46. The essence of economic management methods
TO economic methods include:
2) cost accounting
3) pricing,
4) taxation,
5) investment,
6) subsidizing,
7) currency regulation,
8) customs regulation,
9) economic accounting,
10) lending.
A modern manufacturing enterprise is a complex complex, the coherence of which is ensured by a control mechanism. " Enterprise Management Mechanism- this is, first of all, a hierarchical system of administrative bodies and management structures, with the help of which the main tasks are solved and the goals facing the enterprise are achieved, internal communications are established, performance is monitored and levers of influence are used, covering the activities of all links and employees of the enterprise.
The ultimate goal of management is to ensure the profitability of the enterprise through the rational organization of the production process, including production management and the development of technical and technological base, as well as the effective use of human resources while improving the skills, creativity and loyalty of each employee.
In management science, three groups of methods are used: organizational and administrative, economic and socio-psychological.
Economic methods of management is a set of means and tools that purposefully influence the creation of favorable economic conditions for the functioning and development of enterprises.
The main economic methods are:
Commercial calculation;
Intracompany settlement;
Pricing policy and pricing mechanisms;
Mechanisms and methods for improving the quality and ensuring the competitiveness of products and the enterprise as a whole.
Economic Methods management are closely interconnected and are the basic element of the economic mechanism of management. They are focused on ensuring the sustainable economic activity of the enterprise and its competitive position in the market, which, in turn, provides the enterprise with profit and capital growth in the long term.
basis economic management mechanism is a commercial calculation that determines and ensures the formation of the overall benefit from the activities of the enterprise in specific conditions for making managerial decisions. Commercial calculation aims to create economic conditions and the ability of the enterprise to obtain sustainable profits in the production process using common (universal) mechanisms of the main management functions and in conjunction with other economic methods. At the same time, cost reduction should be ensured at all stages of production and marketing activities in close relationship with the mechanism of intra-company settlement.
In turn, commercial and intracompany settlements are interconnected with specific pricing methods and mechanisms, as well as with ensuring the competitiveness of products and the competitive position of the enterprise in the market.
Equally important is the use of economic incentives that provide for the interest and responsibility of workers and encourage them to take the initiative. Stimulation of employees of the enterprise can be carried out both in material and non-material (moral) forms. Among the material forms of incentives, it is worth highlighting:
Wages, which should be competitive and comparable with wages at similar enterprises in the industry and region;
Social payments, including subsidized meals, selling own products at a discount, paying travel expenses, providing preferential loans, etc.;
Dividends on company shares.
The totality of the impacts of economic methods is always aimed at obtaining benefits from the implementation of a particular business activity.
"The central place in the mechanism of economic management is occupied by planning, as a way to achieve the goal based on the balance and sequence of all production operations and the solution of social problems."
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Similar Documents
Essence and nature of economic methods of management. Ensuring competitiveness. Analysis of the implementation of economic management methods in a particular firm. Ways to improve the implementation of economic management methods.
term paper, added 05/12/2008
Essence of economic management methods. Qualitative indicators competitiveness. The main directions for the introduction of economic management methods at domestic enterprises. Method business case choice management decisions.
presentation, added 04/27/2012
Essence and tools of economic methods of organization management. Pricing policy of the organization, ensuring the competitiveness of the enterprise. Planning and its role in management. Methods of economic substantiation of the choice of management decisions.
term paper, added 12/23/2014
Theoretical basis use modern methods management. Essence, types, tasks and methods of management. Peculiarities modern management. Brief economic characteristic enterprises LLC "Vikor", the main methods of management at the enterprise.
term paper, added 03/11/2012
The concept of "management method". Description of the essence and form of economic methods of management at the enterprise. Mechanisms of economic methods - stimulation of active production activities with subsequent material rewards for the result of labor.
term paper, added 05/09/2012
The role of management methods in the enterprise. Principles of choice of management methods. The role of the manager in terms of administrative methods of management. Administrative management at the enterprise "Belaruskali" and its shortcomings, prospects for improvement.
term paper, added 03/08/2011
System of management methods. Organizational-administrative, economic and socio-psychological methods of management at the enterprise on the example of JSC "Techno". Approaches, methods, techniques by which different kinds management work.
term paper, added 12/23/2013
II. MANAGEMENT
8. Management methods: economic, organizational and administrative, social and administrative
Economic methods of management
Material motivation is used both in the form of material remuneration for the quantity and quality of labor, and in the form of material sanctions (fines) for its inappropriate quality and insufficient quantity. In this case, both individual and collective material interest is applied. That's why economic methods management, on the one hand, should stimulate the activity of the enterprise, regardless of the form of ownership, to meet the needs of society; on the other hand, to serve as a motivator for the personnel of these enterprises.
The main economic method used in management divisions of the enterprise,
– in-house masterpersonal calculation, whose starting points are:
- assigning to the structural unit the resources necessary for economic activity;
– granting the subdivision operational and economic independence by empowering its management with appropriate powers;
– permission to use a predetermined part of the profit at the discretion of the structural unit;
– the application of penalties in case of non-fulfillment by the subdivision of its obligations.
When determining the size and methods of personal economic impact, one should proceed from the position that the well-being of employees must be considered as a source of efficiency for the entire organization.
The economic motivation of personnel consists of three main components:
1) direct material remuneration, wages, bonuses (or bonuses), participation in profits and share capital;
2) additional payments;
3) fines.
The main management methods here are the system wages and bonuses, which should be maximally related to the performance of the performer. It is expedient to associate the remuneration of a manager with the results of his activities in the area of responsibility or with the results of the activities of the entire company.
Organizational and administrative methods of management
Organizational and administrative methods of management - these are methods of direct influence, having a directive, mandatory character, based on discipline, responsibility, power, coercion.
Organizational practices include:
– organizational design;
- regulation;
- rationing.
At the same time, specific persons and specific dates of execution are not indicated.
With administrative methods (order, instruction, briefing), specific performers and deadlines are indicated.
Organizational methods are based on typical situations, and administrative methods are mostly related to specific situations. Usually managerial methods are based on organizational ones.
The essence of organizational regulation is to establish rules that are mandatory for implementation and determine the content and order organizational activities(Regulations on the enterprise, the charter of the company, internal company standards, regulations, instructions, rules for planning, accounting, etc.).
Command methods are implemented in the form:
- orders;
- resolutions;
- orders;
- briefing;
- commands;
- recommendations.
Socio-psychological methods of management
Since the participants in the management process are people, then social relations and their respective management practices are important and closely related to other management practices. These include:
- moral encouragement;
– social planning;
- belief;
- suggestion;
- personal example;
– regulation of interpersonal and intergroup relations;
- creating and maintaining a moral climate in the team.
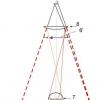
The motives of human behavior have a certain hierarchy, which is usually called the Maslow diagram (pyramid) (Fig. 8.1).
