The direct responsibility of each employer, in accordance with the requirements of Russian law, is the task of keeping military records in the organization - step-by-step instructions for 2020 can be of great help to personnel department employees or the entrepreneurs themselves. At the same time, it must be remembered that the maintenance of military records at the enterprise has many individual features and nuances, failure to comply with which may entail bringing the employer to responsibility.
Military registration in the organization in 2020 - basic requirements and legislative regulation
The current legislation of the Russian Federation assumes that the employer is obliged to ensure the maintenance of military records at the enterprise in relation to employees in his organization - and this function is most often assigned to the personnel department of the organization. At the same time, the legislative regulation of this issue is quite simple and unambiguous. In particular, the employer and the employees themselves should pay attention to the provisions of the following federal regulations, which are devoted to the legal regulation of military registration in organizations:
- Article 65 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In the Labor Code, documents of military registration are mandatory for presentation upon employment for persons liable for military service. Without them, the employer is not entitled to conclude an employment contract.
- Federal Law No. 53 of March 28, 1998. This Federal Law regulates the general principles of military duty, military registration and military or alternative civilian service. In addition, this law also obliges organizations to maintain military records - this applies to both commercial and non-profit organizations, and both budgetary and non-budgetary institutions.
- Federal Law No. 31 dated February 26, 1997. This law at the federal level deals with issues directly related to mobilization procedures. At the same time, the requirements of the aforementioned law apply not only to employees of enterprises, but also to vehicles that are on their balance sheet and are subject to mobilization if necessary.
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 719 dated November 27, 2006. This government decree directly regulates the procedure for maintaining military records in organizations and establishes in its regulations the relevant Regulations on military records, which are mandatory for business entities.
In addition to the above fundamental regulations, military registration and alternative civilian service are also considered in the provisions of individual orders of the relevant authorities, primarily the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation. At the same time, it will be useful for employers to first of all familiarize themselves with the methodological recommendations for maintaining military records compiled by the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated 11.04.2008.
Who is subject to military registration at the enterprise
Not all employees are subject to military registration at the enterprise, respectively, and it is necessary to carry out personnel activities of this nature only in relation to a limited list of persons. According to the current legislation, military registration in organizations applies specifically to their employees liable for military service, which include:
According to the above list of requirements, almost all males are subject to military registration, but women are only in exceptional cases. Accordingly, for violation of the requirements for maintaining military records in relation to women who did not provide documents confirming that they have a military registration specialty during employment, the employer cannot be held accountable - however, such employees can be dismissed for violating the employment procedure.
Legislation defines only one category of males, for whom there is no need to maintain military records without any additional features. It includes persons who do not have Russian citizenship. Thus, in relation to foreigners and stateless persons, there is no need to carry out military registration measures.
The status of underage workers is uncertain in this matter - on the one hand, such male citizens of the Russian Federation receive primary documents of military registration at the age of 16 and are required to present them to the employer upon employment, however, there is no direct requirement to conduct military registration measures regarding these employees in the main regulatory documents . However, the guidelines require employers to submit documentation to the military registration and enlistment office about all working male employees aged 15 and 16, as well as to check that these employees have completed all the necessary military registration documents and notify the military registration and enlistment office of their absence.
It should also be remembered that men, depending on the rank, are removed from the military register at the enterprise and in general when they reach the age limit for their rank. It is 50 years for enlisted personnel, 55 years for junior officers, 60 years for those with the rank of major to colonel, and 65 years for senior officers. For women, the age limit for military registration is 45 years for enlisted personnel and 50 years for officers.
A number of employees are also not subject to military registration if there are specialized grounds. These include - permanent residence outside the Russian Federation and the presence of a residence permit in another state, the presence of an officer's rank and being in the reserve of intelligence and the FSB. Since serving a sentence in places of deprivation of liberty also often implies the possibility of being an employed employee, military records are also not kept for this category of citizens, if they work.
Who should keep military records in organizations - the definition and number of responsible persons
Legislation strictly regulates the procedure for maintaining military records at enterprises. Thus, the number of persons responsible for this procedure is regulated, depending on the total size of the organization's staff. It is supposed to use the following restrictions in this matter and regulate the procedures applied:
- With up to 500 employees. In this situation, the legislator requires the presence of at least one employee working on a part-time basis and ensuring the maintenance of military records in the organization. At the same time, it should be noted that the involvement of specialists on the principle of outsourcing is not allowed - it is the specialist who is in the staff that should be engaged in military accounting at the enterprise, but he can also be a part-time one.
- With a staff of 500 to 2000 employees. This situation presupposes the presence of an employee who would be engaged in military accounting activities in the organization on a full-time basis as his main employment.
- With a staff of 2000 to 4000 employees. In this case, it is necessary to provide for the presence of two employees who are employed full-time in maintaining military records as their main job.
- If the staff exceeds 4000 employees, then for every 3,000 people it is necessary to allocate one more employee of the personnel department who maintains military records.
It must be understood that these figures are minimal - the employer has the right to establish a larger number of employees who would be responsible for maintaining military records of employees in 2020. At the same time, it should also be noted that the legislation also has a number of additional requirements in relation to employees involved in military registration. So, if more than one employee is engaged in military accounting, the employer is obliged to issue in the organization military registration table as a separate separate division.
The above-determined number of employees in the state affects the total staff of the enterprise, and not the number of persons subject to military registration, which should be considered by employers and employees of personnel departments.
It should also be remembered that employees who keep military records at the enterprise belong to a special category of workers, for whom additional legal regulations apply. In particular, the employer must necessarily coordinate the candidacy of each of these workers with the local military commissariat. In the absence of a military registration and enlistment office on the territory of the settlement, this coordination is carried out with local executive authorities. The dismissal of employees keeping military records in the organization in 2020 must also be agreed with the military registration and enlistment office or local authorities, as well as their transfer to other units and other personnel actions.
The employer should take care in advance about the availability of deputies for employees who carry out military registration at the enterprise, since the regulated number of persons maintaining military registration must always be not lower than that established by law at any time. At the same time, the transfer of all cases and duties to deputies should also be accompanied by fairly complex procedural procedures. Therefore, an urgent measure will be the early identification of a larger number of persons responsible for maintaining military records of workers.
