- this is a type of capital of an enterprise, which is formed by issuing shares by this enterprise.
Equity capital is of two types, debt and equity.
- Own - this is a type of share capital, in which of the available own funds produced and sold securities, resembles a whirlpool. From such profits, shareholders receive annual dividends, but only after paying taxes and paying wages.
- Borrowed is a type of capital that is formed mainly by borrowing money. They can be bank loans and loans.
Using the concept of share capital, you can define equity joint-stock company. The main thing is not to confuse net assets and equity. Since net assets are assets, they represent the difference between the company's assets on the balance sheet and all debt obligations they have.
Share capital structure
Share capital includes:
- authorized capital;
- additional capital (capital formed by the emission of income);
- retained earnings (such capital is formed due to the efficient operation of the enterprise);
- reserve capital (capital, using funds net profit).
Share capital cannot exist without a joint-stock company.
A joint-stock company is one of the types of forms of ownership that combines its property and cash in the authorized capital, which is divided into equal shares, and secured by securities - shares.

There are some difficulties in opening a joint-stock company: registration of an enterprise; such an enterprise will be subject to double taxation; when forming a joint-stock company, many shareholders act purely in their own interests.
But, despite such difficulties, the creation of just such a form of ownership can bring enormous profits. Such an organization of people is formed in order to meet social needs and make a profit.
Shareholders
A joint stock company is a legal entity, its participants are shareholders. The liability of a shareholder is determined by the number and value of shares. The price indicated on the share itself is nominal; in the market, such a share will be sold at a certain rate.
In addition to shares, other types of securities can be bought and sold: bills, bonds, etc. The issue of such securities is one of the components of financial capital designed to provide income.
There are several ways to create joint-stock companies. Namely: newly created; created as a result of a merger of legal entities; as a result of the transformation, division or separation of legal entities.

There are two types of joint-stock company: open and closed. A joint stock company has its own authorized capital, which is also called share capital, because. its size is established by the charter of the organization. The capital of shareholders can also be called permitted and nominal capital, it is the property of the companies.
Thus, the share capital is the money of the joint-stock company.
Return on Equity Formula
Return on equity = net income / equity.
In order for the capital of this form of ownership to multiply, there must be efficient system for managing such a campaign and an equally effective system for controlling management. Since equity capital began to exist, it has had ups and downs, revivals and stagnations.
A joint stock company is a form of ownership that combines different kinds capitals. The success of this company depends on the correct distribution of profits.
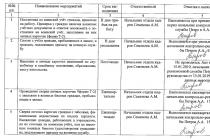
Part 7. Intermediate test
1. Using an accounting equation, fill in the gaps in the following table:
2. Briefly explain the following accounting principles. Illustrate your answer with examples.
– The principle of an independent economic entity
– Materiality principle
- Principle of discretion
3. Robinson Sports produces a complete set of sports equipment. On May 1, the firm received an order from K. Gatting and Son, address: 14 Middle Road, Fakenham, for the following goods:
The company provides a trade discount of 25% off the regular price retail, VAT - 17.5%.
Required:
Prepare a credit note to be sent by Robinson when K. Gatting & Son returned 3 pairs of cricket pads, 1 training suit and 2 table tennis rackets on May 5 as defective.
Calculate the profit that "K. Gatting & Son would have received if all of the conditioned items in the above order were sold at the suggested retail price. Show your calculations for each article.
4. Explain the following terms:
– Invoice
– Credit memo
– Trade discount
– Cash discount
Part 8. Answers to the midterm test
Section 2
Part 1
Accounting, Commercial Organizations
Accounting- identification of facts of economic activity, registration and presentation of information about them to interested users.
At the first stage of accounting (i.e. at the stage identifying) information is collected about the facts, allowing to obtain a reliable idea of the economic activities of a particular commercial organization.
Registration- an ordered and systematized reflection of the facts of economic activity in chronological order.
Performance information about the facts of economic activity is carried out by compiling and distributing financial statements.
Accounting consists of the following steps:
Discovery > Registration > Information submission
internal users accounting information are managers who carry out planning, organization and operational management of the enterprise. These include marketing managers, service heads internal control, officials companies (see Figure 1.1).
in number external users includes investors, lenders, tax authorities regulators, trade unions, buyers and customers, and government planners.