The prerequisites for successful active work on execution lie in the capabilities of performers:
– know (information about targets or activities for which a decision has been made);
– dare (these installations and activities must be “acceptable” for performers, including not violating legal and ethical standards);
- be able (performers must have the means to carry out the assignment);
– want (they must be motivated).
Rice. 8.1. Maslow's pyramid
Under the motive understand the motivation of human behavior, based on subjective feelings of shortcomings or personal incentives.
First of all, the employee should:
- the ability to get the job done;
- define its scope of action;
- clearly formulate goals and objectives;
- create an environment conducive to the task (provide the means, the necessary information, form an organization, use a management style based on the ownership of the performers).
Motivational management concentrates on:
- on the influence on the state of motivation (the degree of identification of an employee with the company, the formation of his motives);
- a sense of his own dignity (respect as a person, messages about his importance for the company, expectations of results from his activities);
– bringing motives into action (the personal interests and capabilities of the employee are discussed);
- strengthening of motives;
– performance appraisal and appraisal (salary review, growth, additional benefits);
- satisfaction of needs;
- ensuring the process of motivation.
Good job to motivate employees:
– to increase turnover and profit;
- improving the quality of products;
- to a more creative approach and activity in the implementation of the achievements of scientific and technical progress;
– increased influx of employees;
- improving their performance;
– greater cohesion and solidarity;
- reducing staff turnover;
- Improving the company's reputation.
Introduction
1. Economic Methods in management
1.1 The essence of economic management methods
1.2 Commercial calculation as the most important economic method of the management mechanism
1.3 Intercompany settlement
2. The use of economic methods in the management of Business Foods LLC
2.1 Organizational and economic characteristics of the enterprise
2.2 Application of economic methods in the management of LLC "Business Foods"
3. Improving the organizational and economic mechanism of enterprise management (on the example of LLC "Business Foods")
Conclusion
Bibliography
Introduction
Changes in the socio-political and economic life of the country required a radical restructuring of the entire management system. At present, it is productive to manage the production economic activity only specialists-managers (managers) can do it, for whom work in the conditions of the market in accordance with its requirements and laws is a way of thinking and acting.
In the current market conditions management especially relevant there is a problem of using modern methods of enterprise management.
The effectiveness of enterprise management directly depends on the set of management methods that the manager chooses. The most common methods of enterprise management are: economic methods, organizational and administrative and socio-psychological methods.
aim given term paper is a characteristic of economic management methods and an analysis of their application on the basis of a commercial enterprise.
As part of our goal, we have to solve the following tasks:
1. reveal the essence of such a category of management as "economic methods";
2. classify existing economic methods;
3. to characterize such common methods in modern management as the use of commercial and intracompany calculation;
4. analyze the application of economic management methods on the example of a trading enterprise;
5. evaluate the effectiveness of the application of economic methods at the enterprise in question and suggest ways to improve the management mechanism.
As object to write this term paper, a large retail chain of the city of Kamyshin was chosen, consisting of eleven grocery stores - Business Foods LLC.
In accordance with the tasks set, the work is divided into three interrelated parts, the first chapter contains a theoretical description of the subject of research, namely, the economic methods of enterprise management, the second chapter characterizes the object under consideration and contains an attempt to analyze the application of economic functions in enterprise management, the third chapter ways of improving the control mechanism of the object of study under consideration are determined.
1. Economic methods in management
1.1 The essence of economic management methods
The manager manages the enterprise with the help of methods and levers of management.
Management method - a set of methods and techniques for influencing the subject of management through its unity on the managed object to achieve the goal.
But in order to finally achieve the goal, it is necessary to influence the members of the managed team with the help of levers and incentives.
The lever (stimulus) of the control action is a means, the use of which allows you to complete the task (goal).
The successful solution of any production and economic task at any level of management requires the complex application by the head of various management methods and incentives to work.
The main management methods in modern management theory are:
economic methods;
Organizational and administrative methods;
Socio-psychological methods.
In this paper, we will dwell in more detail on the study and description of economic methods of enterprise management.
So, economic management methods are a system of methods and ways of influencing performers with the help of a specific comparison of costs and results (material incentives and sanctions, financing and lending, wages, cost, profit, price). The characteristics of economic management methods are presented in table 1.1.
Table 1.1. Characteristics of economic management methods
Name of the group of control methods Group specifics Subgroup name Name of methods Economic methods of management Influence on the material interests of people, focus on the performance of certain indicators or tasks and on remuneration for their performance Economic methods applied at the macro level Forecasts: national programs; government orders; tax policy; price policy, financial and credit policy; investment policy. Economic methods applied at the enterprise (organization) level Planning: balance method; normative method; analytical method; math modeling. Commercial calculation: self-financing; self-sufficiency; self-financing Economic management methods applied in individual worker Incentive methods (wages, bonuses, etc.) Methods of punishment (fines, deductions, etc.) Economic methods of management involve material motivation, that is, orientation towards the fulfillment of certain indicators or tasks, and the implementation of economic rewards for the results of work after their fulfillment. The use of economic management methods is associated with the formation of a work plan and control over its implementation, as well as economic incentives for labor, that is, with a rational wage system that provides incentives for a certain quantity and quality of labor and the application of sanctions for its inappropriate quantity and insufficient quality. The importance of economic methods of management increases sharply in the conditions of the development of market relations focused on making a profit and the highest possible income. Economic methods that are applied at the enterprise level include: Incentive system innovation activities, aimed at increasing the efficiency of this organization and improving the quality of its products. Of great importance in the system of material incentives is effective organization staff wages in accordance with the quantity and quality of labor. Pay is the main motive labor activity and a monetary value meter work force. It provides a link between the results of labor and its process and reflects the quantity and complexity of the work of workers of various qualifications. By setting official salaries for employees and tariff rates for workers, the management of the enterprise determines the standard cost of labor, taking into account the average labor costs for its normal duration. Additional wages allow you to take into account the complexity and qualifications of work, the combination of professions, overtime work, social guarantees enterprises in case of pregnancy or training of employees, etc. Remuneration determines the individual contribution of employees to the final results of production in specific periods of time. The head of the enterprise can apply various wage systems: piecework or time-based, form the material and spiritual needs of workers and ensure the growth of their living standards. The group of economic methods of enterprise management should include: Methods of economic incentives, pricing, financing, lending; Implementation of functions by suppliers and consumers, financial and banking authorities and control over compliance with payment discipline; Rational use of own working capital; Use of the system of remuneration and material incentives for employees of enterprises; Application of economic measures to influence customers, suppliers, contractors, transport workers, etc. As an example of the manifestation of economic methods of personnel management, the following can be cited: Personnel subsidies. Many companies have subsidized canteens and restaurants for their staff. Goods at a discount. Most businessmen allow their employees to purchase goods and services of the company at a discount. Loans. Some employers give their employees interest-free or low-interest loans for various consumer purposes. Private health insurance. Some firms provide private health insurance for their employees. Fast health care workers will also benefit as the worker returns to work sooner. Under a market economic system under conditions free market and complex interaction, the role of economic management methods is enhanced. They become a condition for a radical restructuring of the economic mechanism, the creation of an integral, efficient and flexible system of economic management. 1.2 Commercial calculation as the most important economic method of the management mechanism
The efficiency of social production is determined by both objective and subjective factors. The spiritual and material activity of an employee, his professionalism and humanity also affect the growth of labor productivity, as well as the implementation of the laws of value, supply and demand, competitiveness and equivalence of exchange. So, commercial calculation is a method of managing the economy based on the comparison of economic activity and its results, expressed in monetary terms. Commercial calculation is one of the tools for solving socio-economic problems using a system of cost categories and economic indicators adequate to them. This is a way of resolving contradictions between use value and the value of goods in a socially oriented market economy. Historically, it was this contradiction that "gave birth" to such a category as cost accounting. Cost accounting is a category that is developing in connection with and interacting with the categories of cost, product price, productivity and wages. The organization of commercial settlement in any industry (including trade) is based on a number of principles: 1. Cost recovery and profitability. Commercial calculation provides each normally operating organization with reimbursement of production costs and profit. Each enterprise must receive income sufficient to cover production costs and generate sufficient profits. 2. Economic and operational independence. Each enterprise receives complete economic independence: it independently manages its property, plans and sells finished products, and hires employees. Each enterprise has its own bank account and can receive loans from banks and other credit institutions. It also has an independent balance sheet and a complete accounting system. 3. Liability.