Should an individual entrepreneur keep military records
The questions of whether military registration is mandatory for individual entrepreneurs are relevant for many individual entrepreneurs in the Russian Federation. This is due to the fact that they often become the target of inspections by regulatory authorities and they may sometimes be tried to be held accountable for non-compliance with military accounting requirements. However, this practice is refuted both directly by the regulations on military registration at enterprises, and was separately considered by the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation in Resolution No. an individual entrepreneur should not keep military records in the organization in principle.
Such standards are related to the fact that the legislation prescribes the maintenance of military records to organizations and institutions. At the same time, individual entrepreneurs are individuals, albeit employers. And, since they cannot be attributed to organizations, they should not carry out the indicated personnel procedures. However, they are still required to require military registration documents when hiring employees.
It should also be noted that in order to avoid unnecessary conflicts with inspection bodies, individual entrepreneurs have the right to keep military records of employees - this is not a violation of current legislation. At the same time, it should also be noted that an individual entrepreneur cannot be brought to administrative responsibility for violating the requirements and rules of military registration at an enterprise at all.
Step-by-step instructions for military registration in an organization in 2020
The easiest way to ensure the maintenance of military records in an organization in 2020 is to help step-by-step instructions for employers. It should be noted that the procedure for this issue is quite simple, but may vary depending on the specifics of an individual enterprise. In general cases, for maintaining military records in 2020, you can use the following step-by-step instructions:
This is the basic procedure for maintaining military records in the organization. However, the legislator also imposes additional obligations on the employer in relation to this procedure, which include:
- Maintaining archival documentation. The employer must archive all documents of employees related to military registration, including their personal cards.
- In case of detection of fake documents or false information about the employee in matters of military registration, the employer is obliged to inform the military registration and enlistment office about this circumstance.
- The employer, if the organization belongs to the category of importance for the country's defense, must also book employees in case of mobilization - this procedure will allow you to leave the employees necessary for the activities of the enterprise at their workplaces.
- At the request of the employee, the employer is obliged to provide documents on the military registration measures carried out in relation to him.
- About upcoming military training or mobilization procedures, as well as conscription, the employer must notify the employees subject to these events in advance.
Responsibility for violation of military registration requirements
The current Russian legislation provides for the possibility of holding the employer liable for violation of the requirements for maintaining military records. At the same time, employees of military registration and enlistment offices or local administrations have the right to conduct audits of military registration annually for enterprises with a staff of more than 500 people, and once every three years for enterprises with a smaller number of employees.
All organizations in which military registration must be carried out, regardless of the number of employees, are subject to verification and possible prosecution. The exception is organizations that do not have labor relations at all.
Directly, the issues of administrative responsibility related to military registration in the organization are considered by the provisions of Articles 21.1-21.7 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation and provide for the imposition of fines, depending on the specific misconduct, in the amount of 300 to 1000 rubles. However, it should be remembered that this fine can be applied to each individual employee and a separate fact of violation, therefore, in case of violations of the requirements of the law, with a large number of employees, the amount of material losses of the enterprise due to incorrect military registration can be significant.
Military registration is a mandatory registration of all military personnel. Let's take a look at the steps to maintain military records in the organization.
Organization of military registration and its purpose
Maintaining such records is a mandatory and rather important point in the work of any legal entity. Art. 8 of the Federal Law No. 61-FZ of May 31, 1996. Maintaining paperwork for military service employees is regulated by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 719 dated November 27, 2006 (as amended on June 27, 2017). Military registration and enlistment offices regularly arrange record keeping checks, and fines are assigned for each identified item (Chapter 21 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
The objectives of maintaining this type of accounting are formulated in clause 2 of Regulation No. 719:
- In calm periods of life, accounting is ensuring the fulfillment of military duty by each person who must fulfill it, to control that the ranks of the armed forces are filled with military personnel.
- But during the military situation, the registration of persons liable for military service is designed to help to mobilize all the necessary people in a timely manner and fill state structures with the necessary working resource.
To comply with these goals, the state must have up-to-date information about conscripts, and the relevance of this information is precisely ensured by the employer by registering these persons.
The tasks of military registration are:
- observance by citizens of their military duties provided for by law, the inability to hide from the performance of public duty;
- correct documentation of accounting;
- analysis of the qualitative and quantitative composition of resources intended to protect the state and society.
The following categories of persons are subject to registration (clause 14 of Decree No. 719): men aged 18 to 27 years who are required to be registered at the commissariats at the place of residence and are not in the reserve (conscripts), as well as citizens who are in the reserve ( conscripts).
The law includes women with military registration specialties, as well as men who:
- are in stock;
- dismissed from military service with enrollment in the reserve;
- completed training for reserve officers;
- did not complete military service for various reasons until the age of 27;
- completed alternative service.
There is no need to keep military records, for example, for employees released from military duties (limited fit, unfit, who served in another state), performing civilian alternative service, permanently residing outside the territory of the Russian Federation. Officers who are in the reserve of the SVR of Russia or the FSB of Russia, women, if they do not have a military specialty, are not subject to registration.
We have compiled step-by-step instructions for organizing military registration in an organization, it will help you understand the nuances of the procedure.
Who is in charge of military registration
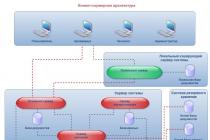
The following persons are responsible for maintaining documentation on the registration of persons liable for military service at an enterprise of state or municipal ownership:
- Organization director.
- Head of Human Resources (or his deputy).
- Clerk, secretary.
The best way to keep records is to create a military registration desk (VOS), but in small organizations this is not realistic. It is created when an institution employs from 2,000 to 4,000 people who are subject to military registration. In this case, two people are allocated for this work. In small organizations, the responsibility is assigned to one of the employees of the personnel department.
Regardless of the presence of a military registration desk, those responsible for accounting perform the following tasks.
- They keep documentation of conscripts and those liable for military service from the personnel of the enterprise.
- Ensure that the personnel of the enterprise perform military duties prescribed by the laws of the Russian Federation.
- Documentation of information about conscription workers.
- Interact with departments of the commissariat, state and municipal authorities on various issues.
Military registration in the organization: step-by-step instructions for 2020
This instruction is intended to help in maintaining military records in an organization in 2020 for organizations with state or municipal ownership.
Step 1. Determine and appoint responsible persons.
Military registration and booking in the organization, as well as the appointment of persons responsible for the implementation of these procedures, is prescribed in the order of the director of the enterprise. The order is issued every year. The form of this paper is proposed in the "Methodological recommendations for maintaining military records in organizations" (Approved by the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation) dated 07/11/2017
Step 2. We develop a work plan for military registration and booking.