Term "bookkeeping" is not synonymous with the concept of "accounting". Accounting refers exclusively to the registration of facts of economic activity, while accounting also provides for their identification, evaluation and presentation of relevant information. Thus, bookkeeping is only a part of accounting.
Commercial organizations
There are different types of commercial organizations:
- Sole proprietorship - an enterprise whose assets are owned by one owner.
– A partnership (partnership) is an enterprise whose assets are owned by two or more partner owners.
– A joint-stock company is an enterprise that is a separate legal entity, whose activities are regulated by the law on joint-stock companies, the property of which is divided into a certain number of shares.
– Other organizations, such as organizations carrying out activities for trust management property, joint ventures, consortiums, etc.
balance equation
Basic balance equation:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
The basic balance equation applies to all economic entities, regardless of size, type of activity and legal form (see Illustration 1.2).
The components of the main balance equation are:
Assets- resources controlled by the company, from which the company expects to receive economic benefits in the future.
Commitments- the current debt of the company, the repayment of which will lead to an outflow from the company of resources containing economic benefits.
Share capital- the share in the assets of the company remaining after deducting all its liabilities.
Share capital includes the following components:
Issued capital consisting of shares placed in exchange for funds contributed by shareholders and reserves representing capital maintenance adjustments (such as equity adjustments resulting from the revaluation of assets and liabilities).
retained earnings, defined as the difference between income and expenses, used for the payment of dividends and the formation of reserves, which represent the target distribution of this profit.
Income represent the total increase in share capital as a result of carrying out economic activities for the purpose of generating profit. This concept includes both revenue arising in the course of the ordinary activities of the company (from sales, remuneration, interest, etc.), and Other income which also fall under the definition of income and may arise in the course of the ordinary activities of the company.
Expenses represent both the costs associated with the consumption of assets or the depletion of resources that arise in the course of the ordinary activities of the company, and other reductions in economic benefits (losses) that fall under the definition of expenses that may arise in the course of the ordinary activities of the company.
The difference between income and expenses results in net profit or net loss:
Revenue/Income > Expenses/Losses = Net Income
Revenue/Income< Расходы/Убытки = Чистый убыток
Business operations
Each operation can be analyzed in terms of its impact on the components of the main balance equation. In addition, the analysis should identify the metrics affected by the operation and the amount of change in each metric (see Exhibit 1.3).
Each business transaction has a double effect on the equation. For example, an increase in the value of a single asset should be accompanied by the corresponding:
– a decrease in the value of another asset, or
– an increase in the liability, or
- increase in share capital.
Check is a unit used in accounting to record the increase and decrease in a single item of assets, liabilities or equity.
IN simplest form an account can be represented as follows: (a) account name, (b) left side or debit, and (c) right side or credit. In its outline, this form resembles the letter "T", so it was called " T-score».
Illustration 1.3
A. Examples of business transactions.
SUMMARY TABLE
BUSINESS OPERATIONS
FOR SEPTEMBER 2001
B. Reflection of accounting data in financial statements.
1. Prepare an income statement and a retained earnings statement based on the September 2001 summary table of business transactions.
REFLECTION OF BUSINESS OPERATIONS
2. Prepare a balance sheet using the month-end account balances from the summary table of business transactions.
Debit and credit, Registration of information in accounting
Terms " debit" And " credit” means “left side” and “right side” respectively.
Recording the amount on the left side of the account is called debit accounts, and on the right side - lending accounts.
When the debit turnover is greater than the credit turnover, the account has debit balance, and if vice versa - credit balance.
Within the system double entry each business transaction is reflected in the same amount on the debit of one account on the credit of another account. Thus, the sum of all debit entries is always equal to the sum of all credit entries.
The following shows the rules for reflecting increase and decrease assets And obligations for debit and credit accounts:
The components of share capital are reflected in various accounts such as Retained Earnings, Earnings and Expenses and accounts relating to issued capital.
The following shows the rules for reflecting the increase and decrease in the components of share capital on the debit and credit of the accounts:
The main balance equation in expanded form is as follows:
Assets = Liabilities + Issued Equity + Retained Earnings
Retained Earnings = Income - Expenses
ILLUSTRATION 1.4
RULES OF DOUBLE RECORDING
RULES
The main stages of registration of information in accounting are:
– Analysis of a business transaction for reflection in the accounts of accounting.
– Record information about the operation in the log.