The enterprise and its employees are financially liable for failure to fulfill their obligations, for the irrational use of labor, material, financial resources and other actions carried out by them within the framework of economic activity. If the enterprise does not fulfill the production plan, its quality deteriorates, defects, downtime are allowed, material resources and equipment are used unsatisfactorily, this causes a decrease in income. This immediately affects relations with consumers (customers), suppliers, banks, etc.; there are delays in settlements, deliveries, payments to the budget, which causes a corresponding reaction (penalties, fines, administrative and, in very difficult circumstances, criminal liability). Along with the responsibility of the enterprise as a whole, there is also the individual responsibility of its employees. Moreover, it can be not only administrative, but also material. 4. Material interest. Next important principle commercial calculation is a material interest. It is achieved by the fact that the enterprise conducts all its current expenses (purchase of raw materials and materials, payment of wages, etc.) exclusively at the expense of own funds. Thus, its expenses and solvency are made dependent on the receipt of income. Thus, the better the company works, the more stable its financial position and solvency. The good work of the enterprise is beneficial, first of all, to its personnel, since at the expense of profit a material incentive fund is formed, through which employees are stimulated for the best results of work. Thus, the increase in wages, material incentives for workers depends primarily on the growth of production, improving the quality of products, increasing the mass of profits and increasing the profitability of production. 5. Control by the ruble. This principle means that the result of the enterprise's work should depend on its own contribution, and not on other reasons, such as inflation, the presence of a non-monetary market. The order of financing is of great importance for the control of the ruble capital investments. By financing, lending to production, banks and other financial and credit organizations act in the direction of a more complete mobilization of production reserves and increase its efficiency. As can be seen from the principles listed above, commercial settlement is a prerequisite for the development of market relations, since it reflects the very essence of a market economy (limitation of state intervention in the economy, almost complete independence of economic entities) and the provision “a market economy without commercial settlement” is nonsense. With such a business model, the question is raised about the approximation of the principles of commercial calculation, indicated above, to a specific employee, a specific workplace. That is, we are talking about the creation of an internal commercial calculation as a tool for increasing labor efficiency, and hence the efficiency of production as the main condition for survival in the conditions, even the most social, but still a market economy. Due to the fact that commercial accounting synthesizes both a management function and economic levers and tools, it contributes to ensuring the profitability of production, the optimal use of capital, the development of technology, and an effective personnel policy. Developing a policy on all these issues, the central authorities use a differentiated approach to individual units, depending on the nature and content of their activities. Commercial calculation uses such economic levers and tools as pricing, production costs, financing and lending. This use is aimed at ultimate goal commercial calculation - obtaining a steady profit. Each of these levers and tools has its own uses. Thus, prices in terms of structure and level adapt to the requirements and conditions of the market. Regarding production costs most attention is given to reducing costs by improving technology, launching new products, improving logistics, increasing labor productivity, saving living labor, and overhead costs. In the field of financing and lending, sources of financing and distribution of capital among production units are determined in advance, as well as obtaining loans and credits on favorable terms. The implementation of the principles of commercial calculation is influenced by the degree and scale of economic relations between enterprises, the type of activity of the enterprise, the nature of the products, that is, the implementation of commercial calculation methods depends on specific conditions. IN modern conditions commercial settlement is carried out, on the one hand, under the conditions of centralized management (the first feature), and on the other hand, under the conditions of independence of enterprises and their divisions. Commercial calculation turns into a method of implementing the functions of planning and control by subordinating the entire economic activity of the organization to the task of fulfilling predetermined and planned indicators. Reimbursement of all expenses from the income received and ensuring a sustainable profit for the organization as a whole is provided for by reducing the cost of material, financial and labor resources. Granting operational independence to enterprises, production units and branches is the second feature of commercial calculation. As a result, within the framework of commercial calculation, such a form of relationships within the enterprise arose, which is defined as intra-production (intra-company) calculation. 1.3 Intercompany settlement
Intracompany calculation is a commercial calculation of production units, workshops, departments, services, etc. covered by the system economic relations, in order to effectively use the available reserves and obtain a higher result of the company as a whole. The main tasks of the new on-farm mechanism of the enterprise are: Increasing the operational and economic independence of the enterprise's divisions with a simultaneous increase in their responsibility for the results of their activities to the enterprise and for the fulfillment of its obligations to the state, customers, suppliers and creditors; Effective coordination of joint production and economic activities of all departments of the enterprise; strengthening the material interest of divisions and employees of the enterprise in the final results of labor; Creation of a mechanism of property relations between employees of the enterprise and its owners; Improving the methods and forms of remuneration based on the principle of assessing its final results in the commodity market; Improvement of working conditions, culture of production and life of employees of the enterprise, strengthening of their social protection at the enterprise; Improving the psychological climate in the workforce, increasing the labor and social activity of its members based on new material incentives for work. Intra-company calculation is based on the principles of combining the operational and economic independence of a structural unit with centralized planned management, self-sufficiency and profitability, material interest and liability, the unity of interests of the individual and the team of the structural unit. Internal calculation is aimed at achieving commercial calculation and contains its elements. Intracompany settlement differs from commercial one in that it is carried out within the framework of own organization, and commercial - between different owners, but this one system economic accounting. There are also differences in prices. In commercial settlement, prices reflect the existing commodity-money relations. Intra-company calculation involves the establishment of internal prices of the organization. Intra-company calculation is used in organizations that have a decentralized management structure and developed intra-economic relations between departments. The basis of economic relations between individual divisions are conditional settlement (transfer) prices, according to which the calculations of one organization (firm) are carried out. The product appears in form only in form, not being a commodity in essence. Prices are set by the management of the organization within the framework of a single pricing policy. Intracompany settlement is carried out on the basis of cost minimization at all stages of production. Paid deductions are also established, which have an impact on production and economic activity, acting as cost regulators. 2. The use of economic methods in the management of Business Foods LLC 2.1 Organizational and economic characteristics of the enterprise
