You are deeply mistaken if you think that a children's microscope is no different from other ordinary toys. A microscope is a "scientific" device that allows your child to touch the magical and mysterious microcosm. This is not another toy that will be on the mezzanine in a couple of hours. This small "scientific laboratory", in terms of functionality, is not too inferior to real biological microscopes. Therefore, it is not surprising that most parents themselves are ready to sit for hours over a microscope, looking and studying the microworld around us. Children's microscope allows the child to independently study the structure of a variety of objects. Of course, at the initial stage, the young researcher will need the help of parents.
Types of microscopes
Experts believe that it does not make sense for a child to immediately buy a “super-sophisticated” microscope with maximum magnification. They recommend that parents look at an inexpensive monocular microscope. These optical devices are usually sold as a set with additional lenses. Together with the eyepiece, such a microscope allows you to achieve a magnification of up to 800x.
And yet, let's take a closer look at what types of microscopes the domestic market offers us. Most often, these devices are classified according to the possible increase in microparticles, which allows one or another type of microscope to be examined.
According to this classification, microscopes are divided into the following types:
- Optical.
- Electronic
- X-ray.
- Scanning.
For a novice researcher, of course, it is preferable to purchase simpler optical microscopes (they are also called “light microscopes”). These microscopes allow you to solve the main tasks of studying almost any object.
Other types of microscopes are usually referred to as "specialized". That is, you need to work with them in the laboratory, with the necessary knowledge.
Popular models of microscopes for children
To date, the stores offer a fairly wide selection of light (optical) children's microscopes.
One of the highest quality is rightfully considered Micromed Eureka40x-1280x . This device is widely used in educational institutions during laboratory work. However, thanks to three batteries and an adapter, this microscope can also be used at home.
The most accessible is MP-450 . This is a double action microscope. The role of lighting is the sun's rays and lighting from the lamp. MP - 450, allowing you to study biological sections and smears.
The Russian consumer market today offers a wide range of not only professional microscopes, but also children's optical instruments at quite affordable prices. They are perfect for research and biology at home.
What can you offer your child to look at under a microscope?
- Leaves of plants. For example, stinging hairs can be seen on a nettle leaf. With sufficient magnification, the petals of garden and wild flowers look incomparable.
- Hair. They are not only different in color for each person and animal, but also in thickness. And this can be seen by looking through a microscope.
- Pollen. With a soft brush, you can transfer pollen from a plant to a glass slide.
- Fruit pulp. It is no less interesting to study the structure of not only the pulp, but also the peel.
- Dirt under the nails can make a real revolution in the mind of a child. Having examined his nails under a microscope, the dirty one will immediately run to the bathroom.
- Money, paper, thread, fur.
- If there is an aquarium in the house, then scraping plaque from its walls will make your child stay in front of the microscope for hours. Plaque must be put on the glass and carefully covered with a second piece of glass. The study of such an unusual substance is best done at medium magnification.
Onion cells under a microscope
How to conduct research - instructions:
- We begin the experiment with the preparation of an optical device. Set up the light.
- Wipe both microscope slides with a clean cloth.
- We dilute a weak solution of iodine and drip a drop on the glass. You can use a pipette.
- After removing the outer scales from the bulb, carefully pinch off a tiny piece of onion with tweezers.
- Carefully place it on the glass in a drop of iodine water.
- We straighten a piece with a needle, and cover the object with a second piece of glass.
- We begin to study the preparation (onion slice) at a slight increase of fifty-six times. On closer examination, we see closely adjacent cells of an elongated shape.
- Then we move on to studying the object at a higher magnification of 300 times. The picture is changing before our eyes. When viewed, a transparent porous shell is visible. In the cavity of the cell there is a viscous substance that does not have a color - the cytoplasm. Having stained it with iodine, you can see the nucleus, and in it the nucleolus. In most cells, cavities are observed, which in biology are called "vacuoles".

Thanks to the microscope, we were able to see the structure of the cell, and find out what it consists of.
Which microscope can be used to see chloroplasts, leukoplasts
To begin with, let's define the very concepts of "Chloroplasts" and "Leukoplasts".
Chloroplasts are green plastids involved in photosynthesis. These are intracellular organelles of plant origin, which contain chlorophyll.
Leukoplasts are absolutely colorless spherical plastids that are part of the plant cell. However, when directly exposed to sunlight, they can be converted into chloroplasts.
Chloroplasts and leucoplasts can be viewed with a conventional light microscope, which is used in most schools. This microscope allows you to consider not only the shape of the plastids, their location, but also to count their number.