It includes the name of each activity, deadlines, responsible persons and performance notes. The marks are certified by the signature of the responsible person.

Step 3. Create a check log.
This is a mandatory document approved by law. It contains data on inspections in this area, detected violations and instructions to eliminate violations.

Step 4. We are developing a regulation on office work for military registration.
The document is intended to streamline the workflow in this area at a state or municipal enterprise. An example provision structure should include:
- General provisions (what the document is intended for, what items are present in it and what they regulate).
- Documentation requirements.
- Rules for preparing documents (indicate which papers must be certified by the signatures of responsible persons, whether it is possible to fill out forms by hand).
- Information about the person responsible for registration, maintenance and storage of papers for military service employees, as well as his functions.
- Rules and procedure for working with documents (when to draw up papers, when to transfer them to external authorities).
- The procedure for storing and transferring papers to the archive.
Step 5. We fill in the primary documents for employment.
When employees are admitted to a state organization, primary documents are filled out for them (Chapter II, clause 17 of Resolution No. 719):
- Registration cards (for conscripts).
- Registration and alphabetical cards (for ensigns, midshipmen, foremen, sergeants, soldiers and sailors of the reserve).
- Primary registration cards (for officers).
- Personal cards (form T-2) containing general information, information about military registration, employment and transfers, attestations, advanced training, awards, vocational training, vacations, social benefits, dismissal.
If earlier papers for employees on which it is necessary to keep records were not kept at the enterprise, these documents are filled out for existing employees.

Step 6. We make out the stand.
Responsible for maintaining records for military service employees usually keep background information on this issue in folders. However, it is better to arrange an information stand. It clearly demonstrates the main points:
- for booking military service;
- on the goals and objectives of registration, maintenance and storage of documentation for military service workers;
- about responsibilities;
- about offenses;
- and an important announcement for conscripts
There are no stand design requirements. Here is an example of how it might look at a state-owned enterprise:

Legislation on military registration
Maintaining documentation for military personnel in state institutions is based on the "Methodological recommendations for maintaining military records in organizations" (Approved by the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation) dated April 11, 2008 and includes:
- Control over the presence in the passports of citizens of the Russian Federation who are accepted for a position in the organization, marks of military duty.
- Filling out personal cards (T-2 form) based on entries in other documents.
- Explaining to employees how to perform their military duties.
- Informing the military commissariats of all changes in the information in the passports of the employees of the organization for which records are kept, and violations.
- Sending within 2 weeks to the military commissariats information about citizens liable for military service who have been hired or fired.
- Annual data reconciliation.
- Alert employees about calls to the military registration and enlistment offices and ensure their attendance.
The form of a personal card for employees of the T-2 enterprise was proposed by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation No. 1. Our instructions for maintaining military records in organizations include filling out this form.
How does the military registration check work?
The verification of military registration is carried out by the military registration and enlistment office or local governments. In companies with more than 500 employees, inspections are usually carried out once a year. In small legal entities, inspections can be carried out no more than once every three years.
Auditors will be particularly interested in the following documents:
- order to maintain military records;
- a work plan for maintaining military records;
- personal cards of citizens for which records are kept;
- accounting check log;
- a receipt for the receipt of military registration documents from citizens;
- official office work on the issue of maintaining military records.
When conducting an audit of the correctness of accounting, the supervisory authority evaluates:
- implementation and organization of military registration in the company;
- completeness and reliability of the information contained in the personal cards of employees for which records are kept.
The results of the verification of military records are entered into the journal
military records reporting
A specialist whose labor function is to maintain military records provides the following reports to the military registration and enlistment office:
- For hired or dismissed employees subject to military registration - within 2 weeks.
- For employees registered with the military or those who are required to be registered with the military - within 2 weeks from the receipt of the request.
- For males 15 and 16 years old - once a year in September.
- For males registering for the next year - once a year until November 01
Organization Responsibility
If an enterprise does not keep records of employees liable for military service and does not transfer data to military commissariats, it will face fines. In paragraph 21 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, their sizes are established depending on the violation, form of ownership and direction of the enterprise.
Both the head of the company and the person appointed responsible for its maintenance may bear administrative responsibility for not maintaining military records. A fine is issued by a person authorized by the military registration and enlistment office:
- if an employee of the state structure of medical and social expertise did not send to the military commissariat within the prescribed period information about persons liable for military service with disabilities - a fine in the amount of 300-500 rubles;
- if an employee of the civil registry office did not send information about the changes to the commissariat - a fine of 300-500 rubles;
- if the person responsible for maintaining the documentation did not provide information to the commissariat about recruited (or dismissed) citizens liable for military service - a fine of 300-1000 rubles.
Reservation of citizens in reserve
The procedure makes it possible to provide personnel (managers, specialists, highly qualified personnel) to enterprises in wartime and during the period when mobilization is announced. Citizens have a deferment from conscription for military service for mobilization, in wartime, from conscription for military training.
To book citizens, a special mobilization commission is created, which is created by the local authority of the municipality. They decide on the list of professions, age, rank. Further lists of positions are sent to the employer. They are brought to the responsible person under the signature. The employer, in turn, selects the appropriate personnel in the company's staff and fills out a special form.
If the organization makes reservations for citizens, then the organization needs to maintain additional documentation. For example, related to the issuance and registration of certificates of deferment (the company receives this form of strict accountability at the military registration and enlistment office), as well as an action plan for the presentation of these certificates. There is no approved form of the plan. The company develops it independently.
How to control
Control over the status of work on booking is carried out at least once every three years.
Maintaining military records in an organization is a set of measures, the responsibility for which is entrusted to the heads of organizations and other responsible persons. In this material, we will consider how to organize the registration of persons liable for military service at the enterprise and what steps need to be taken for this.
The obligation of organizations, regardless of their form of ownership, to keep military records is stipulated in Article 8, paragraph 1, subparagraph 6 of the Federal Law of May 31, 1996 No. 61-FZ "On Defense". The purpose of such accounting is to meet the needs of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation in human resources both in peacetime and in wartime.
Organization of military registration in the organization: step by step instructions
To start keeping military records in an organization (2020), you must complete an algorithm consisting of five steps:
- Appoint responsible persons.
- Determine the circle of employees subject to VU.
- Obtain documents for maintaining a higher education institution.
- Coordinate the order on the appointment of responsible persons with the local military commissariat.
- Perform and supervise accounting duties.