Transferring data from the journal to the appropriate general ledger accounts.
ILLUSTRATION 1.5
REFLECTION OF INFORMATION IN ACCOUNTING
ILLUSTRATION 1.6
ANALYSIS OF OPERATIONS AND THEIR REGISTRATION IN THE JOURNAL
Task: analyze and register the following business transactions in the journal:
BUSINESS JOURNAL
Questions
1. What is the main hallmark all assets?
a. Long service life.
b. High price.
c. Material and material form.
d. Future economic benefits.
2. Choose the most accurate description of the share capital.
a. Assets = Liabilities
b. Liabilities + Assets
c. Share capital + Assets
d. Assets - Liabilities
3. Which of the equations corresponds to the main balance equation?
a. Assets = Equity
b. Assets - Liabilities = Share Capital
c. Assets = Liabilities + Equity
d. All of the above equations.
4. What are the obligations of the company?
a. Future economic benefits.
b. The company's current debt.
c. Values used by the company in the course of its activities.
d. All of the above.
5. What is not included in the obligations of the company?
a. Bills payable.
b. Accounts payable.
c. Payroll debt.
d. Cash.
6. Liabilities of the company represent debt to:
a. debtors;
b. charitable organizations;
c. creditors;
d. underwriters.
7. Share capital can be represented as:
a. share in assets claimed by creditors;
b. the share in the assets claimed by the shareholders;
c. share in the assets claimed by charitable organizations;
d. the share in the assets claimed by the debtors.
8. The main balance equation cannot be represented as:
a. Assets - Liabilities = Share Capital
b. Assets - Equity = Liabilities
c. Share capital + Liabilities = Assets
d. Assets + Liabilities = Share Capital
9. If total liabilities increased by $6,000, does this mean that:
a. assets decreased by $6,000;
b. share capital increased by $6,000;
c. assets increased by $6,000 or share capital decreased by $6,000;
d. assets increased by $3,000 and share capital increased by $3,000.
10. Repayment of receivables in the amount of $400 means:
a. increase in assets by $400, decrease in assets by $400;
b. increase in assets by $400, decrease in liabilities by $400;
c. decrease in liabilities by $400, increase in share capital by $400;
d. decrease in assets by $400, decrease in liabilities by $400.
11. What are income?
a. The value of the assets consumed during the period.
b. General gain share capital in the course of business.
c. Cost of services used during the period.
d. Current or expected cash payments.
12. Net profit arises when:
a. Assets > Liabilities
b. Income = Expenses
c. Income > Expenses
d. Income< Расходы
13. What is reflected in the balance sheet?
a. Income, liabilities and share capital.
b. Expenses, dividends and share capital.
c. Income, expenses and dividends.
d. Assets, liabilities and share capital.
14. What does the income statement show?
a. Changes in share capital over a specific period.
b. Changes in assets, liabilities and equity over a given period.
c. Assets, liabilities and share capital as at the reporting date.
d. Income and expenses for a certain period.
15. What does an asset account debit entry mean?
a. Error.
b. A credit entry has been made to the liability account.
c. Reduction of assets.
d. Increase in assets.
16. Which of the equations is an expanded version of the main balance equation?
a. Assets = Liabilities + Issued Capital - Income - Expenses
b. Assets + Expenses = Liabilities + Issued Capital + Income
c. Assets - Liabilities = Issued Capital - Income - Expenses
d. Assets = Income + Expenses - Liabilities
17. Which of the following characteristics is not a qualitative characteristic of financial statements?
a. Relevance.
b. Reliability.
c. Conservatism.
d. Comparability.
18. To be relevant, information must:
a. have a low acquisition cost;
b. help assess past, present and future events, confirm and correct past assessments;
c. not be presented to external users;
d. used by many companies.
19. Information must be free from material errors and misleading to ensure:
a. comparability;
b. credibility;
c. sequences;
d. forecast.
20. If information is used for forecasting, then this means that it:
a. verified by an external auditor;
b. prepared on an annual basis;
c. confirms or corrects previous calculations;
d. neutral.
21. Information is relevant if it:
a. has been audited;
b. presented for the longer of the two periods: operating cycle or one year;
c. is objective;
d. capable of influencing economic decision making.
