sale of products, the performance of work, the provision of services, the formation of income and cash funds of the enterprise and their use. With the help of this function, control is exercised over the timely receipt of proceeds from the sale of products and the provision of services, the formation and intended use of monetary funds and, in general, the financial resources of the organization, changes financial indicators, compliance with tax laws, etc.
WHAT RELATIONSHIPS ARE BASED ON FINANCE?
At the heart of finance are distributive relations that provide sources of financing for the reproduction process and thereby link together all phases of the reproduction process: production, exchange and consumption. However, the amount of income received by an organization (enterprise) determines the possibilities of its further development. Efficient and rational management of the economy predetermines the possibilities for its further development. And vice versa, disruption of the uninterrupted circulation of funds, the growth of costs for the production and sale of products, the performance of work, the provision of services reduce the income of the organization (enterprise) and, accordingly, the possibility of its further development, competitiveness and financial stability. In this case, the control function of finance testifies to the insufficient impact of distribution relations on production efficiency, to shortcomings in management. financial resources, organization of production. Ignoring such evidence can lead to the bankruptcy of the enterprise. The implementation of the control function is carried out with the help of financial performance indicators of enterprises, their assessment and the development of necessary measures to improve the efficiency of distribution relations. The control function is carried out both directly in the organization and by its owners, counterparties, credit and government bodies.
CASH FUNDS AND RESERVES OF THE ORGANIZATION (ENTERPRISE).
The formation of monetary funds of an organization (enterprise) begins from the moment of its creation; it is the most important aspect of the organization. In accordance with the law, the organization creates an authorized capital. His minimum size It is established by law depending on the form of ownership and determines the minimum amount of property of an enterprise that guarantees the interests of its creditors.
The authorized capital is the main initial source of own funds of the organization (enterprise). In accordance with the Civil Code, the size of the authorized capital cannot be less than the amount that guarantees the interests of its creditors. It serves as a source of formation of the main and working capital, which in turn are directed to the acquisition of fixed assets, intangible assets, working capital.
WHAT IS THE OWN CAPITAL OF THE ORGANIZATION (ENTERPRISE)?
Equity capital is the difference between the total assets of an organization (enterprise) and its liabilities, that is, its debts. Equity capital, in turn, is divided into
PERMANENT part - authorized capital and
VARIABLE, the size of which depends on financial results activities of the organization (enterprise).

WHAT IS INCLUDED IN VARIABLE CAPITAL?
VARIABLE CAPITAL includes:
EXTRA CAPITAL,
RESERVE CAPITAL,
RETAILED EARNINGS AND
SPECIAL FUNDS.

EXTRA CAPITAL is created due to the increase in the value of property as a result of the revaluation of fixed assets; share premium (the excess of the sale price of shares of the nominal price minus the costs of their sale); gratuitously received monetary and material values for production purposes. It can be used to pay off the depreciation of property, revealed as a result of its revaluation, to pay off losses resulting from the gratuitous transfer of property to other enterprises and persons, to increase the authorized capital, to pay off the loss identified based on the results of the enterprise's work for the reporting year.
Result and ultimate goal of economic activity commercial organization- profit. After tax payments, profit is formed, which remains at its disposal, from which are formed: reserve capital (fund) and other similar reserves, as well as an accumulation fund and a consumption fund.
RESERVE CAPITAL (RESERVE FUND)- the monetary fund of the organization (enterprise), which is formed in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation and constituent documents. The source of its formation is deductions from the profits remaining at the disposal of the organization (enterprise). In all cases, the maximum amount of reserve capital cannot exceed the amount determined by the owners of the organization and fixed in its founding documents. For joint-stock companies(open and closed type) and organizations with foreign investments, the formation of reserve capital is determined by law. Its value must be at least 5% of their authorized capital. Thus, the maximum amount of reserve capital is directly dependent on the amount of authorized capital. The reserve capital is formed by mandatory annual deductions until it reaches the amount established by the Charter of the company. It is intended to cover the losses of the reporting year, the payment of dividends in the absence or insufficiency of the profit of the reporting year for these purposes, the redemption of the company's shares. In world practice, the maximum amount of reserve (reserve) capital ranges from 10 to 40% of the authorized capital. The availability of reserve capital for an economic entity is the most important factor in the stability of its activities in a market economy, a condition for ensuring sustainable financial condition.
Reserve funds also include reserves for the depreciation of investments in securities, reserves for doubtful debts, reserves for future expenses and others created in joint-stock companies to redeem bonds and buy back shares.
RETAINED EARNINGS- the profit of the organization remaining after paying taxes, forming a reserve fund, paying dividends, and used for reinvestment purposes.
SAVINGS FUND- funds intended for the development and expansion of production. The use of these funds is associated both with the development of the main production in order to increase the property of the enterprise, and with financial investments for profit.