How to conduct an experiment?
The main function of chloroplasts is to attract insects and animals to pollinate plants and distribute seeds. The most convenient object for consideration, according to experts, is a slice of red pepper. For examination, a thin slice of the skin of red pepper is taken. A drop of water is placed on a glass slide and the object under study is placed in it. From above it is covered with a second glass. Chromoplasts are best seen in the thinnest parts of the cut.
Leukoplasts can be perfectly seen in an ordinary potato tuber. It is necessary for the experiment to take the thinnest slice of potato and place it in a drop of water on a laboratory glass. We cover the object with a cover glass. Even discolored leucoplasts are perfectly visible, but if they are stained with iodine, they become bright blue.
Disputes under the microscope - how to conduct an experiment
Children (as well as adults) really like to watch the dancing spores of horsetail - an ancient plant that caught dinosaurs. Each horsetail spore has special adaptations - elaters. They are designed to spread the plant with the help of air masses. Their fuel is a change in humidity. When examining horsetail spores, cover glass is not used. To make the disputes "dance" on them, it is enough to breathe, but carefully, otherwise they will simply scatter.

When water hits the spores, they shrink. In this case, an amazing dance can be observed - only when they are completely dry.
Flies, butterflies and other insects under the microscope
At home, finding an insect for examination under a microscope is not as difficult as it seems. All you need to do is step out onto the balcony. There, as a rule, you can find a lot of various corpses of insects. Having chosen a suitable object, it must be (with the help of a needle) carefully transferred to the viewing glass, and covered with a cover glass as carefully as possible.
Any child, touching the wing of a butterfly, noticed that pollen remained on his fingers. Looking through the eyepiece, one can understand that this is not dust at all, but small scales of wings. With the help of a microscope, a child will be able to study not only the structure of an insect, its wings and limbs, but also understand that each of its scales has a different shape.
Is it possible to see bacteria and germs under a microscope at home
Bacteria and some microbes can be seen even with an ordinary microscope without additional devices. Just for this you need to prepare hay infusion. It is in this infusion that after a while a hay stick is formed, which serves as food for the voracious shoe ciliates. These microbes look like small reflective sticks. 800 x magnification is sufficient for consideration. Infusoria in its appearance resembles a shoe, it is narrowed in front, expanded in the back. Hence the unusual name. Microbes are found everywhere in our life, they are able to exist even without the presence of air.

If you have a microscope at home with a magnification of 600-800x, then you can see the mass of bacteria in plaque diluted in a drop of water. True, they look far from presentable - very small balls, strings, sticks.
Scientists grow entire colonies of individual microorganisms, but for this they use special nutrient media.
In conclusion, I would like to say a few words about safety precautions when working with a microscope.
- Even a children's microscope is a complex optical instrument and should be treated accordingly.
- At first, you should not let the child twist and turn the screws unnecessarily. Parents should immediately explain to the child what the parts of the microscope are called and what they are for.
- It is better to work with glass slides together.
The microscope is the perfect gift for a child of any age. After all, this optical device will help expand knowledge about the world around us. The child will feel like a real scientist, before whom the mysterious microworld reveals its secrets. The world under the microscope is a miracle accessible to everyone. And if a child wants to look into the depths of space, then a few simple ones will help with this. Details in another article on our website.
Hi all!
A short review of a children's toy microscope.
I wanted to see what it was, but I didn’t want to spend a significant amount offline.
With points, the microscope came out about 800re.
The microscope is really a toy, quite a budget frankly cheap one.
What happened to me - look under the cut.
Draw your own conclusions.
We're talking about this one. 
Plastic, illuminated, with eyepiece height adjustment. There are 3 objective lenses (rotate). And a small set. 
Additional information - with what compared and purchase screen
Initially, after walking around the children's shops, the child asked for something like this. 
The options are almost all the same, they differ slightly in design and equipment - usually there is a lot of unnecessary garbage (petri dishes, pipettes, bottles), and also in expensive kits there are instructions and descriptions of experiments. 
As a matter of fact, having estimated one to the other, he took it out of habit on the zhirbeste.
Almost the same microscope cost about 800 rubles (including points). 
Please note: the device is a child's toy, therefore, compared with real laboratory microscopes, it will be fundamentally wrong. This microscope should not be used for PCB repair or any other serious needs. Plastic lenses give a not very enlarged image, as well as a little clarity. Despite the indicated 1200x. Its backlight is weak, and the design and strength are like a child's toy.