Military registration in the organization: step by step instructions 2020
Based on the described algorithm, detailed instructions for maintaining military records in organizations are presented below.
Step 1: appointing responsible persons
The head of the company is responsible for the state of the WU in the company. Such a norm is enshrined in paragraph 9 of Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 27, 2006 No. 719 "On approval of the Regulations on military registration". The responsible person appointed by the head is directly responsible for maintaining records. To do this, the enterprise issues an appropriate order, and the function of maintaining the WU is fixed in the official duties of the employee.
Depending on the number of employees who are at the university, the number of specialists who will conduct this activity is determined. In accordance with paragraph 19 of Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 27, 2006 No. 719, the number of military service employees is determined as of December 31 of the previous year. Then, based on the standards of paragraph 12 of Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 27, 2006 No. 719, the number of responsible employees is determined.
In large enterprises where there are two or more employees responsible for keeping records, a separate unit is created, called the military accounting table. Such a unit is located in a separate room, equipped with metal cabinets for storing documents.
Step 2: determining the circle of military servicemen
According to paragraph 14 of the Resolution, military registration is subject to:
- conscripts;
- conscripts.
Conscripts include males aged 18 to 27 years who are required to be registered with the military and who are not in the reserve. As for those liable for military service, the circle of such persons is quite wide. These include:
- all categories of military in reserve;
- persons who received a deferment from military service;
- persons exempted from military service;
- persons who have completed alternative civilian service;
- citizens who have served in military departments;
- women with military specialties.
Not subject to military registration, in accordance with paragraph 15 of the Resolution:
- persons exempted from conscription for military service in accordance with Article 23 of the Federal Law of March 28, 1998 No. 53-FZ "On military duty and military service";
- persons permanently residing outside the Russian Federation;
- women who do not have a military specialty;
- reserve officers of the SVR or FSB.
Step 3: Obtaining Documents for Record Keeping
Military registration and booking in the organization is carried out on the basis of the following documents:
- certificate of a citizen subject to conscription for military service - for conscripts;
- a military ID or a certificate in exchange for it - for those liable for military service.
Step 4: approval at the local military commissariat
According to paragraph 22 of the "Methodological recommendations for maintaining military records in the organization", the draft order on the appointment of responsible persons is coordinated with the local military commission. In addition to coordination, department employees can give an introductory briefing on record keeping, provide sample forms, etc.
Step 5: Execution and control of record keeping
After all the steps listed above are completed, the responsible employee or department proceeds directly to the performance of their duties. In particular, the company must provide the following information to the military registration and enlistment office:
- information about hired or dismissed citizens who must be on military registration;
- lists of men who will turn 17 next year, as well as once a year (in September) lists of men aged 15 and 16.
On the basis of a military card or certificate of a citizen subject to conscription, the necessary information is entered into a personal card in the T-2 form.
In addition, the company must maintain the following documents:
- a work plan for maintaining military records and booking citizens in the reserve;
- an order on the organization of military registration and reservation of citizens in reserve;
- log of checks of the state of military registration and booking of citizens in reserve;
- a file of personal cards of the form No. T-2 and No. T-2 GS for citizens in the reserve and citizens subject to conscription for military service;
- receipts for the receipt of documents of military registration and roots from them;
- organization accounting card (KUO form No. 18).
The list provided is not exhaustive. In different regions and at different enterprises, there may be a need to maintain other additional documents. It is also worth saying that responsible employees should carry out methodical work and explain why the organization of military registration is needed, and its purpose.
Responsibility for evasion and errors in maintaining military records
The correct and timely maintenance of the WU is in the interests of the head of the organization and the responsible employee. After all, for evading compliance with this requirement, administrative liability is provided. In particular, the following penalties are provided:
- untimely submission to the military registration and enlistment office of information about citizens subject to initial registration at the university, as well as about those who are or are not registered - from 300 to 1000 rubles (and part 3 Article 21.4 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
- failure to notify citizens about the summons to the military registration and enlistment office - from 500 to 1000 rubles ().
Fines can be issued based on the results of an audit conducted by representatives of the military registration and enlistment office. At large enterprises where the number of employees is more than 500 people, it is held once a year. At small enterprises - once every 3 years.
First of all, the auditors pay attention to the completeness and reliability of the information provided, as well as to the correctness of the RIA. The results of the check are reflected in the corresponding journal.
Every organization is required to keep military records. To avoid fines, find out who is subject to military registration, prepare the necessary documents and submit information about employees to the military registration and enlistment office in time.
In the article:
Download the documents required for work:
What categories of citizens of the Russian Federation are subject to military registration
Military records in an organization are often the responsibility of personnel officers who are charged with collecting, systematizing and updating information about the performance of military duties by employees. The work is carried out in two directions - general accounting and booking of citizens in reserve (GPZ).
For failure to provide information about citizens subject to registration, failure to notify an employee of a call to the military enlistment office and other violations in the field of military registration (VU), the law provides for administrative liability (Articles 21.1, 21.4, 21.2 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). In order to avoid problems during the next inspection, you need to clearly know which categories of citizens are subject to military registration, and timely draw up lists of employees that meet the established criteria.
Attention! Personnel officers have two new responsibilities for military registration. Now to look for evaders is the task of the employer.
Who is not included in the lists:
- foreign workers are not considered liable for military service, therefore they are not included in the lists (Article 1 of Law No. 53-FZ of March 28, 1998, Article 15 of Law No. 115-FZ of July 25, 2002);
- women who do not have a military specialty;
- currently serving in the military;
- permanently residing outside the Russian Federation;
- serving sentences in prisons.
The General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation approved the Guidelines dated July 11, 2017, which lists all categories of personnel subject to registration. These include:
- Men of military age not enlisted in the reserve (18-27 years old)
- Men in the reserve and exempt from conscription
- Men over 27 years of age who did not serve in the army due to a delay
- All citizens who have been discharged from the military or who have served in alternative service
- Women who received military specialties
- Specialists trained at military departments of educational institutions
Important! All eligible employees are taken into account, including those working remotely, part-time or on an external part-time basis.
Reservation of citizens who are in reserve is entrusted to individual employers by order of the Interdepartmental Commission of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation, executive authorities and local governments. The organization receives ready-made lists of positions and professions or extracts from them. On the basis of the documents received, it is necessary to book employees suitable for the requirements and fill out the forms of form No. 4 (issued at the military registration and enlistment office). As a rule, we are talking about valuable specialists, representatives of rare professions, highly qualified managers. Reserved citizens are exempt from conscription for military training and service during mobilization.