CONSUMPTION FUND- funds allocated for social needs, financing of non-production facilities, one-time incentives, compensation payments and other similar purposes.
MONETARY FUND is formed in organizations that sell products for export and receive foreign exchange earnings.
SINKING FUND is created in the process of using capital and, by its economic nature, is intended to finance the simple reproduction of fixed assets. Use of the variable part equity to fulfill payment obligations to the budgets of different levels and banks is carried out in a non-fund form.
SECTION 2. FINANCIAL RESOURCES OF THE ORGANIZATION (ENTERPRISE). PRINCIPLES OF THE ORGANIZATION OF FINANCE.
WHAT ARE THE FINANCIAL RESOURCES OF THE ORGANIZATION?
The financial resources of an organization (enterprise) are a set of own cash and non-cash income and receipts from outside (attracted and borrowed), accumulated by an organization (enterprise) and intended to fulfill financial obligations, finance current costs and costs associated with the development of production.

The notion should be highlighted "CAPITAL"- part of the financial resources invested in production and generating income at the end of the turnover. In other words, capital is a converted form of financial resources.
According to the sources of education, financial resources are divided into own (internal) and attracted on different terms (external), mobilized in the financial market and received in the order of redistribution (Figure 1).
1. The main share in own financial resources is PROFIT, which remains at the disposal of the organization (enterprise) and is distributed by decision of the governing bodies. Depending on the financial policy of the organization (enterprise), the profit remaining at its disposal can be used as follows:
2) fully invested in other projects not related to the activities of the organization;
3) reinvested in the development of the organization in full;
4) is distributed in the first three directions.
Obviously, the latter option is the most preferable, it is only important to observe economically justified proportions of its distribution.
The second most important source of own financial resources are depreciation deductions - a monetary expression of the cost of depreciation of fixed production assets and intangible assets. They are of a dual nature, as they are included in the cost of production and then, as part of the proceeds from the sale of products, they go to the settlement account of the enterprise, becoming an internal source of financing for both simple and expanded reproduction.

Figure 1. The composition of the financial resources of the organization (enterprise).
The accumulated depreciation deductions form the DAMORIZATION FUND intended for the reproduction of depreciated fixed assets.
Not all profit remains at the disposal of the organization (enterprise), part of it in the form of taxes and other obligatory payments goes to the budget system. The profit remaining at the disposal of the organization (enterprise) is distributed by the decision of the governing bodies for the purpose of accumulation and consumption and reserves. The profit allocated for accumulation is used for the development of production and contributes to the growth of the property of the enterprise. Profit directed to consumption is used to solve social problems.
Attracted, or external, sources of formation of financial resources can be divided into own, borrowed, received in the order of redistribution and budget allocations. This division is due to the form of capital investment.
In the capital market, there are two options for raising funds:
EQUITY FINANCING and
DEBT FINANCING.
1) With equity financing, the issue and placement of its shares on the stock market is carried out.
2) The second option involves the issuance and placement of bonds (term securities), that is, the provision of capital on the basis of a bonded loan. If external investors invest money as entrepreneurial capital, then the result of such an investment is the formation of attracted own financial resources.
ENTREPRENEURIAL CAPITAL is the capital invested in the authorized capital of another organization (enterprise) in order to make a profit or participate in the management of an organization (enterprise).
LOAN CAPITAL is transferred to an organization (enterprise) for temporary use on the terms of payment and repayment in the form of bank loans issued for different periods, funds of other organizations (enterprises) in the form of promissory notes, bonded loans.
Funds raised in the financial market include funds from the sale of own shares and bonds, as well as other types of securities.
Funds received in the order of redistribution include insurance indemnity for occurred risks, financial resources received from concerns, associations, parent companies, dividends and interest on securities of other issuers, budget subsidies.
Budget allocations can be used both on a non-refundable and reimbursable basis. As a rule, they are allocated for financing government orders, individual investment programs or as short-term state support for organizations (enterprises) whose products are of national importance.
Financial resources are used by the organization (enterprise) in the process of production and investment activities. They are in constant motion and remain in monetary form only in the form of cash balances on current account in a commercial bank and at the cash desk of an organization (enterprise). taking care of financial stability and a stable place in the market economy, the organization (enterprise) distributes its financial resources by type of activity and in time. The deepening of these processes in the modern market economy leads to the complication of financial work, the use of special financial instruments in practice.
PRINCIPLES OF THE ORGANIZATION OF FINANCE.
WHAT ARE THE PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIZING FINANCE?
In the economic literature there is no unity about the principles of organizing finance. Their number differs significantly in different economic textbooks and teaching aids. Most authors believe that the financial activity of an organization (enterprise) is based on the following principles (Figure 2):
ECONOMIC INDEPENDENCE;
SELF-FINANCING;
LIABILITY;
INTEREST IN PERFORMANCE RESULTS;
FORMATION OF FINANCIAL RESERVES;
EXERCISING CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL AND ECONOMIC ACTIVITIES.