Light source: white LED
You will need 2AA/LR6 batteries to operate (not included)
Offhand, I can offer the following options for experiments with children:
You can see tree leaves and flower petals, slices (thin slices) of fruits and vegetables, animal fur and human fingerprints, fabric and paper fibers. It turns out to be interesting to consider thin sections of a ficus leaf or bulb. If you drop oil (for example, vaseline) on a glass slide, it will be more convenient to fix the object. For example, you can put 2-3 hairs or hairs. It is also interesting to look at the crystals of salt, sugar. Well, and so on.
Examples of experiments can be searched on the Internet, for example, "".
So, everything was standard - packaging-postal package. 

Inside the box.
The usual box for a children's microscope. We have them exactly the same, only with a plus in the price tag. 
Additional packaging photos





Inside is a foam cell with a set laid out in its place.

Comes with:
Optical microscope itself 1 pc
5 plastic slides
2 sample bottles
1 storage box and several labels
1 tweezer.

The appearance of all this goodness.


The microscope has two knobs - adjusting the height of the illumination and the height of the head. Additionally, the focus is adjustable on the eyepiece. The part with lenses is rotatable, you can choose 3 magnification options: 100x, 400x, 1200x. The backlight is turned on with a small slider, you must first install 2 AA batteries from the bottom (not included).
Now let's get ready for the experiments.
I must say right away that transmitting an image from an optical microscope is a whole problem. I took pictures on slippers on a smartphone camera, after leaning it against the eyepiece. Not everything is clear. The live image is a little bit sharper (the autofocus on the eyepiece does not work on the camera). But still, I tried to convey the best I could.
1) Thread.
We take the simplest cotton (?) thread, tear off a piece and fill it on a glass slide. 
We press on the subject table. 
Here's what you can see at 1200x magnification. 
2) Maple leaf.
You can see the leaf structure, veins. The sheet is translucent, which is very convenient. 
We clamp a piece on a piece of glass on a subject table. 
Turn on the backlight 

Here's what you see through the eyepieces 
3) Slice the bulb. Rather, I considered the film from the onion. 

We separate the layers of the onion, tear off the film 
We straighten it on a piece of glass, preferably without folds 

Large onion cells are visible. But what is inside the cells is not visible. Yes, the image is blurry. 
4) Human hair.
There are no intermediate photos, that's what you can see in the eyepiece. 
5) Fly (midge) 
Preparing the drug) 
With a fly it's more interesting. The limbs and wings are clearly visible. But the carcass of the fly is not translucent. 
Small hairs or scales visible on wings 