The object of study of this course work is a limited liability company "Business Foods". Business Foods Limited Liability Company (hereinafter referred to as Business Foods LLC) is a private commercial enterprise and carries out its activities in accordance with the Charter of the enterprise, the Constitution of the Russian Federation and the current legislation of the Russian Federation. LLC "Business Foods" is an independent legal entity, registered by the Decree of the Head of the Administration of the city of Kamyshin, Volgograd Region in the Unified State Register legal entities in November 1997. The company is located at: 403881, Russia, Volgograd region, Kamyshin, st. Donskaya 181. LLC "Business Foods" is a part of the group of companies "Business Systems". The company is successfully operating in the market food products Kamyshin since February 15, 1998 The main activity of the company is the retail trade in food products. The sale of food products is carried out through the network retail stores"Crossroads", "Gastronom", "Business Foods". On this moment LLC "Business Foods" operates a network of eleven self-service stores. The stores offer a wide range of products, while work is being done to improve the work of stores by expanding, saturating, deepening the range of food products, constantly studying the opinions of consumers regarding the working conditions of stores, the culture of customer service, and maintaining the image of the company. Retail sale of goods is carried out for the following groups of goods: Groceries: alcoholic beverages, non-alcoholic beverages, flavor products, prepared foods, baby food, confectionery, animal feed, dairy products, pasta and cereals, seafood, meat products, vegetables, fruits, nuts, edible fats, fast food, baked goods, eggs and egg products, tobacco products. Non-food items: toothpaste, washing powder, personal care products, etc. The mission of the company is to create a base of loyal consumers and take a leading position in the food trade in Kamyshin by satisfying the needs of customers in high quality food products, providing the company with the maximum annual income. As strategic goal The management of the company highlighted the following - capturing a 50% share of the food market through the development of a network of retail stores and wholesale food products. To achieve the company's strategic goal, it is necessary to optimize the work of existing areas and consider the possibility of creating a new promising direction for a chain of stores, such as a "discounter". Within the framework of the goal, it is necessary to solve the following tasks: Increase in turnover; Attracting new customers to stores and retaining existing ones; Formation of a stable positive image of the company "Business Foods", as a company selling quality goods; Formation potential buyer preference to buy food only in Business Foods stores; Creating the most favorable atmosphere in stores, customer-friendly service and maintaining this image; Encouraging end customers to purchase products from the wholesale store of Business Foods. Business Foods LLC is characterized by a linear-functional organizational structure. The company is headed CEO, which is subordinate to all structural divisions of the enterprise: Executive Director; Sales department; Marketing department; Department information support; Human Resources Department; Legal department; Storage facilities. The organizational and economic structure of the enterprise in question is presented in Appendix A. At the moment, the number of employees of Business Foods LLC is 113 people. The composition and structure of employees of Business Foods LLC is presented in Table 2.1. The management of the enterprise is carried out on the basis of a centralized management uniting all employees. The direct management of the enterprise is carried out by the Managing Director, appointed and dismissed from his post by the Board of Founders in accordance with the current legislation. Table 2.1. The composition and structure of employees of Business Foods LLC in dynamics from 2003 to 2005
executives administrative staff sales staff technical service personnel The meeting of founders establishes the management structure, staffing, distribution official duties, wages, as well as the size of allowances and additional payments to official salaries and the procedure for bonuses. Consider the dynamics of sales of the company "Business Foods" since the opening of the first store (see Table 2.2). Table 2.2. The dynamics of sales of the company "Business Foods" as a whole for the company since the start of the activity
Sales proceeds, thousand rubles Growth factor The company increases its turnover every year by opening new stores and transferring existing ones to round-the-clock operation. Figure 2.1. the position of the enterprise on the life cycle curve is clearly presented. Business Foods is currently in a growth phase, as evidenced by the following facts: Intense competition in the food market in Kamyshin; Annual growth in sales volumes; Recognition of stores by customers and the constant attraction of new customers; The price level is largely constant. Sometimes there may be slight price fluctuations as demand changes; Marketing costs remain either at the same level or increase slightly. Sales volume and profit "Business Foods"
Stage Stage Stage Stage Stage development derivation growth maturity decline product to market Rice. 2.1. The life cycle of the enterprise LLC "Business Foods" The management of the enterprise organized operational and long-term control over the financial activities of the enterprise. Also, the planning of financial indicators is organized on an ongoing basis. Forecast data on the development of the enterprise at the moment are presented in Table 2.3. The solution of all the tasks of the company will require, in addition to financing the current tasks of ensuring the activity of capital investments in the material and technical base, information and software and human resources(human resources), as well as working capital. The amount of capital investments for these positions will be 378.3 thousand dollars in marketing, 737 thousand dollars in technology modernization and 2047 thousand dollars in working capital. Table 2.3. Financial plan for the development of the company (planning horizon - 5 years)
Indicators Total area
Turnover per sq. m. USD
Monthly turnover, thousand dollars
Annual turnover, thousand dollars
Profitability to turnover % Net profit years thousand dollars (turnover * profitability to turnover).