Figure 2. Principles of organizing finance.
WHAT IS ECONOMIC INDEPENDENCE?
ECONOMIC INDEPENDENCE lies in the fact that, regardless of the organizational and legal form of management, an organization (enterprise) independently determines its economic activity, the direction of investment of funds in order to make a profit. In a market economy, the rights of organizations (enterprises) in the field of commercial activities investments, both short-term and long-term. The market stimulates organizations (enterprises) to search for more and more new areas of capital investment, the creation of flexible industries that meet consumer demand. However, one cannot speak of complete economic independence. The state regulates certain aspects of the activities of enterprises. Thus, the relationship of enterprises with budgets of different levels is regulated by law, off-budget funds; the state determines the depreciation and tax policy.
WHAT DOES THE PRINCIPLE OF SELF-FINANCING MEAN?
SELF-FINANCING means full payback of costs for production and sale of products, investment in the development of production at the expense of own funds and, if necessary, bank and commercial loans. The implementation of this principle is one of the main conditions for entrepreneurial activity, which ensures the competitiveness of an organization (enterprise). In developed market countries, companies with high level self-financing specific gravity own funds exceeds 70%. The main own sources of financing of organizations (enterprises) in the Russian Federation include profit and depreciation. But the total amount of own funds is not sufficient for the implementation of serious investment programs. Currently, not all organizations (enterprises) are able to fully implement this principle.
Organizations (enterprises) of a number of industries National economy, producing products and providing services necessary for the consumer, for objective reasons, cannot ensure its sufficient profitability. These include individual enterprises of urban passenger transport, housing and communal services, Agriculture, defense industry. Such organizations (enterprises) receive allocations from the budget on different terms.
WHAT DOES THE LIABILITY PRINCIPLE MEAN?
MATERIAL RESPONSIBILITY means the presence of a certain system of responsibility for the conduct and results of economic activity. financial methods implementations of this principle are different for individual organizations(enterprises), their managers and employees. In accordance with Russian law, organizations (enterprises) that violate contractual obligations (terms, product quality), settlement discipline, allow untimely repayment of short-term and long-term loans, late repayment of bills, violation of tax laws, pay penalties, forfeits, fines. In case of inefficient activity, the bankruptcy procedure may be applied to the organization (enterprise).
For leaders of an organization (enterprise) the principle liability implemented through a system of fines in cases of violation by the organization (enterprise) of tax legislation.
Individual employees of an organization (enterprise) are subject to a system of fines, deprivation of bonuses, dismissal from work in cases of violation of labor discipline, marriage.
HOW IS THE PRINCIPLE OF INTEREST IN PERFORMANCE RESULTS IMPLEMENTED?
INTEREST IN PERFORMANCE RESULTS determined by the main purpose of entrepreneurial activity - profit. The interest in the results of economic activity is equally inherent in the employees of the organization (enterprise), the organization itself (enterprise) and the state as a whole.
At the level individual workers the implementation of this principle can be ensured by decent wages at the expense of the payroll fund and part of the profit allocated for consumption in the form of bonuses, remuneration based on the results of work for the year, remuneration for long service, financial assistance and other incentive payments, as well as payments to employees of a joint-stock company interest on bonds and dividends on shares.
For an organization (enterprise), this principle can be implemented by the government pursuing an optimal tax policy and observing economically justified proportions in the distribution net profit consumption fund and accumulation fund.
The interests of the state are ensured by the profitable activities of the organization (enterprises), the completeness and timeliness of settlements with the budget for tax payments.
WHAT IS THE PRINCIPLE FOR FORMING FINANCIAL RESERVES?
The provision of financial reserves is associated with the need to form them to ensure entrepreneurial activity, which is always associated with risk due to possible fluctuations in market conditions. In a market economy, the consequences of the risk fall directly on the entrepreneur, who independently makes decisions, implements the developed programs with the risk of non-return of invested funds. Financial investments organizations (enterprises) are also associated with the risk of receiving an insufficient percentage of income compared to inflation rates or more profitable areas of capital investment. Finally, direct miscalculations can be made in the development of the production program.
Financial reserves can be formed by enterprises of all organizational -legal forms property from net profit, after paying taxes and other obligatory payments to the budget system.
At the same time, it is advisable to keep the funds allocated to the financial reserve in liquid form so that they generate income and, if necessary, can be easily converted into cash capital.
WHAT IS BASED ON THE PRINCIPLE OF EXERCISING CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL AND ECONOMIC ACTIVITIES?