Once again, I remind you that the quality of the received images is affected by the way they are taken - the leaning smartphone camera. Live sensations are somewhat different, although plastic lenses do not give a particularly clear picture.
Instead of a conclusion: buying on zhirbest helped me save a certain amount of money from buying the same offline. The child looked, tried, calmed down. And I drew conclusions about the quality and the necessary functionality. The review has a slight increase, weak backlight. Want something more.
Of the minuses, I note the lack of examples of experiments in the kit, you have to look for everything and invent it yourself.
You could include instructions. Or at least a link to an online experiment guide.
Another of the minuses is the general fragility of the structure and a rather blurry image.
Perhaps my next children's microscope will be like this
In addition to the above (the picture is clickable), here are two options in tao ( and ).
In any case, I have everything))))
I hope it was useful))))
Report.
Progress.
Practical work №1.
By discipline: "Microbiology, sanitation and hygiene in the food industry." Topic: Studying the device of a microscope according to a drawing and mastering the technique of microscopy.
Practical work No. 1
Preparatory part
| Content | Time | WMD |
| 1. Construction. Greetings. Reporting lesson objectives. 2. Combat exercises: Fulfillment of the commands “Become!”, “Equal!”, “Attention!”, “At ease!”, “To the right!”, “To the left!”. 2. Walking and its varieties: a) normal c) on the toes of the hand on the belt c) on the heels of the hand behind the head e) on the outside of the feet 3. Running and its varieties: shins e) attached right and left side d) back forward | 30sec 2min 3min 3min 5min | Appearance (presence of a sports uniform) Monitor the correct posture Running at an average pace |
| Main part | ||
| 5. Teach general educational exercises turning left and right by stepping over, jumping a) imitation of exercises turning left and right by stepping over, jumping c) performing exercises turning left and right by stepping over, jumping 6. Fix general educational exercises opening to the width of the arms raised to the sides. a) performing exercises opening to the width of the arms raised to the sides. 7. Improve general educational exercises discrepancy in predetermined places. a) performing exercises divergence in predetermined places. 8. Improve running in alternation with walking a) running in alternation with walking | 5min 3min 3min 3min 5min | Monitor the correct execution Monitor the correct execution Monitor the correct execution Monitor the correct execution |
| Final part | ||
| 10. Exercise to restore breathing: Slow walking, while inhaling, raise your hands to the top, while exhaling, lower them down. 11. Construction. Summing up the lesson. 12. Homework | 1min 1min 30sec | Arrange exit from the gym Outdoor games |
Spas - Klepiki 20__
Subject: Studying the device of a microscope according to a drawing and mastering the technique of microscopy.
Target: To study the device of a microscope and master the technique of microscopy.
Work equipment: Microscope, workbook, pen.
1. Uncover the microscope. 2. Carefully put on the desktop and inspect the appearance. 3. Learn the basic details of the microscope and write in your workbook.
1. Draw a picture of a microscope. 2. Describe how to use a microscope.
1 - stand. 2 - micrometric screw. 3 - coarse screw. 4 - removable light filter. 5 - box with micrometer screw. 6 - tube holder. 7 - eyepiece. 8 - tube. 9 - revolver. 10 - Lens. 11 - subject table. 12 - capacitor. 13 - iris diaphragm. 14 - condenser handle. 15 - mirror.
1. The microscope is removed from the case and carried to the workplace, holding it with one hand on the tripod handle, and with the other on the tripod leg. It is impossible to tilt the microscope to the side, because the eyepiece may fall out of the tube.
2. The microscope is placed on the desktop at a distance of 3-5 cm from the edge of the table with the handle towards you.
3. Set the correct illumination of the field of view of the microscope. To do this, looking into the eyepiece of the microscope, a mirror directs a beam of light from a desktop illuminator lens. When properly set, the field of view of the microscope will appear as a well-lit and evenly illuminated circle.
4. The preparation is placed on the object table and fixed with clamps.
5. First, the specimen is examined with an 8* lens, and then it is moved to a higher magnification. To obtain an image of an object, it is necessary to know the focal length (the distance between the lens and the specimen). When working with an 8* lens, the distance between the preparation and the lens is about 9 mm, with a 40* lens - 0.6 mm and with a 90* lens - 0.15 mm. The microscope tube must be carefully lowered down using the macrometric screw. Watching the lens from the side, and bring it closer to the preparation (without touching it) at a distance slightly less than the focal length. Then, looking into the eyepiece, the same screw, slowly turning it towards itself, raises the tube until the image of the object under study appears in the field of view.
After that, by turning the macrometric screw, the lens is focused so that the image of the lens becomes clear. The macrometric screw must be rotated carefully, but not more than half a turn in one direction or another. When working with an immersion objective, a drop of cedar oil is first applied to the preparation and, looking from the side, the microscope tube is carefully lowered with a macrometric screw so that the tip of the objective is immersed in the oil drop. Then, looking into the eyepiece, the tube is very slowly raised with the same screw until an image appears. Fine focusing is done with a macrometric screw.
6. When changing lenses, adjust the illumination intensity of the subject. By lowering or raising the condenser, the desired degree of illumination is obtained. For example, when viewing a preparation with an 8* lens, the condenser is lowered, when switching to a 40* lens, it is slightly raised, and when working with a 90* lens, the condenser is raised up to the limit.
7. The preparation is considered in several places by moving the stage with side screws or moving the slide with the preparation manually. When examining a preparation, the macrometric screw should always be used in order to examine the preparation in its entire depth. Before replacing a weak lens with a stronger one, the place of the preparation, where the object under study is located, must be placed exactly in the center of the field of view and only after that turn the revolver with the lens.
8. During microscopy, keep both eyes open and use them alternately.
9. After finishing work, remove the preparation from the object table, lower the condenser, place an 8* objective under the tube, remove immersion oil from the front lens of the 90* objective with a soft cloth, and put the microscope back in its case.
The microscope is one of the most interesting and popular scientific instruments, since childhood, immersing people in the world of small details that cannot be seen with the ordinary eye. The process of using this device does not seem complicated, however, in order to get the maximum benefit from a session of studying an object, you need to know the principle of operation and the nuances of its operation. The rules for working with a microscope contain instructions for the preparation of the instrument, its setup, use and care. Observing them will not only make the learning process more efficient, but also extend the life of the device.
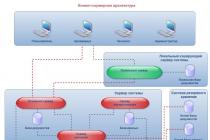
Device and principle of operation of the device
An ordinary microscope is formed by several functional parts, including mechanical, lighting and optical. For the convenience of physical handling of the device, a carrying and regulating equipment is provided, which includes a tripod, base, holders and adjustment units for working parts. This is the mechanical basis of the device. A mirror or special lamps are responsible for the direction of the light flux. In the latest models, an LED is connected to improve the quality of the image presentation.
As for the reproducing part, it is formed by a group of lenses that provide sufficient magnification. All the components described in the complex determine the principle of operation of the microscope, which is based on the optical magnification of objects through lenses. Actually, the entire design of the device is designed for convenient technical organization of the process. The user is required to at least place the object under study on the glass slide, and then adjust the mechanical part with the eyepiece and objective. The further process will depend on the specific objectives of the study.
Features of the work of electronic models
Modern microscopes are equipped with an electronic control and data reporting system. The power of the optical part is also increased, providing an increase of up to 10,000 times. Energy support fundamentally distinguishes the electron microscope. The principle of operation is based on the use of charged particles whose energy is at least 200 keV. Directed electron flows are formed by a conventional cathode made of a latan alloy or tungsten.