Total capital investment
Balance of investment operations, thousand dollars (financed by bank loans)
Capitalization of the company, thousand dollars
Return on equity, %
The management of the company pays great attention to work with personnel in order to improve the efficiency of their activities. There is currently an escalation competition in the city, in particular among grocery stores. Therefore, in order to maintain its position in the city market and for further successful development, the company "Business Foods" constantly monitors the situation in the food market, using marketing research methods. One of the directions marketing research firms is a competitive analysis. First of all, to achieve this goal, the company's management decided to organize a marketing department at the enterprise. The marketing department of Business Foods has existed since 1999. This unit is headed by the head of the marketing department, who reports to the leading specialist in retail network, wholesale specialist and advertising specialist. The marketing department actively cooperates with other departments of the company. So, together with the commercial department, the functions of the marketing department include the formation of a product range, the analysis of the sale of product groups, price monitoring, and the development of recommendations for increasing sales of products. 2.2 Application of economic methods in the management of LLC "Business Foods"
So, the main economic methods of enterprise management are considered at the macro level: Planning: balance method; normative method; analytical method; math modeling. Commercial calculation: self-financing; self-sufficiency; self-financing At the micro level: The system of wages and other forms of material incentives for employees; Responsibility system with appropriate application of rewards and sanctions for the quality and efficiency of work; A system for stimulating innovation activities aimed at improving the efficiency of the organization and improving the quality of its products. Let's consider the application of the above management methods by the management of Business Foods LLC. Let's start with an analysis of the use of the planning function in the enterprise. Improving management is associated with the management of the finances of an enterprise or firm. A plan is a system of goals and strategies to achieve them. The program is a set of measures for the implementation of strategies. Budget - planned financial estimates and projected financial results, financial design of programs and calculation of the costs required for this. That is, the budget is financial plan, which allows you to compare costs and results in financial terms for the upcoming period of time. Therefore, the budget (financial plan) is the basis of intra-company management. Accordingly, budgeting - technologies for compiling, adjusting, monitoring and evaluating the execution of financial plans - are the basis of intra-company management technologies. Budgeting helps to set resource spending limits and profitability and efficiency standards for certain types of goods and services, types of business and structural divisions of the enterprise. Budgeting allows you to make an enterprise or firm "transparent", and therefore attractive to investors. Budgeting also allows you to solve the problems of optimizing financial flows, balancing sources of income Money and their use, determine the volumes and forms, conditions and terms external funding solve other managerial tasks. The organization of work on intra-company planning at Business Foods LLC is built according to the "top-down" method - the company's management determines goals and objectives, in particular, profit targets. Then these indicators are detailed and included in the plans of departments. LLC "Business Foods" carries out its activities on the basis of the principles of commercial calculation, self-sufficiency and self-financing. Let us calculate the main indicators that testify to the effectiveness of the application of these principles. 1. Profitability (this indicator is calculated in Table 2.3) for 2005 is equal to: Profitability of sales - 5%; Return on equity - 16%. Let's compare the received indicators with similar indicators for 2004. Profitability of sales - 3%; Return on equity - 15%. Comparison of these indicators shows the presence of positive dynamics. The return on turnover in 2005 increased by 2% compared to the previous reporting period, while the return on equity increased by 1%. The positive dynamics of sales profitability indicates an increase in the profitability of the enterprise in 2005 and an increase in efficiency entrepreneurial activity(increase in the profit of the enterprise from the ruble of sales). The positive dynamics of the return on capital characterizes the increase in the efficiency of the used invested funds (an increase in the profit of the enterprise per ruble of investments). 2. Turnover 2.1. Fixed assets turnover ratio (capital productivity) [Formula 1] FAT 2005 = 296,844,000 rubles / RUB 89,820,000 = 3.30 FAT 2004 = 241,000,000 rubles / RUB 75,996,000 = 3.17 Comparison of the current indicators of the turnover of fixed assets and similar indicators of the previous year shows a positive trend. The growth of capital productivity is one of the factors of intensive growth in the volume of sales. An increase in capital productivity leads to a decrease in the amount of depreciation deductions per ruble finished products or buffer tank. 2.2. Asset turnover ratio [formula 2] TAT 2005 = 296,844,000 rubles. / RUB 198,800,000 = 1.49 TAT 2004 = 241,000,000 rubles / RUB 179,652,000 = 1.34 When comparing the asset turnover in 2004 and 2005, we also observe a positive trend, on the basis of which we can conclude that the growth of the capital productivity index was influenced by the dynamics of the total assets of the enterprise. Inventory turnover ratio [formula 3] ST 2005 = 207,790,800 rubles / RUB 15,414,000 = 13.48 ST 2004 = 168,700,000 rubles / RUB 14,995,000 = 11.25 So, at the enterprise LLC "Business Foods" there is an increase in the inventory turnover ratio, which, of course, is positive factor. Turnaround time decreased by 5 days. As can be seen from the calculation, the main economic indicators of the activity of a trading enterprise have a positive trend, which indicates the effectiveness of enterprise management. Consider the application of economic management methods at the micro level. Payroll planning at Business Foods LLC is as follows: 1. The remuneration of an employee consists of the following parts. a) official salary (the same for all employees holding the same positions). b) allowances depending on length of service (the same for all employees with the same length of service at a given enterprise). c) allowances depending on the efficiency of the enterprise, provided to the departments where this employee works (different in size depending on the role that this or that employee performs in ensuring the profit of the enterprise). d) allowances depending on the specific contribution of each employee to the results of the enterprise's activities (personally for each employee, depending on personal initiative in ensuring the achievement of the enterprise's goals. 2. The official salary is determined on the basis of the certification of the employee and his qualifications 3. The seniority bonus is established by the enterprise in accordance with regulations, depending on the number of years of work in this enterprise. In the absence of regulations, the amount of the allowance is set by the management, based on the financial capabilities of the enterprise. It is set as a percentage of the official salary. 4. The allowance for the efficiency of the enterprise is determined on a progressive scale as a percentage of the official salary (taking into account the inflationary allowance) depending on the efficiency of the enterprise, Determined by the ratio of the increase in profits per employee to the amount of the official salary and bonuses for length of service. 5. The allowance for a specific contribution of an employee to the achievement of the enterprise's goals is set personally for each employee on the proposal of the manager and is approved weekly, monthly, quarterly by the management of the enterprise. Table 2.4. the dynamics of the average wages of employees of LLC "Business Foods" from 2002 to 2005 inclusive is presented. This table provides information on the average existing salaries, unfortunately, it was not possible to obtain information about the bonus system used at this enterprise. It is only known that the remuneration of senior management directly depends on the implementation of planned financial indicators, such as the profitability and profitability of the enterprise, and the remuneration of sales staff headed by managers of outlets depends on the implementation of the plan for turnover. Table 2.4. Dynamics of average salaries by categories of employees of the company "Business Foods" for the period from 2002 to 2005