At the heart of the control over the financial and economic activities of the organization (enterprise) is the control function of finance. Control over the financial and economic activities of an organization (enterprise) is primarily carried out by the financial service of the organization (enterprise), which checks the financial activities, planned and targeted use of financial resources, and the implementation of key financial indicators. Control over the financial and economic activities of organizations (enterprises) is carried out by credit organizations during the issuance and repayment of loans. Tax authorities check the timeliness and completeness of payment of taxes and other obligatory payments.
Departmental control over the audit of financial and economic activities is carried out by the control and audit departments of ministries and departments in their subordinate organizations (at enterprises).
Independent financial control is carried out by audit firms. The main purpose of audit control is to verify the reliability of financial and accounting statements. The results of such a check are extremely important for potential investors. In general, control helps to reduce costs and, accordingly, increase the income of the organization (enterprise).
SECTION 3. FINANCIAL MECHANISM OF THE ORGANIZATION (ENTERPRISE).
WHAT IS THE FINANCIAL MECHANISM OF THE ORGANIZATION?
Financial management of an organization (enterprise) is carried out with the help of financial mechanism- part of the economic mechanism, which is a set of forms and methods of managing the finances of an organization (enterprise) in order to achieve maximum profit.

WHAT SUBSYSTEMS IS THE FINANCIAL MECHANISM COMPOSED OF?
The financial mechanism consists of two subsystems: MANAGING and MANAGED.
WHAT IS THE FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT SYSTEM INCLUDED?
The FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT SYSTEM of an enterprise includes:
FINANCIAL METHODS, FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS, LEGAL SUPPORT, INFORMATION AND METHODOLOGICAL SUPPORT FOR FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT.

WHICH METHODS USED IN FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT ARE FINANCIAL METHODS?
FINANCIAL METHODS used in financial management include: financial accounting, financial analysis, financial regulation, financial planning, financial control, settlement system, system of financial sanctions, credit operations (trust, pledge, leasing, etc.), taxes, insurance, etc.

With the help of the use of certain financial methods, the impact of financial relations on economic processes, the management of the movement of financial resources and the assessment of the effectiveness of their use based on the analysis of financial indicators are carried out.
WHAT IS A FINANCIAL INSTRUMENT?
In accordance with the International Accounting Standard "Financial Instruments: Disclosure and Presentation"
A FINANCIAL INSTRUMENT is any contract that gives rise to a financial asset for one entity and a financial liability or equity instrument for another entity.
In other words, this is any document that is evidence of a debt, the sale of which the seller is provided with financing. With the help of financial instruments, any operations in the financial market are carried out. Without their use, it is impossible to raise additional capital, make financial investments, make settlements with counterparties, etc.
Financial instruments are divided into primary and secondary (derivatives).
PRIMARY FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS include: receivables and payables for current operations, loans, bonds, shares, promissory notes.
SECONDARY or DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS include financial options, futures and forwards, interest rate and currency swaps.
A FINANCIAL ASSET can be in the form of cash, a contractual right to receive cash or another financial asset from another organization (enterprise), a contractual right to exchange a financial instrument with another organization (enterprise), a capital instrument of another organization (enterprise).
A FINANCIAL LIABILITY is any contractual obligation:
Transfer cash or other financial asset to another organization;
Exchange financial instruments with another organization (enterprise) on potentially unfavorable terms (forced sale of receivables).
Operations with financial instruments are always accompanied by financial risks. Information support allows users financial reporting assess the degree of riskiness of financial instruments.
THERE ARE THE FOLLOWING TYPES OF FINANCIAL RISKS.
1. PRICE RISK includes not only potential losses, but also potential profits. Price risk is divided into the following types:
CURRENCY - the risk that the value of a financial instrument will change as a result of changes in the exchange rate of a foreign currency;
INTEREST RATE - the risk that the value of a financial instrument will change as a result of a change in the market interest rate;
MARKET - the risk that the value of a financial instrument will change as a result of a change market prices regardless of what factors caused these changes.
2. CREDIT RISK is the risk that one of the counterparties involved in a financial instrument will not be able to liquidate an obligation and cause losses to the other party.
3. LIQUIDITY RISK, or financing risk, is the risk that an entity may encounter difficulty in raising funds to meet its debt obligations. financial instrument by a certain deadline. It may arise from an inability to quickly sell a financial asset at a cost close to its fair value.
MARKET VALUE is the amount that could be received from a sale or that would be payable when purchasing a financial instrument in an active market.
FAIR VALUE is the amount for which an asset could be exchanged or a liability settled in an arm's length transaction under comparable terms and conditions.
4. CASH FLOW RISK - the risk that the value of future cash flows associated with a monetary financial instrument will fluctuate. In the case of a floating rate debt instrument, such fluctuations may result in a change in the effective interest rate on the financial instrument, usually with a change in its fair value.

WHAT IS THE BASIS FOR THE LEGAL SUPPORT OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT?