22. What most accurately reflects the following qualitative characteristics?
23. The going concern assumption assumes that the company:
a. will be eliminated in the near future;
b. will be acquired by another company;
c. is a dynamically developing enterprise;
d. operates and will continue to operate for the foreseeable future, will not be eliminated, and the scale of its activities will not be significantly reduced.
24. The going concern assumption is not applicable when:
a. the company is just starting its activity;
b. liquidation of the company is expected;
c. fair value exceeds the cost;
25. To determine the materiality of a financial statement item, an accountant should compare it with all of the following except:
a. total assets;
b. total liabilities;
c. the total number of employees;
d. net profit.
26. Dixon's entry-level accountant made accounting entries for transactions for the year ending 31 December 2000. The Comptroller questioned the correctness of these entries. Net income for the year, based on the accounting entries below, was $250,000.
1. A company purchased a wastebasket worth $20.
2. Inventory costing $16,000 has a replacement cost of $22,000.
3. Equipment purchased in liquidation sale for $12,000, fair value of equipment is $20,000.
Exercise
For each entry, indicate the accounting principles or requirements that were violated and determine the correct amount of net income for 2000.
27. Indicate which of the following items relates to assets, liabilities or equity by identifying each item with the appropriate code:
28. The Wine Company's total assets at the beginning of the year were $800,000 and total liabilities were $300,000. Answer the following questions.
(1) What is the year-end share capital if total assets increased by $250,000 during the year. and total liabilities decreased by $150,000?
(2) What is the year-end total assets if total liabilities increased by $360,000 and equity decreased by $130,000 during the year?
(3) What is the year-end total liabilities if total assets decreased by $90,000 and equity increased by $190,000 during the year?
29. Jacquet Carpet Cleaning included the following items in the balance sheet:
Assets (excluding cash) ……. $150,000
Obligations……. $90,000
Share capital ……. $60,000
All assets were sold for cash.
Exercise
Prepare a balance sheet immediately after the sale of assets for cash for each of the following options:
31. Fill in the gaps in the following balance equations.
32. Analyze the following transactions performed by the joint-stock company and complete the table using the “+” sign to indicate an increase and the “-” sign to indicate a decrease in the components of the main balance equation.
33. Below are a number of transactions carried out by Baxter. Under each transaction, list its effect on assets, liabilities, and equity.
For example: Case open. Cash deposited.
Answer: Increase in assets and increase in share capital.
Paid monthly public utilities.
A showcase was purchased for cash.
Paid for the repair of the security system.
Billed customers for services rendered.
Received funds from customers on the issued invoice (operation 4).
Dividends declared to holders of ordinary shares.
Dividends paid to holders of ordinary shares.
Paid annual rent.
Received cash from customers for services rendered.
34. Prepare the income statement, retained earnings and balance sheet for Ben Gray based on the following data for September 2000.
(3) Share capital - ordinary shares, retained earnings
(a) $252,000 ($350,000 – $98,000 = $252,000)
(b) $95,000 ($178,000 – $83,000 = $95,000)
(c) $452,000 ($202,000 + $250,000 = $452,000)
32. (10 min.)
Reduction of assets and reduction of share capital. The assets don't change. Reduction of assets and reduction of share capital. Increase in assets and increase in share capital. The assets don't change. Increase in liabilities and decrease in share capital Decrease in assets and decrease in liabilities. Increase in liabilities and decrease in share capital. Reduction of assets and reduction of share capital. Increase in assets and increase in share capital.
34. (15 min.)
BEN GRAY DDS
Gains and losses report
For the month ending September 30, 2000
Service revenue……….. $25,000
Costs for wages……….. $ 10,000
Dental equipment expenses……….. 3,500
Rental expenses……….. 2,000
Utility costs……….. 700
Total expenses……….. $16,200
Net Income……….. $8,800
BEN GRAY DDS
Monthly retained earnings statement,
ending September 30, 2000
Plus: Net income……….. 8,800
Minus: Dividend 6,000
BEN GRAY DDS
Balance sheet
September 30, 2000
Part 2 "Accounting on an accrual basis"
Assumption of periodicity
According to periodicity assumption economic activity businesses can be divided into certain periods time. Reporting periods are usually month, quarter or year. An accounting period of one year is called fiscal year.
Principle of income recognition
The main issue that arises when accounting for income concerns the moment of their recognition.
Principle of income recognition means that income is recognized in the reporting period in which it is earned.