Let's calculate the indicators characterizing the effectiveness of the use of economic methods of personnel management. Acceptance turnover ratio [formula 4] Kn 2005 = 15 people / 113 people = 0.13 Kn 2004 = 20 people / 123 people = 0.16 Comparing the indicators of turnover by acceptance, we observe a positive trend in the reduction of this coefficient. Retirement turnover ratio Quarter 2005 = 20/113 people = 0.18 Quarter 2004 = 30/123 people = 0.24 Comparing the indicators of turnover by retirement, we observe a decrease in this ratio, which indicates stabilization personnel policy and human resource management in general. Labor productivity The most general indicator of labor productivity is the average annual sales of products by one sales worker: , [formula 6] where TP is the volume of sold marketable products in value terms; H - the number of sales workers. GV 2005 = 296,844,000 rubles. / 77 people = 3,855,117 rubles/person GV 2004 = 241,000,000 rubles. / 84 people = 2,869,048 rubles/person As a result of the adopted management decision to reduce the number of stores and, accordingly, the sales staff, and improve the efficiency of the remaining outlets, the indicator of sales staff productivity increased. Economic effect from the implementation of this management decision amounted to 3,855,117 rubles. - 2,869,048 rubles. = 986,069 rubles. per sales employee or 986,069 rubles per person. * 77 people = 75,927,313 rubles. annual effect. The turnover rate of employees of the management apparatus of LLC Business Foods in 2004 was: Ktu 2004 = (number of managerial employees who resigned of their own free will + number of managerial employees dismissed for violations of labor discipline) / average headcount managerial employees = 3+1 /15 = 4/15 = 0.27 Ktu 2005 \u003d 2 + 0 / 14 \u003d 2/14 \u003d 0.14 So, in 2005, the turnover rate of managerial personnel in comparison with 2004 decreased by 0.13, or almost by half. This is a positive factor, indicating an increase in the efficiency of enterprise management. In 2004, the qualification level of personnel engaged in enterprise management was as follows: out of 15 management employees, 10 people had higher education and 5 people had specialized secondary education. Of the 10 managers with higher education, 5 people had economic specialization and work experience in management for at least 3 years. In 2005, the qualification level of personnel managing the enterprise was as follows: out of 14 management employees, 11 people had higher education and only 3rd - secondary special. Moreover, out of 11 managers with higher education, already 6 people had an economic specialization. The obtained data testify to the increase in the qualification level of enterprise management in 2005 in comparison with the previous reporting period. The increase in this level was also influenced by the holding of training seminars within the framework of the ongoing personnel policy. Based on the analysis, the following conclusions can be drawn: as the main management methods at Business Foods LLC, economic management methods are used. The main management methods here are at the macro level: the principles of cost accounting, self-financing and self-sufficiency introduced into the management, as well as the system of activity planning, enterprises based on the principles of budgeting; at the micro level: the system of wages and bonuses. Moreover, the remuneration of each employee is directly related to the results of his activities in the area of responsibility or to the results of the activities of the entire company. 3. Improving the organizational and economic mechanism of enterprise management (on the example of LLC "Business Foods") The system efficiency of the organizational and economic mechanism of enterprise management depends on how rationally the management is organized, that is, on the composition and number of links, their subordination, distribution of functions. In other words, the effectiveness of the management system is determined by the quality of the organizational structure and management processes. As part of the analysis of the organizational structure of the enterprise, we consider the composition of structural links, as well as their linear and functional subordination. The current organizational chart (see Annex A) fairly accurately reflects the composition structural divisions enterprises. All units indicated on it are adequately reflected also in staffing and actually function. However, the proposed scheme lacks a more detailed description of such a block as management, namely, from this organizational structure it is difficult to understand that the management of the enterprise is not carried out directly by the managing director, but is supervised by the manager management company"Business Systems". Also, the proposed scheme does not reflect the deputy managing directors who are in relation to him in linear submission and are responsible for various functional blocks, such as: Deputy Director for General Affairs; Deputy Director for Commerce; Deputy Director for Finance; Deputy Marketing Director. Analysis of the actual subordination showed that most of the support units (information department, personnel department, technical department and security department) report to the Managing Director not directly, but through the Deputy Director for General Affairs. Let's analyze the level of workload on managers. The load level is determined by the number of employees who are directly subordinate. Managing director - 4 people (listed above); Commercial Director - 14 people (of which 11 are managers of retail outlets, the head of the accounting department and the head of the central warehouse, the head of the transport department); Financial director - 2 people ( Chief Accountant and head of the audit department); Marketing Director - 3 people (employees of the marketing department); Director for General Affairs - 5 people (Head of the Information Support Department, Head of the Human Resources Department, Head of technical department, Head of Security and Lawyer). An analysis of the level of workload on managers showed that only the managing director has a level of workload close to the average. The CFO and Marketing Director are the least loaded. Of greatest concern is the workload level of the commercial director and the cross-functional workload of the director of general affairs. As part of the analysis of the management system by functions, a description of the main functions and their distribution by structural divisions was carried out. At the same time, significant functions that are implemented in practice without being assigned to a specific structural unit or official have not been identified. At the same time, a possible source of problems may be the insufficient volume and completeness of the performance of functions inherent in every efficiently operating commercial enterprise. Among the functional areas, innovation and the marketing block are of the greatest concern, among managerial functions(management processes) the worst situation is in the area of analysis and decision-making. When analyzing the duplication of functions, the sphere of commercial analysis was noted as possible sources of problems, as well as the situation with the division of responsibility in the field of organizing merchandising in each commercial enterprise. Here the interests of two blocks intersect - the marketing department and the commercial department. It is necessary to clearly delineate the zones of their influence and exclude duplication of functions. The greatest concern is the actual position of the marketing department in the organizational system of the enterprise. Despite the fact that in organizational structure LLC "Business Foods" this division is assigned the role of one of the main, in fact, the department performs secondary functions, serving the commercial and financial departments. It is also necessary to note the detachment of the marketing department from making strategic management decisions. Although, it would seem, in the absence of a company development department, a huge burden should fall on the marketing department and it should be assigned the role of a central, strategically important division of the enterprise. That is why we propose to make some changes to the management system: 1. Take into account that organizational culture acts as a social side of the indicator of the effectiveness of the management activities of an enterprise. Therefore, it is necessary to introduce Japanese management methods into the management system of Business Foods LLC, the core of whose philosophy is the recognition of social responsibility. 2. We suggest the management of Business Foods LLC to review the structure of the marketing department at the enterprise and its actual position and dependence on other departments. The main Japanese management methods that are quite possible to apply in these conditions are: 1. Job security and creating an environment of trust. The leaders of Japanese enterprises believe that the stability of the team allows you to raise the motivation of workers, strengthen the sense of community, helps to learn from experienced workers (quality circles, rationalization). This is especially necessary to pay attention to the management of LLC "Business Foods", given the high rates of staff turnover (including management), which not only actually take place, but about which there are "persistent rumors". 2. The constant presence of management in production. The leader must eliminate all difficulties right on the spot. If a long time has passed since the incident, the cause may go unnoticed and this will create a chronic sense of apathy among workers for the difficulties encountered or lead to irresponsibility. Thus, it follows from this that Japanese managers are not worried about the decrease in output, not the decrease in quality, but the apathy and irresponsibility of the workers. The same situation often occurs in outlets. Naturally, we do not call on the managing director to urgently go to the store for each conflict situation, but it is necessary to show interest in the sales staff and their work, to learn first-hand information. 3. Glasnost and corporate values. This idea is based on the rule that all levels of management and salespeople use general information on the policies and activities of the firm. Constant meetings with focused information improve relationships and affect productivity. Knowledge of the problems of the enterprise develops a sense of common responsibility among employees. 4. Management based on information. Improving human relationships: coherence, group orientation, harmonious relationships. These are key management tasks. But it is also important to organize the collection of the right data, systematically analyze it and use it to improve economic efficiency businesses and quality customer service. IN this issue again the question arises about the role of the marketing department in Business Foods LLC and about the intersection of the functions of the marketing department and the commercial department. 