Financial management, development of the financial policy of an organization (enterprise) is impossible without appropriate legal support. It is based on the current legislation, legislative and regulatory acts regulating entrepreneurial activity, determining the financial relations of organizations (enterprises) with the budget system, banks, insurance companies, suppliers and consumers.
WHAT IS THE BASIS OF INFORMATION SUPPORT FOR FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT?
Financial management of an organization (enterprise) is impossible without information support- information necessary for managing economic processes and contained in the database of information systems. In its turn Information Systems include systems for storing, processing, converting, transmitting, updating information using computer and other technology. The information base necessary for managing the finances of an organization (enterprise) is quite extensive and includes information of a financial nature. Depending on the organizational and legal form of management, industry affiliation there may be certain differences in the system of financial indicators that form the information base.
The information base of an organization (enterprise) includes the economic indicators of its activities, financial stability, solvency, financial statements and other indicators characterizing the financial condition of the organization (enterprise). The information base also includes information about commodity, stock and currency exchanges, information from financial authorities and institutions of the banking system. The state and quality of information support have a direct impact on the adoption management decisions. When developing the financial policy of an organization (enterprise), organizing cash flow management, identifying emerging trends and developing measures to strengthen its financial stability, an analysis of financial indicators is carried out.
Gavrilova A.N., Popov A.A. Finances of organizations (enterprises): study guide. M .: KNORUS, 2011.- 576 p.
Karanina E.V. Finance: a textbook for students, bachelors, undergraduates in economic and managerial areas of training and specialties of all forms of education and for a wide audience. - Kirov: FGBOU VO "VyatGU", 2015. - 230 p.

Kolchina N.V. and others. Finance of organizations (enterprises): a textbook for university students studying in economic specialties, specialty 080105 "Finance and Credit" / ed. N.V. Kolchina. - 5th ed., revised. and additional – M.: UNITI-DANA, 2012. - 407 p. - (Series "Golden Fund of Russian textbooks").
Lapusta M.G., Mazurina T.Yu., Skamay L.G. Finance of organizations (enterprises): textbook - M .: INFRA-M, 2011. - 575 p.
Fridman A.M. Finance of organizations (enterprises): textbook - M.: Dashkov and K 0, 2013. - 488 p.
Communication functions financial management.
Influence of inflation on the investment process.
The impact of inflation on the investment process is mostly negative. It manifests itself in the fact that depreciation of the depreciation fund occurs, and therefore, a lack of funds is revealed for the renewal of fixed assets. As a result, the investment fund decreases, the investment opportunities of the enterprise decrease. Such an impact can be reduced by using the method of accelerated depreciation of fixed assets, as well as limiting the growth of consumption funds. The negative impact is also manifested in the fact that in the future investors will receive investment income in depreciated money, and investment costs are currently being incurred. In conditions of inflation, preference should be given to investment projects with fast deadline payback. It is also reasonable to invest in the most protected from it areas with a rapid turnover of capital - these are financial markets, speculative transactions with securities, trade, real estate transactions, etc.
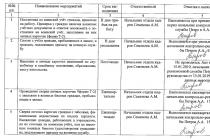
Lecture #5, 6. Communication function - the implementation of external financial relations.
IN modern concepts strategic management the enterprise one of the main roles is played by the dynamics of its development and behavior in the external environment. One of the main factors of communication is financial management. The communication function of financial management consists in the implementation of financial relationships with federal, subfederal and municipal authorities, contractors, customers, creditors, borrowers, investors, founders, etc. These relations should at least be conflict-free, and ideally they should contribute to the development of the enterprise and the solution of its strategic goals. Financial management at the enterprise should be adequate to the requirements of the external environment.
The financial environment of entrepreneurship is a set of mutual multilateral business connections enterprises with subjects and objects of financial relations. The system of financial relations of an economic entity includes relations in the field of education, formation, disposal and use of financial resources. These relations can be both within the economic horizontal and vertical. Currently, relations with higher organizations are developed at enterprises with federal and municipal property and at state enterprises. Similar relations were revived on a new basis and within financial holdings. This is the relationship of subsidiaries and affiliates with the parent company - the holder of their controlling stake (shares). IN market conditions relations of the financial horizontal are of primary importance. Each business entity is, on the one hand, a supplier of products (works, services), and on the other hand, their buyer. Elements that form the business environment.
Entrepreneurial environment- social economic situation, including the degree of economic freedom, the presence of an entrepreneurial corps, the dominance of the market type of economic relations, the possibility of forming business environment and use necessary resources. The formation of an entrepreneurial environment is a manageable process. At the heart of management methods are measures related not to the impact on business entities, but to the design of favorable conditions for the emergence and rapid development of such entities. Formation of the business environment includes the following elements:
Adoption of a national program to stimulate entrepreneurship, creation of an entrepreneurial infrastructure (of all institutions of entrepreneurial activity);
Changing public economic and socio-economic thinking;
Changing social psychology. The development of entrepreneurship leads to the growth of national wealth and the welfare of the nation.