Joint-stock or corporate form of management involves the pooling of capital. A joint stock company (JSC) will provide an opportunity to concentrate capital by attracting investors through the purchase of shares. Share capital is used to implement large-scale projects (construction railways, canals, ships, etc.), where individual capital is not enough even with the possibility of using bank loans. A joint-stock company (corporation) attracts funds from various investors, which is issued in the form of securities. Initial capital JSC is formed from the capital of the founders and by selling securities (stocks and bonds) to the public.
The supreme management body of the joint-stock company is the meeting of shareholders. It is convened at least once a year. A JSC member has a number of votes proportional to the number of ordinary shares he owns. Voting principle: one share - one vote. The controlling block of shares provides the majority of votes to its owners at the meeting of shareholders and gives control over the activities of the company. The risk of the owners of shares is limited by the limits of the share they contributed to the joint-stock company. By acquiring controlling stakes in subsidiaries, parent companies significantly expand the sphere of domination over foreign capital. When carrying out risky transactions in subsidiaries, the risk of parent companies is limited only to their block of shares. Joint-stock companies are the leading link in the economy of developed countries.
Influence on the company's activities begins with the acquisition of a 25% share of the share capital, which is called the blocking minority. formally property large enterprises belongs to all shareholders owning shares of this enterprise. In fact, the role of small shareholders is insignificant. All decisions are made only by large owners and managers. Small owners are deprived of the opportunity to influence the processes taking place in a joint-stock company, and can only count on additional income in the form of dividends.
A large number of owners of a JSC leads to the need to hire a company manager. Therefore, there is a distinction between the right of ownership and the right to manage property, delegated by the shareholders to the management of the company. Between meetings of shareholders, the management of the current affairs of the company is entrusted to the board of directors, elected at general meetings. The board of directors determines the structure of the corporation and appoints the management staff. Thus, ownership and disposal of property in a joint-stock company are divided between the management (managers) of the company and its owners (shareholders).
The authorized capital of JSC is represented by a certain number of securities in the form of bonds and shares. Bond - a debt security whose owner has lent to its issuer the amount of money indicated in the face value of the bond. The bond entitles its owner to receive a fixed interest income from the issuer within the stipulated period and return the se face value at the end of this period (called redemption of the bond). The owner of the bond is the creditor of the issuer of this fixed income security.
Promotion - a perpetual equity security, indicating that its owner has contributed a certain amount of money to the capital of a joint-stock company and giving the right to receive income called a dividend. The owner of the share is a co-owner of the enterprise. Its share in the total capital is determined by the number of shares it has in monetary terms.
Dividend - part of the net profit of JSC.
Shares are divided into ordinary (ordinary) and preferred (preferential). Preferred shares do not give the right to vote at the shareholders' meeting, but guarantee fixed dividend payments. Ordinary shares do not guarantee the amount and obligatory payment of dividends, but give the right to vote to their owners at shareholders' meetings.
According to the nature of the order, the shares are divided into nominal and bearer. The owner of registered shares is registered in the general register of shareholders. The movement of such shares from one person to another is necessarily recorded in the register and is not permitted by the charter of the JSC in all cases. Bearer shares are impersonal, and their owners are not known to the public.
Funds received by the company from shareholders in payment for shares become the property of the company. The shareholder is not entitled to demand these funds back from the company. To convert shares into cash, they must be sold on the securities market at a market rate, which may be higher or lower than the initial (nominal) price of the share. By selling shares, the owner sells his share of ownership and the right to an annual dividend. The share price is determined by the amount of the dividend and the rate bank interest:
Dividend value / Bank interest rate = Share price
Determining the market rate is called a quote given by the stock exchange. Investing money in the purchase of JSC shares attracts people with the hope of getting high income. However, fluctuations in the market price of shares make them a risky form of investment.
After paying income tax, net profit remains, which is distributed by decision of the board of directors and approved for general meeting shareholders in the following order:
- - to expand production;
- - to form a reserve fund;
- - for the payment of bonuses to the management of JSC;
- - the remaining part is intended for payment on securities in the following order:
- a) interest on bonds;
- b) fixed dividends on preferred shares;
- c) dividends on ordinary shares, the amount of which depends on the total amount of profit and on the distributed share.