The first steps of a personnel officer when hiring a conscript
What documents of military registration is maintained by the employer
Maintaining military records in an organization requires the execution of a number of documents - both for internal use and for transfer to the military registration and enlistment office. First of all, the employer issues an order to organize military registration.
Order on the organization and maintenance of military records
If the VU will be conducted by an employee of the personnel department on a part-time basis, do not forget to make the appropriate changes to the employment contract, staffing table and time sheet.
Attention! To find out if the applicant is liable for military service, look at the 13th page of the internal passport, where the corresponding stamp is placed.
In addition, the employer is entrusted with carrying out explanatory measures with employees, as well as compiling and maintaining:
- file cabinets of personal cards (forms No. T-2, T-2GS) for all employees who are in the reserve and are subject to conscription for military service;
- log of checks of the state of military registration;
- organization accounting cards (CMO) in form No. 18.
How to keep military records in an organization: step by step instructions
Absolutely all enterprises are required to keep military records, regardless of the field of activity and organizational and legal form. It will help you to understand the intricacies of the process and understand how the organization of military registration in the organization begins, step by step instructions.
Step-by-step instructions: we keep military records in the organization
Step 1. Appoint a responsible person. This can be either a company secretary or an employee of the personnel department, or a main employee or an entire unit (military registration desk) engaged exclusively in maintaining military records.
Step 2. Determine which categories of employees you will work with. Focus on the requirements of the Guidelines, approved. General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation on April 11, 2017 and Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 719 of November 27, 2006. If the enterprise maintains not only general records, but also reservations of citizens staying in reserve, additionally develop documents in accordance with the annexes to the Instruction approved by the resolution of the Interdepartmental Commission on Reservations No. 664c dated February 3, 2015.
Step 3. Register the employer with the local military commissariat. Here you can also get an introductory briefing, guidelines, sample documents and advice on controversial or atypical cases. Registration of separate divisions is carried out at the location of branches and representative offices, and not the parent organization.
Step 4. Prepare all the necessary documents: magazines, cards, lists. If possible, automate part of the paperwork using special programs for the formation of workflow.
You can master the methods of competent document management at the HR School:
Step 5. Keep your military records up to date. At least once a year, check the data of personal cards with documents provided by employees or representatives of the military registration and enlistment office, make the necessary changes.
Step 6: Meet reporting deadlines. The employer is obliged to provide the military registration and enlistment office or local authorities with the following information:
- about male employees who turn 17 next year - the age of initial military registration (every year before November 1);
- about male employees aged 15 and 16 (annually in September);
- on the employment and dismissal of employees subject to military registration - within two weeks from the date of the event;
- about employees who are at the VU - upon request within two weeks.
It is very important not to limit yourself to paperwork only, but to conduct a full-fledged methodological training of personnel: explain the procedure for mobilization, hand over summonses, and promptly report calls to the military enlistment office.
VU maintenance checks are carried out regularly. If the company does not yet maintain military records, start with organizational issues: register at the military registration and enlistment office, appoint a responsible officer. If records are kept, an audit will not interfere: check the data and make sure that you report to the military registration and enlistment office on time, and all the necessary documents are stored in the personnel department or the military registration desk of the enterprise.
1. Under the military account is understood the state system of accounting and analysis of the draft and mobilization human resources available in the country.
The organization of military registration in state authorities, executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, local self-government bodies of settlements (urban districts) and organizations is included in the content of mobilization training and mobilization.
Military registration is provided for by the military duty of citizens and is provided by the state system for registering draft and mobilization human resources, within the framework of which a set of measures is taken to collect, summarize and analyze information about their quantitative composition and qualitative state (hereinafter referred to as the military registration system). The functioning of the military registration system is provided by the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation, the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation, the Foreign Intelligence Service of the Russian Federation, the Federal Security Service of the Russian Federation, the executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local governments and organizations.
Military registration of citizens of the Russian Federation is organized in accordance with the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the federal laws "On Defense", "On Military Duty and Military Service", "On mobilization training and mobilization in the Russian Federation" and the Regulations by Decree
2. The main goal of military registration is to ensure the complete and high-quality staffing of conscription human resources of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation, other troops, military formations and bodies in peacetime, as well as to ensure during periods of mobilization, martial law and in wartime:
a) the needs of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation, other troops, military formations, bodies and special formations in mobilization human resources by way of early assignment (assignment) of citizens in the reserve to their composition;
b) the needs of public authorities, local governments and organizations in labor resources by assigning (booking) to them the required number of managers and specialists from among the citizens in the reserve working in these bodies and organizations.
3. The main tasks of military registration are:
a) ensuring the fulfillment by citizens of military duty established by the legislation of the Russian Federation;
b) documentary registration of military registration information about citizens who are on military registration;
c) analysis of the quantitative composition and qualitative state of conscription and mobilization human resources for their effective use in the interests of ensuring the defense of the country and the security of the state;
d) carrying out planned work to prepare the required number of military-trained citizens who are in reserve to ensure the transfer of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation, other troops, military formations and bodies from peacetime to wartime, during the period of mobilization and maintaining their staffing at the required level in wartime.
4. Military registration is carried out constantly and covers all categories of citizens subject to military registration. The main requirement for the military registration system is to constantly ensure the completeness and reliability of data that determine the quantitative composition and quality of the draft and mobilization manpower.
5. Military registration in military commissariats, local governments and organizations are subject to:
a) male citizens aged 18 to 27 who are required to be registered with the military and who are not in the reserve (hereinafter referred to as conscripts);
Males in reserve;
Dismissed from military service with enrollment in the reserve of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation;
Successfully completed training under the training program for reserve officers at military departments at state, municipal or state-accredited non-state educational institutions of higher professional education in the relevant areas of training (specialties) and graduated from these educational institutions;
Those who did not complete military service due to exemption from conscription for military service;
Those who did not complete military service in connection with the provision of deferrals from military service or were not called up for military service for any other reason, upon reaching the age of 27;
Dismissed from military service without military registration and subsequently put on military registration in military commissariats;
Passed alternative civilian service;
Female, having the corresponding military registration specialties specified in the annex to the Regulations on military registration.
6. Military registration of persons liable for military service is divided into general and special.
Those liable for military service who, in accordance with the established procedure, are reserved for state authorities, local governments or organizations for periods of mobilization, martial law and in wartime, as well as those serving in the internal affairs bodies, the State Fire Service, institutions and bodies of the criminal -executive system, bodies for control over the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances in positions of rank and file and commanding staff.