External financial relations:
relations of the enterprise with the budget and extra-budgetary funds (for example, the transfer of taxes by the enterprise);
relations of the enterprise with direct participants and institutions of the financial risk infrastructure (banks, stock exchanges, insurance companies);
relations of the enterprise with partners in operating activities (suppliers, buyers of finished products, sellers of fixed assets);
relations of the enterprise with the bodies of the production infrastructure (transport, communication institutions).
Internal financial relations:
relationship between head and subsidiaries arising within financial and industrial groups;
the relations of the enterprise with its founders - these relations are tripled regarding the formation of fixed capital;
relations with staff;
relations between the structural divisions of the enterprise.
State regulation of financial activity of an enterprise- this is the process of legal regulation of the conditions for the formation of their external and internal financial relations and the implementation of the main types of financial transactions by them.
State regulation includes the following areas:
regulation of the formation of the management information base financial activities enterprises;
tax regulation;
regulation of credit operations;
regulation monetary circulation payment forms;
currency regulation;
regulation of investment operations;
regulation of the securities market;
regulation of insurance operations in the financial market;
regulation of the order and forms of rehabilitation of enterprises;
Reorganization is the financial recovery of the enterprise.
10) regulation of bankruptcy and liquidation of enterprises.
Principles of organization of enterprise finance
The principle of economic independence, its implementation is ensured by the fact that business entities, regardless of the form of ownership, independently determine their costs of funding sources, as well as the direction of investing funds in order to make a profit.
Until the 90s. from above they established what to produce, to whom to supply and prices for products. The enterprise calculated on all obligations and if there was profit, then it was taken in the form of deductions of the free balance of profit to the budget.
At this stage, the independence of the enterprise is limited only by certain norms: the state establishes tax percentages, depreciation rates, etc.
The principle of independence and self-financing it means full payback of costs for the production and sale of products, as well as investment in the development of production at the expense of own funds and, if necessary, at the expense of bank loans. But self-sufficiency does not yet apply to industries where there is state regulation of prices: agriculture, transport, the coal industry, housing and communal services - subsidies are issued there.
The principle of material interest, its implementation can be ensured by decent wages, the optimal tax policy of the state, as well as the observance of economically justified proportions in the distribution of net profit to the consumption and accumulation fund. The tax at the enterprise should not exceed 30%. Decent wages should be provided at the expense of the wage fund and profit directed: for consumption in the form of bonuses, remuneration based on the results of work for the year, for length of service, financial assistance and other incentive payments, as well as payments to employees of interest on bonds and dividends on shares .
The principle of liability- means the presence of a certain system of responsibility for the conduct and results of economic activity, i.e. this principle is implemented in case of loss-making operation of the enterprise, its inability to satisfy the requirements of creditors. This principle is also reflected in fines and penalties.
The principle of securing financial reserves, the enterprise should form reserve funds in case of unforeseen circumstances.
Financial relations of enterprises - a system of relations with state bodies, the tax system, budgets, banks and other credit institutions, insurance companies, and so on, as well as monetary relations expressing the formation and use of monetary funds in the process of the circulation of enterprise resources, the formation of its cash income and savings .
Financial relations are divided into internal and external.
Internal financial relations:
- - formation of the authorized capital of business entities;
- - formation and distribution of cash income: revenue, gross and net income, profits, cash assets of the enterprise;
- - Relations with employees on payment of wages.
- -financial relations with own structural divisions
- -relations within production associations and relations of the enterprise with its subsidiaries.
External financial relations
relations with other economic entities in the process of formation and distribution of revenue (non-material relations);
- - fines, penalties, forfeits; - lease relations;
- - issue and sale of securities;
- - Team work;
- - commercial lending;
The organization of the finances of economic entities is carried out on the basis of a number of principles that correspond to the essence of entrepreneurial activity in market conditions:
economic independence. The implementation of this principle is ensured by the fact that an economic entity, regardless of the form of ownership, independently determines the direction of its expenses, sources of their financing, guided by the desire to maximize profits.
Self-financing. This principle means full payback of costs for the production and sale of products, investment in the development of production at the expense of own funds and, if necessary, bank and commercial loans. The implementation of this principle is one of the main conditions for entrepreneurial activity, which ensures the competitiveness of the enterprise.
Material liability. It means the presence of a certain system of responsibility for the conduct and results of economic activity. The financial methods for implementing this principle are different for individual enterprises, their managers and employees of the enterprise.
material interest. This principle is objectively predetermined by the main goal of entrepreneurial activity - profit making.
Providing financial reserves. This principle is connected with the need to form financial reserves to ensure entrepreneurial activity.