Founder's profit- this is the difference between the amount received by the founders from the sale of shares during their issues and the actual capital invested in the JSC by the founders. This specific type of profit exists only on the basis of share capital, and the profit is appropriated before the start of the functioning of the company. The essence of this is that the funds of the shareholders are redistributed in favor of the founders. The extraction of the founder's profit occurs due to the sale of shares above their nominal price and the increase in the volume of sales of shares in excess of the established share capital.
The stock of JSC securities is a phenomenon called fictitious capital. The amount of fictitious capital usually exceeds the amount of real capital (buildings, machinery, equipment, raw materials, finished products etc.) several times. Securities are sold on the stock market, and here the connection between real and fictitious capital is lost.
In the balance sheet of a corporation, the share of owners is called shareholders' equity, as shown below.
Please note that the section equity The corporate balance sheet consists of two parts: (1) share capital And (2) retained earnings. Share capital represents the initial investment of shareholders in a corporation. Retained earnings are profits earned by a corporation since the start of business, less losses, dividends, or equity transfers.
In many countries, the amount of retained earnings is the basis for calculating the maximum possible distribution of past profits to shareholders. Retained earnings are not funds to be distributed to shareholders. Retained earnings represent earnings reinvested in the corporation.
In accordance with the principles of completeness of information reflection, the “Share capital” section of shareholders’ equity of the corporate balance sheet contains significant information about the share capital of the corporation: types of shares, their nominal value, the number of shares authorized for issue, the number of shares issued and in circulation. The information contained in the Equity section of shareholders' equity is the subject of the remainder of this chapter. A detailed discussion of retained earnings is given in the chapter on earnings and retained earnings.
Share capital
The unit of ownership in a corporation is a share. The shareholder receives a share certificate showing the number of shares in the corporation that shareholder holds. He can transfer his property as he sees fit. To transfer to another person, the owner of the share must sign the share certificate and give it to the secretary of the corporation.
In large corporations that have been listed on specially established stock exchanges, it is difficult to keep records of shareholders. Such corporations issue millions of shares, and within a single day, several thousand shares may change hands. Therefore, such corporations often appoint independent registrars and transfer agents, which are usually banks or trust companies that perform secretarial functions. They are responsible for conducting the transfer of shares of the corporation, maintaining the register of shareholders, compiling the list of shareholders for shareholders' meetings and paying dividends.
When issuing shares, corporations often involve underwriters who act as intermediaries between corporations and potential investors. For a fee, usually less than one percent of the sale price, the underwriter secures the sale of the shares. In the equity and share premium accounts, the corporation records the amount of net proceeds from the issuance of shares, i.e. the amount paid for shares by purchasers, net of underwriter's fees, legal fees, certificate printing costs, and other costs directly attributable to the issuance of shares.
Capital authorized for issuance
In most countries, when a corporation applies for registration, the draft articles of association must specify the maximum number of shares the corporation is allowed to issue. This amount represents the capital that is allowed to be issued. Most corporations receive permission to issue more shares of stock than is necessary at the time of their incorporation. This allows the corporation to issue more shares in the future to raise additional capital.
For example, if a corporation plans to expand its operations in the future, then unissued shares, permitted in the articles of association to be issued, will be a possible source of capital. If all of the authorized capital was issued at once, then the corporation would have to apply to the state for permission to amend the charter to increase the number of shares in it authorized to be issued.
The articles of association also indicate the face value or nominal value of those shares that were allowed to be issued. The face value, or face value, is an arbitrary amount, often set by law, that must be printed on each share. This value is reflected in the "Share Capital" accounts and represents the authorized capital of the corporation.
The authorized capital is equal to the number of issued shares multiplied by their nominal value; it is the minimum amount that can be shown as share capital. The face value, or par value, is usually not comparable to the market or book value of the shares. When a corporation is created, an entry can be made in the general ledger showing the number and description of shares authorized to be issued.
Issued and outstanding capital
Issued capital represents shares sold or otherwise transferred to shareholders. For example, a corporation is allowed to issue 500,000 shares, but the corporation may choose to issue only 300,000 shares at the time the corporation is organized. The holders of these 300,000 shares own 100% of the property of the corporation. The remaining 200,000 shares are unissued. They do not confer any rights or privileges until they are released.
Capital in circulation are shares issued and outstanding. A share is not considered to be outstanding if it has been redeemed by the corporation that issued it or returned to that corporation by a shareholder. In such cases, the number of shares issued will be greater than the number of shares outstanding. Those issued shares that have been repurchased and held by the corporation are called treasury shares, which we will discuss in more detail later in this chapter.