The rest of those liable for military service are on the general military register.
With regard to persons liable for military service working in federal executive bodies in which military service is provided for by law, who are on a general military record, the military commissariats, if there are applications from the indicated federal executive bodies, draw up plans for sending them to work in positions of civilian personnel in these bodies during periods mobilization, martial law and in wartime.
10. The procedure and features of the military registration of citizens serving in the internal affairs bodies, the State Fire Service, institutions and bodies of the penitentiary system and bodies for controlling the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances in the positions of ordinary and commanding staff are determined by the Regulations on military registration , approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 27, 2006 N 719.
Military registration of persons liable for military service serving in the internal affairs bodies, the State Fire Service, institutions and bodies of the penitentiary system, bodies for controlling the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances is carried out by military commissariats at the place of residence or place of temporary stay of these citizens. In these bodies and institutions, military registration of citizens is carried out in the manner determined by the Regulations on military registration in relation to organizations.
Removal from general military registration and admission to special military registration of citizens who entered the service in the internal affairs bodies, the State Fire Service, institutions and bodies of the penitentiary system, bodies for controlling the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances to the positions of ordinary and commanding staff and having special ranks, is carried out in military commissariats at the motivated petitions of the indicated bodies and institutions, sent to the military commissariats at the place of residence or place of temporary stay of citizens, with the application of personal lists.
11. With regard to employees of criminal police units (criminal investigation, operational search, organized crime, special technical measures), in which the law provides for a service that does not allow the disclosure of information that reveals the belonging of specific individuals to the personnel, the procedure for providing information and registration of military registration documents are determined by the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation in agreement with the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation.
12. In order to calculate length of service, confer the first special rank, assign a pension upon dismissal of employees of the penitentiary system, military commissariats, on reasoned petitions signed by the head of the Federal Penitentiary Service, heads of territorial bodies of the penitentiary system, send personal files to these institutions and bodies military employees. Work with personal files in institutions and bodies of the penitentiary system should not exceed one month from the date of receipt of personal files. After the expiration of the specified period, personal files are returned to the military commissariats in the prescribed manner.
13. Documents of the military registration of persons liable for military service serving in the internal affairs bodies, the State Fire Service, institutions and bodies of the penitentiary system, bodies for controlling the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances are stored in military commissariats in places that exclude access to them by unauthorized persons , in printed form. Work with these documents is allowed only to persons determined by order of the military commissar.
When citizens are dismissed from service, the internal affairs bodies, the State Fire Service, institutions and bodies of the penitentiary system and the bodies for controlling the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances oblige these citizens to appear within two weeks from the date of dismissal to the military commissariat at the place of residence for setting up military registration and notify in writing of their dismissal the military commissariats at the place of residence of citizens.
14. The heads of the relevant internal affairs bodies, the State Fire Service, institutions and bodies of the penitentiary system, bodies for controlling the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances annually, before October 1, submit documents confirming their service to the military commissariats at the place of residence of conscripts in these bodies, as well as training in educational institutions of these bodies.
15. Control over the implementation of military registration of citizens serving in the internal affairs bodies, the State Fire Service, institutions and bodies of the penitentiary system, bodies for controlling the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances, is assigned to the military command and control bodies of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation and the military commissariats.
The procedure for organizing military registration of citizens with military ranks of officers and staying in the reserve of the Foreign Intelligence Service of the Russian Federation and the reserve of the Federal Security Service of the Russian Federation is determined by the heads of these federal executive bodies.
16. Military commissars, in accordance with the Instruction on the organization of interaction between military commissariats, internal affairs bodies and territorial bodies of the Federal Migration Service in the work to ensure the fulfillment of military obligations by citizens of the Russian Federation:
a) draw up annually (until January 15) and send lists of citizens to the city district department of internal affairs and the military commissariat of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation:
evaded military duty in the past year and not found by the beginning of the current year;
to whom it was not possible to hand over summonses of the military commissariat to appear at events related to conscription for military service (hereinafter referred to as summonses) in the prescribed manner;
not consisting, but obliged to be registered with the military, and identified in the course of joint events.
These lists are updated at least twice a month;
b) analyze the information received from the city district departments of internal affairs and subdivisions of the territorial bodies of the Federal Migration Service (hereinafter referred to as the territorial bodies of the FMS of Russia) about citizens who are not registered, but are obliged to be registered with the military, as well as about citizens who have acquired citizenship of the Russian Federation and are subject to military registration;
c) inform the city district bodies of internal affairs and the territorial bodies of the Federal Migration Service of Russia about the results of the analysis, the completeness and quality of the information provided about citizens who are obliged to be, but not registered with the military;
d) take measures to notify and put on military registration of citizens who are not, but are obliged to be on military registration, and citizens who have acquired citizenship of the Russian Federation;
e) organize the notification of citizens about the appearance at events related to the initial registration for military registration and conscription for military service, keep records of the results of the notification;
f) appoint annually (until January 10) officials responsible in the military commissariat for carrying out joint activities with city and district internal affairs agencies and territorial bodies of the Federal Migration Service of Russia to ensure the fulfillment of military duties by citizens;
g) during the course of the next conscription of citizens for military service, send written appeals to the relevant city and district department of internal affairs to ensure the arrival at events related to conscription for military service, personally indicated in the written appeal of citizens who could not be notified in the prescribed manner, with an attachment subpoenas to be served on them in the event of establishing the actual location, in accordance with Appendix No. 1 to the said Instruction;
h) carry out in accordance with the established procedure the accounting of written appeals sent to the city district bodies of internal affairs and the results of their consideration;
i) attach to the documents of military registration kept in the military commissariat, or to the personal files of male citizens aged 18 to 27 years old, who are obliged to be on military registration and not in the reserve (hereinafter referred to as conscripts), materials on the measures taken to ensuring the fulfillment of military obligations by citizens, received from the city and regional departments of internal affairs and territorial bodies of the Federal Migration Service of Russia;