5. Quality-oriented management. Why such attention to quality? Otherwise, the Japanese explain, the consumer loses confidence in our products. This ideology is shared by everyone working in the company. And the personal pride of the leader is manifested in the organization of work, quality control. Unfortunately, many consumers still complain about the quality of service in the analyzed stores, frequent underweights, short cuts and simply impolite service from the sales staff indicate the absence of quality-oriented management at the enterprise, or this process simply has not yet borne fruit. 6. Maintaining cleanliness and order. This activity is considered one of the most important, it is considered as necessary condition high quality service. The task of the Japanese leader is formulated as follows: to establish a discipline that would serve as a guarantee of quality control and increase productivity through attention to cleanliness and order. However, maintaining discipline and order can be difficult due to reasons such as: the habits of the workers, their lifestyle, qualifications, as well as economic conditions. In the second direction, we propose the introduction of an integrated structure of the marketing department, which provides for the process of transferring part of the hardware functions and related departments to other departments of the company. It is necessary to shift the emphasis in the functional purpose of this department at the enterprise. If, at the moment, the main functional purpose of the department is: Current analysis of the implementation and selection of the most popular commodity items; Monitoring of prices for commodity items in the city; Analysis of the competitive environment. Then, it is necessary to give this structural unit the role of the main link in the preparation of management decisions, namely, to focus on the need for a deeper study of the market, the preparation of alternative justifications for implementation in the activities of the enterprise modern forms organizing the trading process, preparing a justification for the need to change the size of the existing trading network, calculating economic feasibility activities of each outlet. The function of the current analysis of sales and the allocation of the most popular commodity items must be determined by the department that is directly involved in accounting for sales, namely, the commercial one. Conclusion
In conclusion, I would like to note once again that the choice of methods of influencing subordinates is the basis of management. To select the right methods of influence, the manager receives, transforms, analyzes and uses various types of information, thanks to which he has the opportunity to choose the right method of influence. Economic, organizational, administrative, moral and many other factors determine interpersonal relationships in the workforce, which allow you to influence it purposefully. Economic methods act as different ways of influencing managers on staff to achieve their goals. With the positive use of economic methods, the end result is manifested in good product quality and high profits. On the contrary, if economic laws are misused, ignored or neglected, low or negative results can be expected. After analyzing the activities of a major trading network LLC "Business Foods" can be concluded about the rational use of economic methods in enterprise management. This is reflected in the positive dynamics of the main economic indicators, wage growth and a systemic indicator of management efficiency. There are also small distortions in the organization of its management in the activities of the enterprise. In particular, the neglect of the main strategic functions of the marketing department. That is why one of the ways to improve the management system of Business Foods LLC is to adjust the functional purpose of the marketing department and change the structure of this unit. An important omission on the part of management is a misunderstanding of the enormous importance of such a factor as organizational culture. Implementation of methods to increase the level organizational culture, will undoubtedly affect the effectiveness of the application of economic methods in the management of the enterprise in question. Bibliography 1. Anikin B.A. top management for the leader. – M.: INFRA-M, 2000. 2. Bakanov M.I., Sheremet A.D. Theory economic analysis. Moscow "Finance and statistics" 2002. 3. Vikhansky O.S., Naumov A.I. Management: Textbook for economics. specialist. universities. - M .: Higher. school, - 1994. 4. Volkova K.A. etc. Enterprise: strategy, structure, position on departments and services, additional instructions. – M.: NORMA, 1997. 5. Voronov A.A., Katichev V.F. Indicators and methods for evaluating the effectiveness of the organizational and economic mechanism for managing an industrial enterprise. Management in Russia and abroad. - 2004. - No. 4.-S. 98–108. 6. Gerchikova I.N. Management: Textbook. - 2nd ed., revised and supplemented - M .: Banks and stock exchanges, UNITI, 1995. 7. Goldstein G. Fundamentals of management. tutorial.: Taganrog: Publishing House of TRTU, 2003. 8. Gorshkova A.A. Management: Textbook. – M.: UNITI, 2000. 9. Grishchenko O.V. Analysis and diagnostics of financial and economic activity of the enterprise: Textbook. Taganrog: Publishing House of TRTU, 2000. 10. Kuzin B., Shakhdinarov G., Yuriev V.K. Methods and models of firm management: Proc. Benefit. - St. Petersburg: Peter, 2001. 11. Kunz G., 0 "Donnel S. Management: system and situational analysis of managerial functions. / Translated from English: - M .: 1981. 12. Meskon M., Albert M., Hedouri F. Fundamentals of management. Per. from English. – M.: Delo, 2000. 13. Methods and models of rational management in a market economy: development of management decisions: Proc. allowance / ed. Chavkina A.M. – M.: FiS, 2001. 14. Models and methods of personnel management: Russian-British textbook / Ed. E.B. Morgunova (Series "Library of the journal" Personnel Management "). - M .: CJSC "Business School" Intel-Sintez ", 2001. 15. Moiseeva N.K., Aniskin Yu.P. Modern Enterprise: competitiveness, marketing, renewal. – M.: Vneshtorgizdat, 1993.
[formula 5]
The term " Management"(from English management - management, leadership, administration, direction, the ability to dispose, own, manage) or Production Management - the development and creation (organization), the most efficient use (management) and control of socio-economic systems. In institutional areas focused on: entrepreneurship, state socio-economic systems, non-profit organizations etc.
Thus, the essence of management is management. Economic methods, based on their name, are an integral part of the economy, therefore, economic management methods reflect both economic provisions both laws and laws of management. Thus, when they talk about the relationship between economics and management, they mean, first of all, economic methods of management.
The key element of the enterprise management mechanism in a market economy is the methods and models of managerial influence on economic activity to create economic conditions for the effective implementation of entrepreneurial activity, ensuring sustainable benefits from this activity.
The main economic methods (models) in the management of an enterprise, which ensure its effective functioning in market conditions of management, are
- commercial settlement;
- intracompany settlement;
– pricing policy and pricing mechanisms;
- mechanisms and methods for improving the quality and ensuring the competitiveness of products and the enterprise as a whole.
Economic methods of management- With methods of influence through the creation of economic conditions that encourage employees of enterprises to act in the right direction and achieve solutions to the tasks set for them .
Economic methods of management in management is a set of means and tools with the help of which a targeted impact on internal enterprise variables(goals, objectives, structure, technology and people) to create favorable economic conditions to ensure its effective functioning and development in a market economy.
The economic mechanism of management includes the main functions and methods of managing the economic activity of an enterprise, focused on increasing productivity and production efficiency while constantly adapting the activity of the enterprise as a whole to changes in market conditions and the behavior of all its participants. IN domestic practice the economic mechanism of enterprise management is usually called the economic mechanism.
Economic methods of management and the economic mechanism of management as a whole are determined by the socio-economic nature of the market economy and environment enterprises. They are focused on creating conditions for its development in the organization of production and marketing of products and services on the market. These methods involve the definition of requirements and the formation of qualitative changes in the activities of the enterprise for effective management, taking into account objective factors external environment in which he has to function. The content of managerial influences during the implementation of such changes is focused on the management of the enterprise with the aim of its effective functioning in market conditions of management. It must also take into account the objective trends in the development of social production, its concentration and internationalization, as well as the deepening of the specialization of science-intensive production and the increase in its capital intensity. This is due to the need to introduce achievements into production scientific and technological progress to form and maintain the competitive position of the enterprise, as well as to ensure sustainable growth of its productivity in the face of fierce competition in the global market.