The principle of financial control. The implementation of this principle at the enterprise level provides for such an organization of finances, which provides the possibility of exercising intra-company financial control based on internal analysis and audit.
Thus, the finances of organizations are the main link in the financial system. Enterprise finance - a set of monetary or financial relations arising from business entities regarding the formation of actual and (or) potential funds of funds, their distribution and use for the needs of production and consumption.
All principles of organizing the finances of economic entities are in development and for their implementation in each specific economic situation, their own forms and methods are applied, corresponding to the level of development. productive forces and industrial relations.
In modern economic conditions, commercial banks are becoming an important element of the market infrastructure.
Since commercial banks are created and operate in the form of limited liability partnerships or joint-stock companies, their activities are possible only if they receive their own profit. Thus, the relationship between enterprises and banks is built taking into account mutual interests and should be beneficial to both parties.
Relations between the organization and the bank arise about settlement and cash and credit services, as well as in connection with the emergence of new services characteristic of a market economy. An important feature of these relations is their contractual nature. The initiative to conclude contracts comes from an enterprise that independently chooses a bank for its settlement, cash and credit services.
For settlement services, the enterprise concludes a bank account agreement with the bank, which is necessary for the organization of cashless payments. In accordance with the agreement, the bank opens settlement and other accounts for the enterprise as a client, credits funds received from both the enterprise and the enterprise to them, debits the amounts from the enterprise’s account on its behalf to the accounts of suppliers, creditors, relevant budget and extra-budgetary funds. In addition, the bank undertakes to accept from the client enterprise and issue to him or on his behalf cash, pay interest for keeping money in accounts.
The main account of the enterprise as a legal entity is a current account. The company has the right to open several settlement accounts in different banks. The proceeds from the sale of products (works, services) are credited to the settlement account, and settlements are made on it for the obligations of the enterprise. Other accounts - current, loan, currency - the organization has the right to open in any number in different banks. A settlement subaccount is opened for an enterprise that has separate structural units outside of its location. At their location, bank accounts are opened in the name of the enterprise. Since the settlement subaccount is of secondary importance, it accumulates the proceeds from the unit for subsequent transfer to the main settlement account of the enterprise.
Current accounts are opened for branches, departments and other non-self-supporting divisions of the enterprise. Limited settlement operations are carried out on them, mainly related to wages and administrative and economic expenses.
When opening a current currency account in a bank, a transit currency account is automatically opened, to which foreign currency transfers are received from foreign economic activity enterprises. After the sale of part of the foreign exchange earnings, the balance of foreign exchange funds is transferred to the current account.
In the process of settlement and cash services between the enterprise and the bank, certain financial relations are formed, accompanied by the movement of funds and affecting the formation of income of the enterprise and the bank.
Many banks charge a fee for opening customer accounts and carrying out settlement and cash transactions in order to reimburse the costs of their conduct. Others, to attract clientele, open current accounts for free. Each bank pays a certain fee in favor of the latter for keeping the funds of enterprises with it (the exception is a transit currency account). The amount of the fee is set by mutual agreement, if we are talking about the checking account. The enterprise places temporarily free funds on fixed-term deposit accounts on the terms of the bank, which sets interest on deposits depending on the terms of money storage.
The organization's expenses for paying for bank services are included in the cost of products (works, services), income received from keeping funds in bank accounts are accounted for as part of the enterprise's balance sheet profit as non-operating income. Banks are not entitled to control the settlements of the enterprise with the budget, other enterprises or other non-cash payments, although they are carried out in the prescribed forms. However, the bank has some responsibility for compliance with the rules settlement discipline, which is installed regulations Central Bank RF and is determined by agreements between the enterprise and a commercial bank. For untimely or incorrect debiting of funds from the accounts of the enterprise, as well as for untimely or incorrect crediting of funds received by the enterprise, it has the right to require the bank to pay a fine in its favor in the amount of 0.5% of these amounts for each day of delay. The agreement between the bank and the enterprise may also provide for other (additional) forms of liability.
The responsibility of enterprises to the bank is established in bank account and deposit agreements, loan agreements.
Note that the role of credit in ensuring the normal functioning of the enterprise in modern conditions is certainly important.
Bank loans are the most important source of providing financial resources for the needs of enterprises related to the production and sale of products. Temporary need for funds especially often arises in enterprises where there are seasonal fluctuations in production volumes and product sales. But it can arise as a result of a time gap between the arrival of sources certain types costs and the need for funds for this purpose, for example, about the implementation of repair work. Industrial associations and enterprises operating on a self-financing basis are credited on the basis of the aggregate of material reserves and production costs.
The general principle of checking credit collateral is as follows. The actual debt is compared with the sum of the excess paid balance of stocks of valuables and production costs within the plan and goods shipped in the amount of their balance balance.