Ordinary shares
A corporation can issue two main types of shares - ordinary and preferred. If only one type of shares is issued, then they are called ordinary. Ordinary shares are the residual equity of a corporation.
This means that in the event of liquidation of the company, the turn to satisfy the claims of holders of ordinary shares comes only after the turn of all creditors and holders of preferred shares. Since common stock is usually the only stock that gives its holders the right to vote, it is a way to control the activities of a corporation.
Availability of authorized capital is a prerequisite for the functioning of an organization carrying out production or other commercial activity. The authorized capital performs three functions:
starting - is the source of the organization's property;
share - establishes the share of participation of each owner in the authorized capital;
guarantee - guarantees the fulfillment of obligations to third parties.
Depending on the organizational and legal form of commercial organizations, the authorized capital as an integral part of equity capital can act as:
authorized capital (in JSC and LLC);
share capital (in partnerships);
share fund (in production cooperatives);
statutory fund (in unitary enterprises).
For accounting purposes in organizations that have passed state registration, these concepts are reduced to the concept of authorized capital.
Authorized capital (UK)- this is a set of contributions (contributions) of the founders (owners) to the property of the organization in the amounts specified in the constituent documents. The value of the authorized capital characterizes property size, guaranteeing the interests of the organization's creditors. The value of the UK must be indicated in the constituent documents of the organization. The minimum size of the authorized capital is stipulated by federal laws: for a newly established OJSC it is 1000 minimum wages, for a closed joint-stock company or LLC - 100 minimum wages. The minimum size of the share capital and share fund is not established by law. Changing the size of the UK is possible only after making changes to the register of state registration. As a result of ongoing operations, changes in the size of the authorized capital are not allowed.
To account for the authorized capital, its changes and settlements with the founders, the following accounts:
passive account 80 "Authorized capital". Designed to summarize information about the state and movement of the authorized capital of the organization;
active-passive account 75 “Settlements with founders”. Designed for all types of settlements with the founders (participants) of the organization. Sub-accounts can be opened for account 75:
75/1 "Settlements on contributions to the authorized (share) capital"
75/2 "Calculations for the payment of income"
active account 81 "Own shares (shares)". Designed to account for repurchased own shares and shares.
In the balance sheet, the share capital reflected in section III"Capital and reserves" on the line "Authorized capital".
The procedure for the formation of the authorized capital during the establishment (creation) of the organization
Consider the formation of the authorized capital in joint-stock companies and in limited liability companies.
Formation of the authorized capital of joint-stock companies
Authorized capital of joint-stock companies is formed at the expense of the contributions of participants through exchange these contributions to shares and consists frompar value of shares acquired by shareholders. A share is a unit of ownership in a joint-stock company. The promotion has the following attributes: cost (price) and earnings per share. There are the following types share price: nominal, balance sheet, liquidation, exchange rate (market). earnings per share acts as a dividend and represents a part of the JSC's profit received during the reporting period, which is distributed among shareholders.
Joint stock companies can be open and closed. Shares of an open joint stock company can be purchased by any investor. Shares of a closed joint stock company are distributed among predetermined participants.
Stock by way of granting rights to owners are divided into two groups:
ordinary shares;
privileged.
Ordinary shares have the same nominal value and grant their owners the following rights:
participation in the general meeting of shareholders of the company with the right to vote on all issues of its competence;
receiving part of the company's net profit (dividend) for the current year;
participation in the distribution of the property of the company during liquidation after satisfaction of the requirements of the owners of preferred shares specified by the charter.
Preference shares provide their holders with certain privileges in comparison with ordinary shares. The owner of preferred shares receives income in the form of a percentage of the nominal value of the shares, regardless of the results of the organization's activities.
When establishing a joint-stock company the following conditions must be met:
the payment price of the shares must not be lower than their par value;
the form of payment for shares is determined by the founders;
money, securities, other types of property, property rights, etc. can be a contribution to the authorized capital. Evaluation of non-monetary contributions is made by agreement of the parties. In the cases established by the laws "On Limited Liability Companies" and "On Joint Stock Companies", an independent appraiser is invited;
the payment period for the shares is determined by the founders, but at least 50% of the shares must be paid within 3 months from the date of state registration joint-stock company, the rest - within a year from the date of state registration.