j) if there are grounds and sufficient data indicating the occurrence of an event of an administrative offense, they draw up a protocol on an administrative offense in relation to citizens who are or are required to be on military registration who did not appear on calls (summons) of the military commissariat or other body that carries out military registration, at the established time and place without good reason, who left for a new place of residence or place of temporary stay for a period of more than three months, left the Russian Federation for a period of more than six months without being removed from military registration, arrived at a new place of residence or place of temporary stay or returned to the Russian Federation without military registration within the established time limits, as well as those who did not inform the military commissariats or other bodies that carry out military registration at the place of residence about a change in marital status, education, place of work or position, place of residence within the district , cities without district division or other municipality, as well as those who evaded a medical examination or examination by the direction of the commission for placing citizens on military registration or from a medical examination by the direction of the draft commission;
k) if it is impossible to draw up a protocol on an administrative offense, they send written appeals to the appropriate city and district department of internal affairs in accordance with Appendix No. 2 to the said Instruction on the delivery of citizens in respect of which proceedings are being carried out on an administrative offense in accordance with subparagraph "k" of paragraph 4 of the said Instruction, to the office of the internal affairs body or to the premises of the local self-government body of a rural settlement for drawing up a protocol on an administrative offense. The appeal indicates the official of the military commissariat, appointed to ensure, together with the city district department of internal affairs, actions to implement the appeal;
l) when preparing for the consideration of cases of administrative offenses listed in subparagraph "k" of paragraph 4 of the Instructions, they issue a ruling on the appointment of the time and place for the consideration of the case and the summons of the citizen in respect of whom the case is being considered, of which this citizen is notified in the prescribed manner. If the consideration of the case is postponed due to the failure to appear without a valid reason of the specified citizen, they issue a ruling on his bringing in in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on administrative offenses, which is sent to the city district department of internal affairs;
m) arrive at the premises of the internal affairs body or at the premises of the local self-government body of a rural settlement to draw up a protocol on administrative offenses provided for by Chapter 21 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. A protocol is drawn up on the delivery of a citizen or a corresponding entry is made in the protocol on an administrative offense or in the protocol on administrative detention;
o) provide the city and district internal affairs agencies and territorial bodies of the Federal Migration Service of Russia with the necessary information material on the fulfillment of the duty of citizens for military registration, their responsibility for failure to fulfill military registration duties and referral forms for placing citizens on military registration;
o) inform the heads of municipalities about the heads of organizations in which violations in the field of military registration have been committed - at least once a year, about the results of work to establish the whereabouts of citizens who evade military registration, conscription or military training - monthly , and during the period of the initial registration of citizens for military registration and conscription for military service - weekly;
p) analyze, summarize and submit annually (until January 15 and July 30) to the military commissariat of the subject of the Russian Federation information on the results of the search for citizens who are not performing military duty, and on ensuring measures related to military registration and conscription;
c) make a note in the passport of a citizen of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the passport) about his attitude to military duty upon initial military registration:
citizens put on military registration;
female citizens after they receive a military registration specialty;
persons who have acquired citizenship of the Russian Federation;
male citizens who for some reason have not previously been registered with the military in a timely manner;
r) make a note in the passport about the attitude towards military duty to a citizen who is in the reserve and has reached the age limit for being in the reserve or who has been declared unfit for military service for health reasons - upon deregistration.
5. Heads of city district bodies of internal affairs or persons performing their duties (hereinafter referred to as - heads):
a) upon receipt of written requests from military commissars to ensure the arrival of citizens who failed to serve the summons to events related to conscription for military service, take the necessary measures to establish the actual location of these citizens and hand them a summons to arrive at the military commissariat for these events ;
b) send to the military commissariats materials on the measures taken to establish the actual location of citizens who are not fulfilling their military duty, including those who evade measures related to military registration and conscription, as well as summons backs with signatures of citizens to whom they were handed over to be included in military registration documents or personal files of conscripts stored in the military commissariat;
c) upon receipt of requests from military commissars for the delivery of persons in respect of whom proceedings are being conducted on an administrative offense in accordance with subparagraph "k" of paragraph 4 of this Instruction, take the necessary measures to establish the actual location of these citizens and their delivery;
d) if it is impossible to deliver the person within the time specified in the appeal, as well as in the absence of the person to be delivered, immediately notify the initiator of the delivery, indicating the circumstances preventing the execution of this appeal;
e) upon receipt of the decision of the military commissar on the bringing of a person in respect of whom proceedings are being conducted on an administrative offense, organize the bringing of this person in the prescribed manner;
f) carry out a record of personal appeals received from military commissars, appeals for the delivery of persons evading military duty, determinations on the drive, as well as an analysis of the results of their consideration;
g) organize the conduct of control and observation cases, in which materials are systematized on the results of work on interaction with military commissariats in the field of implementing measures related to military registration, conscription for military service;
h) organize, in accordance with the requirements of regulatory legal acts, the search for citizens who are not fulfilling military duty related to military registration and conscription, if there is a criminal case initiated against these persons;
i) send weekly during the period of initial registration of citizens for military registration and conscription for military service to the chairmen of draft commissions of municipal districts, urban districts and intra-city territories of cities of federal significance information on the results of measures taken to ensure the fulfillment of military duty by citizens.
6. Territorial bodies of the FMS of Russia:
a) when issuing and replacing passports, they make a note in them about the attitude to the military duty of citizens when they provide military registration documents (certificate of a citizen subject to conscription for military service; military ticket of a soldier (sailor), sergeant (foreman), ensign (midshipman); military ID of a reserve officer; temporary certificate issued in exchange for a military ID);
b) when citizens apply to the territorial bodies of the FMS of Russia for registration at the place of residence (registration at the place of stay for a period of more than three months), deregistration at the place of residence (deregistration at the place of stay), they check the presence of marks in their passports about their to military duty, inform citizens who are not registered, but are obliged to be registered with the military, about their obligation to be registered with the military at the place of residence (place of stay for a period of more than three months);
c) in the absence in the passport of a citizen who is not registered, but is obliged to be registered with the military, marks on the attitude to military duty and the absence in the military registration documents (lack of the opportunity (or refusal) to submit military registration documents) marks of the relevant military commissariats on admission to the military registration, give the citizen a referral for military registration at the military commissariat at the place of his residence (at the place of stay for a period of more than three months) in accordance with Appendix No. 3 to the specified Instruction;
d) send within two weeks to the military commissariats information on cases of identifying citizens who are not registered, but are obliged to be registered with the military, as well as information about persons who have acquired citizenship of the Russian Federation and are subject to military registration, in accordance with Appendix No. 4 to this Instruction.
17. Persons liable for military service accepted for the positions of the commanding staff of the federal courier communications are removed from the military register and are specially registered with the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation (Article 8 of the Federal Law "On Federal Courier Communications" dated December 17, 1994 N 67-ФЗ ).