In practice, the verification of the security of the bank institution is carried out simultaneously on the totality of stocks and costs and goods shipped. If the debt exceeds the planned amount of the loan, the institution of the bank, together with the enterprise, considers the reasons that caused the excess need for a loan.
A decision may be made to provide a loan for temporary needs for the full or partial amount of excess inventories and production costs, as well as goods shipped. If these measures allow you to bring the debt to the planned period, then the bank institution can provide a loan for temporary needs.
If it is impossible to bring the debt on the loan to the planned level within the established time limits, as well as in the event of an overdue debt on bank loans, lending is limited within the planned amount of the loan.
If the planned amount of the loan is exceeded due to the above-planned growth of goods shipped, the payment terms for which have not yet come, they are accepted for lending without limitation in amount and term. In this case, the bank does not apply sanctions.
When checking, the balances of work in progress, finished products and goods shipped are accepted for crediting at the actual cost, but not higher than the planned one, and all other stocks and costs - at the balance sheet estimate. The value of inventories is reduced by depreciation of valuables, a provision for future expenses or losses, and trade discounts if goods are accounted for on the balance sheet at retail or wholesale prices.
The bank can provide loans for expenses in fixed assets if the enterprise does not have enough funds from incentive funds. Analysis of the relationship between the enterprise and the bank for such loans is to check intended use loans and the effectiveness of the activities carried out at the expense of them.
Lending is a method of return financing of an enterprise. It is a traditional banking service. The enterprise has the right to receive a loan both in the bank where it has a current account and in any other bank. Lending is carried out on the basis of a loan agreement that defines the rights and obligations of the parties, as well as liability for violation of the terms of the agreement, taking into account the nature of the loan and the financial condition of the borrowing enterprise.
Depending on the nature of the enterprise's needs for borrowed funds, a short-term loan (up to a year), medium-term (from one to three years) and long-term loan (over three years) are distinguished.
For the use of the loan, which must be repaid within the period established by the agreement, the company pays interest to the bank. Interest rates depend on the period of use of borrowed capital, taking into account supply and demand. Interest rates may vary from bank to bank.
The practice of Russian banks in the field of lending shows that their activity in this area consists almost entirely of short-term loans concentrated in the area of trade and purchasing business. Mostly borrowed funds are focused on intermediary operations, which are characterized by a quick turnover of funds and high profits.
Because banks lend to commercial basis, the principles of lending are the security of the loan, target nature, urgency, payment and repayment of the loan. In this case, this determines the preferences for specific types of credit operations and their overwhelming numerical superiority. Relations with the financial and credit system are diverse. First of all, it is relations with budgets. various levels and off-budget funds related to the transfer of taxes and deductions. Tax system Russia is imperfect and does not contribute to normal production activities. World experience shows that it is possible to reduce high inflation rates only through the support of production and the development of investments. This should be directed mainly tax, as well as credit and customs policy. In particular, in many countries a certain part or all of the increase in production is not taxed. This is beneficial for both the enterprise and the state, since taxes from such enterprises are received in full, and in a year they increase sharply.
Relations with the insurance link of the financial system consist of transfers of funds for social and medical insurance, as well as insurance of the company's property.
The financial relations of enterprises with banks are built both in terms of organizing non-cash payments, and in obtaining and repaying short-term and long-term loans. The organization of non-cash payments has a direct impact on the financial position of enterprises. Credit is a source of working capital formation, expansion of production, its rhythm, improvement of product quality, helps to eliminate temporary financial difficulties of enterprises.
Currently, there are a number of problems in relations between enterprises and banks. The practice of non-cash payments is primitive: advance payment, barter, cash, large non-payments. A loan is very expensive, so its share in the formation of working capital of enterprises is very low (on average, no more than 10%). Long term loan practically does not apply to investment financing. Non-traditional banking services have not been developed either.
The conditions for the emergence of finance are the formation, distribution and use of cash income, which consists of three functions: distribution, control and regulation.
distribution function
Responsible for providing financial resources for each link in the system. The main task is to distribute the national income in accordance with the needs of the state and the population. Income is generated from taxes and proceeds from the sale of goods and services.
The distribution of income allows:
- to evenly develop branches of the national economy;
- strengthen the state, economy and defense capability of the country;
- improve the standard of living of the population.
control function
Economic feasibility and compliance with current legislation are mandatory components of the control function. Control is necessary at all levels of the movement of finance and in any financial transaction. Financial control- a tool for the prevention of economic offenses, allowing:
- control the production of goods and services;
- monitor the process of spending resources;
- reduce costs and losses;
- prevent waste.
Regulating function
Regulation is aimed at improving the economic situation or overcoming the crisis. The main levers of regulation are tax and credit policy. IN state regulation need:
- public sector;
- money turnover;
- public finance;
- foreign economic activity;
- economic security.