The function of a kind of controller is performed by magnetic lenses. They correct the movement of electrons in the tube of the apparatus. As a result, some of them are scattered, while the other part bypasses the sample, providing visual information about the structure of the object. It is important to emphasize that the principle of operation of this type of microscope allows close interaction with computer technology. Already in the process of research, the operator can display a picture of the target object with a detailed graphic study on the monitor. The research process may include special programs for automatically compiling the characteristics of an object based on the information received.
Rules for working with a microscope for schoolchildren
When using this appliance for the first time, you should be familiar with the basic instructions for handling it. These rules include:
- The position in the process of work should be sitting.
- Before examination, all optical equipment is wiped with a napkin.
- The device should be in front of the user about 3 cm from the edge of the desktop.
- Change of position during the study is undesirable.
- After placing the object on the glass slide, a small magnification is adjusted.
- The luminous flux, if present, is directed to the area where the object is located, and the lens approaches it up to 1 cm.

- You can look into the eyepiece with only one eye, and you should manually adjust the optimal sharpness using the coarse adjustment screw. It is important to emphasize here that the rules for working with a microscope prohibit lowering the lens precisely at the moment of observation through the eyepiece. This limitation is due to the fact that the front lens can damage the glass during such manipulations.
- After the work is completed, the magnification is again set to low, the lens is raised, and the working glass is cleaned.
Common mistakes made when working with the device
There are two categories of errors associated with the control of the microscope and its functional organs. They are associated with the control of lighting equipment and the transition between magnification modes. As for the light, the errors concern two points:
- Third-party objects in the room fall into the field of view. The situation can be corrected by rebuilding the capacitor (lowering) to a level until the interference is eliminated.
- Incorrect fixation of the lens on the optical axis. As a result, part of the view may be shaded. The problem is solved by turning the design revolver until it clicks.
Also, the rules for working with a microscope require careful attention to setting up optics. When going from low magnification to high magnification, there is often a lack of focus. This can be caused either by the fact that the object has moved out of the field of view, or by incorrectly positioning the coverslip downwards.