The amount of funds transferred to local self-government bodies of settlements and local self-government bodies of urban districts is determined based on the number of citizens who are on the primary military register as of December 31 of the previous year, and the methodology for calculating the cost standard approved by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Subventions are credited in accordance with the procedure established for the execution of the federal budget to the accounts of the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and through the regional compensation funds formed as part of the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation are transferred to the budgets of settlements and urban districts.
The procedure for spending and accounting for subventions, as well as for withdrawing transferred powers, is established by the Rules for spending and accounting for subventions provided to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation for the exercise of powers for primary military registration in territories where there are no military commissariats, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 29, 2006 N 258.
Subventions are transferred in the manner established for the execution of the federal budget to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation to the accounts of the territorial bodies of the Federal Treasury opened for cash services for the execution of the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
Subventions are reflected in the regional compensation fund, formed as part of the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, for subsequent distribution between the budgets of municipalities in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation for the exercise by local governments of settlements and local governments of urban districts of the powers of primary military registration in territories where there are no military commissions.
36. On a quarterly basis, no later than the 7th day of the month following the reporting quarter, local governments submit to the authorized executive body of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation a report on the expenditure of the granted subventions in the form established by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation in agreement with the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation.
Local governments are responsible for the misuse of subventions.
37. On a quarterly basis, no later than the 15th day of the month following the reporting quarter, the authorized executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation submit to the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation a report on the expenditure of the provided subventions in the prescribed form.
The Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation transfers subventions in accordance with the established procedure to the personal accounts of the military commissariats of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation for subsequent distribution to the authorized executive bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
Local self-government bodies of settlements and local self-government bodies of urban districts quarterly submit a report to a specially authorized body of state power of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation
Not later than the 15th day of the month following the reporting quarter, state authorities of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation submit to the federal executive body in charge of the development and implementation of state policy, legal regulation in the field of defense, the federal executive body in charge of on the development of state policy and legal regulation in the field of budgetary activities, a unified state financial, credit, monetary policy, a report on the expenditure of subventions provided, indicating the number of military registered employees who carry out primary military registration (released military registered employees and part-time employees ).
Funds for the exercise of powers to carry out primary military registration are of a targeted nature and cannot be used for other purposes.
In case of misuse of subventions, the corresponding funds are collected to the budget of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation for subsequent transfer to the federal budget in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Control over the targeted use of subventions by the constituent entities of the Russian Federation is entrusted to the Federal Service for Financial and Budgetary Supervision and the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation, as well as the Accounts Chamber of the Russian Federation.
Control over the targeted use of subventions by local governments is assigned to the authorized bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, the Federal Service for Financial and Budgetary Supervision and the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation, as well as specially authorized bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
38. The implementation by local self-government bodies of settlements or local self-government bodies of urban districts of primary military registration shall be terminated if a military commissariat is created on the territory of a settlement or urban district. In this case, the implementation of primary military registration by local self-government bodies of settlements or local self-government bodies of urban districts is terminated from the 1st day of the month following the month of the creation of the military commissariat.
39. Pursuant to paragraph 7 of the Regulations on military registration, the procedure for organizing military registration of citizens with military ranks of officers and staying in the reserve of the Foreign Intelligence Service of the Russian Federation and the reserve of the Federal Security Service of the Russian Federation is determined by the heads of these federal executive bodies.
40. When registering or deregistering citizens at the place of residence, the internal affairs bodies identify citizens who are obliged to be, but are not registered with the military, report them to the relevant military commissariats or other bodies that carry out military registration, and after putting these citizens on military registration (removal from military registration) is carried out by their registration or deregistration.
In accordance with the Administrative Regulations for the provision by the Federal Migration Service of the state service for the registration of citizens of the Russian Federation at the place of stay and at the place of residence within the Russian Federation, approved by order of the Federal Migration Service of September 20, 2007 N 208, no later than seven days from the date of arrival Citizens submit the following documents to a new place of residence for registration at the place of residence:
Identification document;
Application for registration at the place of residence in form No. 6 (Appendix No. 6 to the said Regulations);
A document that is the basis for moving into a dwelling (application of the person (persons) who provided the citizen with a dwelling, an agreement, a certificate of state registration of the right (ownership of the dwelling), a court decision recognizing the right to use the dwelling or another document or its proper certified copy confirming the right to use the premises). For registration it is enough to present one of the listed documents.
Citizens who have been de-registered at their place of residence before arriving at a new place of residence submit an address sheet of departure in form N 7 (Appendix N 7 to the Regulations), issued by the authorized body at their former place of residence.
When registering military personnel undergoing military service under a contract, and members of their families who arrived at a new place of military service, at the addresses of deployment of military units in the imprint of a stamp on registration at the place of residence, address sheets of arrival and in paragraph 8 of the sheet of statistical registration of arrival in form N 12P (Appendix N 12 to the said Regulations) the address of the military unit is indicated, and if the subdivision of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation does not contain the term "military unit N 00000", the details of the registration stamp at the place of residence indicate the full or acceptable abbreviated name of the relevant body military command and its address.
41. Military registration of persons liable for military service serving in the internal affairs bodies, the State Fire Service, institutions and bodies of the penitentiary system, bodies for controlling the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances, is carried out by military commissariats at the place of residence or place of stay of these citizens. In these bodies and institutions, military registration of citizens is carried out in the manner determined by this Regulation in relation to organizations.
Removal from general military registration and admission to special military registration of citizens who entered the service in the internal affairs bodies, the State Fire Service, institutions and bodies of the penitentiary system, bodies for controlling the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances to the positions of ordinary and commanding staff and having special ranks, is carried out in military commissariats at the motivated petitions of the indicated bodies and institutions, sent to the military commissariats at the place of residence or place of stay of citizens, with the application of personal lists.
42. Documents of the military registration of persons liable for military service serving in the internal affairs bodies, the State Fire Service, institutions and bodies of the penitentiary system, bodies for controlling the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances are stored in military commissariats in places that exclude access to them by unauthorized persons , in printed form. Work with these documents is allowed only to persons determined by order of the military commissar.
When citizens are dismissed from service, internal affairs bodies, the State Fire Service, institutions and bodies of the penitentiary system, bodies for controlling the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances notify the military commissariats at the place of residence or place of residence of citizens in writing about this, indicating the grounds for dismissal.