Management methods are the ways in which management functions are implemented.
In the system of management methods, there are:
– Administrative method;
– Economic method;
– Socio-psychological method.
Administrative Management Methods is a set of ways and means of influencing personnel based on authority and discipline. The main feature is the direct impact on the object and the behavior of the performers in a certain environment. The form of expression is the orders and orders of a higher authority, which are binding on the lower. Based on a clear delineation of the rights, responsibilities and duties of the managing body, which are enshrined in the provisions of structural units, instructions and functional duties officials.
Organizational and administrative method- operational impact on manufacturing process, on the one hand, the adoption of promising and effective solutions on the improvement of the management and production system, on the other hand. To classify these methods, it is considered more rational and acceptable to divide them into three groups: organizational-stabilizing, disciplinary and administrative.
Organizational-stabilizing impact is carried out:
· At organizational regulation the structure of the enterprise, a functional set of its bodies and officials are defined. The basis is the law on enterprises, that is, it has the character legal regulation the entire control system.
· Rationing- setting standards, that is, a framework for lower and upper limits, norms, rules for the interaction of services and departments.
· Instructing - creating conditions for the implementation of processes that do not depend on the individual qualities of people, but follow from the requirements of the management system.
Management cannot carry out the management process without administrative influence, when specific tasks are set for the managing and managed systems - to provide technical, organizational and economic regulation of the production process, preventing deviations, restoring the previously provided parameters. The administrative influence is provided through orders, orders, statutory instructions.
In order for the administrative impact to be effective, it is necessary to organize strict control over its implementation.
Control and verification of execution- necessary parts of any administrative document. The control function is an important component of the management process. Both the current and the final control of the implementation of the production task, allow you to achieve the most effective result in management activities.
Mastering the effective use of methods of organizational and administrative management is the key to the success of a manager at any level.
Under economic methods of managing is understood as a set of means and tools that purposefully influence the creation of favorable conditions for the functioning and development of the company. The economic levers of the economic mechanism correspond to the socio-economic nature of the company and are one of the factors in the development of production and exchange on a market basis.
Socio-psychological methods are based on the motivation of the needs and interests of the individual, the team, on their professional connections and communication, they initiate creative and professional activity. The essence of socio-psychological methods is to use an effective mechanism of work by influencing the non-economic interests of employees and economic counterparties.
These management methods involve mechanisms based on moral and emotional incentives to maintain a positive microclimate in the workforce. Socio-psychological management methods affect a person through satisfaction and persuasion, using various methods: persuasion, suggestion, “infection with an idea”, etc. Modern management a company cannot do without socio-psychological methods of management, which always complement both administrative-command and economic methods of management.
In the conditions of production of a post-industrial society, a creative approach to solving economic problems is of particular importance, the success of which is largely facilitated by the creation of optimal working conditions, both for an individual employee and for the entire creative team, team working on the project. A business, creative environment and a healthy microclimate in the team are the most important factors that have a beneficial effect on production results.
Labor collective- This social group, for the effective existence of which it is necessary to observe a certain order aimed at maintaining an atmosphere of cooperation and mutual assistance.
The main purpose of the activity of the labor collective is the fulfillment of the production task, for the sake of which, in fact, this collective was created. As the labor collective exists, certain goals and objectives arise and disappear, a significant part of which relates to the social and spiritual life of people working in this collective. These goals and objectives stem from the public interest and contribute to the formation labor relations. If within the team there is an imbalance of the unified will of the team, existing labor relations, then contradictions in views arise, elements of a struggle of opinions appear, and the like, which leads to the collapse of the team.
To preserve and maintain the team in a working condition, it is necessary that all its members obey the same requirements: internal work schedule, production discipline, the norms of law and morality that have developed in the team, local acts of the company, informal requirements and traditions that have developed in this team.
Special control methods are the controls social processes occurring in the workforce, based on sociological research and scientific approaches. Research covers various aspects of the life of the labor collective, this and special assessment jobs, and the level of qualification of employees, morbidity and industrial injuries, relationships with colleagues, the psychological state of employees and much more.
In practice, apply different methods collection of social information, depending on the situation, but in general, making it possible to ensure its completeness, reliability, objectivity and timeliness. The most common are interviews, questionnaires, document analysis, creation of structural maps, observation, social experiment.
· Psychological methods
Psychological methods are a set of mechanisms for influencing interpersonal relationships aimed at creating an optimal psychological microclimate. The emotional background that accompanies the production process is extremely important for achieving a positive result when performing production tasks. The positive reaction of the employee to the task being performed has a direct positive impact on the personal result, and, ultimately, on the collective result of the entire company. Therefore, it is extremely important for the leader to direct significant efforts to create conditions for a comfortable psychological climate in the team. Ways of implementation can be varied and multifaceted: from a clear goal setting, the formation of creative, small groups, to the personal motivation of an employee. To implement the principle of labor humanization, that is, the creation of comfortable external working conditions: the design of the workplace, recreation areas, the exclusion of monotony in work, etc., it is also necessary to take into account the compatibility of workers united in groups according to various criteria: sympathy, education, emotionality and etc.
A skilled leader skillfully applies motivation system employees. These are moral motives (praise, awarding diplomas, etc.), and professional (prestigious courses, promotion, etc.), and material (bonuses, salary increases, etc.). most effective motivation is the internal interest of a person in the performance of a certain work. The manager is obliged to understand the factors that influence the attitude of the employee to work: traditions, professional pride, the prospect of growth, the attractiveness of work, etc. The same working conditions have different effects on employees, so it is important to modify them.
· Industrial Pedagogy
Mastering the basics and applying in practice the tools and methods of industrial pedagogy is the responsibility of every leader. Every leader must:
· acquaint employees with the prospects for the development of society, so that employees can clearly understand the place and role of the company in the labor market, as well as the prospects for its development;
· acquaint employees with the mission, goals, objectives and results of the company;
Involve employees in the formation of the goals and objectives of the company, so that they consciously and systematically increase the requirements for them;
when planning, setting tasks, monitoring the activities of an employee, take into account his individual characteristics;
Guide employees to choose the best solutions production task, take them into account personal qualities when issuing an individual task and determining the method of stimulation.
Question
What are the main economic methods in management?
The main economic methods (models) in enterprise management are: commercial calculation; intracompany settlement; pricing policy and pricing mechanisms; mechanisms and methods for improving the quality and ensuring the competitiveness of products and the enterprise as a whole.
The main economic methods (models) in enterprise management are: commercial calculation; marketing, rationing, instruction, control and verification of performance, motivation system.