Maintenance and care of the microscope
After finishing work with the help of screws, you should raise the tube, remove the preparation from the glass slide and bring the device to the non-working position. As already mentioned, optical parts should be wiped, which will preserve their integrity. These are the most sensitive structural elements, damage to which can adversely affect the quality of observations. How to work with a microscope to preserve the integrity of the lenses? First of all, the appliance should always be placed on a level surface, which minimizes the risk of falling. Direct contact with the surfaces of optical parts is completely minimized - the only exception can be a soft cloth with cleaning solutions. It is recommended to store the microscope in a case, and it is better to keep the same lenses with other sensitive elements in plastic bags.
Conclusion
To date, there are many new types of this device that offer new research opportunities. In this regard, the rules for working with a microscope are also changing, in particular, requirements are introduced for the organization of electrical communications, program control, etc.

This applies to electronic models, but mechanical devices do not lag behind in their development. They are equipped with more ergonomic and functional controls, efficient new generation optical fittings and a wide range of optional tools like the same LEDs.
When working with a microscope, you must follow the operations in the following order:
1. Work with a microscope should be sitting;
2. Inspect the microscope, wipe the lenses, eyepiece, mirror or electric light from dust with a soft cloth;
3. Set the microscope in front of you, a little to the left, 2-3 cm from the edge of the table. Do not move it during operation;
4. Fully open the diaphragm, raise the condenser to its highest position;
5. Always start working with a microscope at a low magnification;
6. Lower the lens 8 - into the working position, i.e. at a distance of 1 cm from the glass slide;
7. Set the illumination in the field of view of the microscope using an electric illuminator or a mirror. Looking into the eyepiece with one eye and using a mirror with a concave side, direct the light from the window into the lens, and then illuminate the field of view as evenly and as much as possible. If the microscope is equipped with an illuminator, then connect the microscope to a power source, turn on the lamp and set the required brightness of combustion;
8. Put the micropreparation on the stage so that the object under study is under the lens. Looking from the side, lower the lens with a macro screw until the distance between the lower lens of the objective and the micropreparation is 4-5 mm;
9. Look into the eyepiece with one eye and turn the coarse adjustment screw towards yourself, smoothly raising the lens to a position at which the image of the object will be clearly visible . You can not look into the eyepiece and lower the lens. The front lens can crush the coverslip and scratch it;
10. Moving the preparation with your hand, find the right place, place it in the center of the microscope field of view;
11. If the image does not appear, then it is necessary to repeat all the operations of points 6, 7, 8, 9;
12. To study an object at high magnification, first place the selected area in the center of the microscope's field of view at low magnification. Then change the lens to 40 x by turning the revolver so that it is in its working position. Use a micrometer screw to achieve a good image of the object. On the box of the micrometer mechanism there are two risks, and on the micrometer screw there is a point that must always be between the risks. If it goes beyond their limits, it must be returned to its normal position. If this rule is not observed, the micrometer screw may stop working;
13. Upon completion of work with a high magnification, set a low magnification, raise the objective, remove the preparation from the working table, wipe all parts of the microscope with a clean cloth, cover it with a plastic bag and put it in a cabinet.
Work order
Exercise 1. Using microscopes, tables and workshops, study the device of light microscopes (MIKMED-1, BIOLAM and MBS-1) (Fig. 1). Remember the names and purpose of their parts.
Task 2. At low and high magnifications of the microscope, learn to quickly find objects on permanent micropreparations.
Temporary Preparation Technique
Take the glass slide out of the container, holding it by the sides. Place an object in the center of the glass. 
Figure 2. Subject (A ) and coverslips (b ) glass
Pipette 1-2 drops of water onto the object.
Take the coverslip by the side edges and place it with the side edge on the drop of water, then slowly lower the glass onto it.
Attention! There should be no air bubbles between the slides, the cover slip should not be thrown onto the drop from above, it should be pushed into the drop from the side, as it were.
Remove excess water with filter paper;
Place the prepared micropreparation on the stage and examine first at low magnification, then at high magnification.
In the event that the micropreparation was made inaccurately, there are air bubbles between the glasses, the steps should be repeated.