Miscellaneous different types plans are regularly drawn up by the management of enterprises. The success of the work and the achievement of high results largely depend on how clearly, qualitatively and in detail they are drawn up. This is a kind of benchmark that helps the company move in the right direction, taking into account the external situation and the degree of resource availability.
Plans and planning
Planning is an activity by definition promising state and functioning of the firm. It plays a huge role in the activities of the organization and has several important functions:
- determination of the prospects for the development of the enterprise;
- savings material resources;
- reducing the risk of ruin and bankruptcy due to unforeseen fluctuations in the economy;
- timely response to changes in market conditions;
- improving work efficiency.
A plan is an approved document that contains a specific list of actions, goals, methods and digital indicators compiled for a specified period. In addition, it includes information on available and missing resources, which are designed to ensure that the results obtained are as close as possible to those previously announced.
Planning principles
All types of plans are drawn up on the basis of certain principles:
- objective necessity dictated by modern economic conditions;
- all indicators must be specific and have a numerical dimension;
- the plan should have clear time limits;
- all figures must be realistic and justified (should be based on the availability of resources in the enterprise);
- the form of the program should be flexible so that it is possible to adapt to changes in the external and internal environment;
- planning should be carried out comprehensively and cover all areas of the enterprise;
- programs for all structural divisions should not contradict each other;
- all drawn up and certified plans are binding;
- focus on achieving maximum economic results;
- at each of the stages, several alternatives should be developed, among which the optimal one is subsequently selected.
Compliance with these principles allows you to make plans real, detailed, and most importantly - effective.

What are the plans
In accordance with various classification criteria, the following types of plans are distinguished (for better clarity, we have presented the material in the form of a table).
| sign | Kinds |
| By time | Short term. Medium-term. Long-term. |
| By goals | Tactical. Operational. Strategic. |
| By accuracy | Detailed. Enlarged. |
| By scope | Corporate. |
| By content | Production and sale of products. Supplies. Personnel. Costs. Financial investment. Social. |
| By landmark | Reactive (due to any events or on the basis of previous experience). Interactive (provide for the interaction of past, future and present indicators). |
All of the listed qualification signs can exist both separately and intersect in one planning document.

Business plan
To attract investment or to get a loan to develop your own business, you need to correctly present your idea. To do this, you need to draw up a business plan, which is information about the organization, as well as its financial indicators. It consists of the following sections:
- to begin with, a short summary is drawn up that reflects the general content of the document;
- further describes the goals of the project, as well as the tasks that are designed to ensure their achievement (this component of the plan should reflect not only the philosophy of the organization, but also its focus on material results);
- information about the company's activities;
- analysis of the situation in the industry, as well as a description of the competitive environment;
- target audience and markets;
- marketing strategy and promotional activities;
- production technology;
- organizational structure and measures to ensure activities;
- information on the planned number and structure of personnel;
- financial part (this component of the plan should contain calculations of all economic indicators);
- enterprise responsibility;
- unforeseen circumstances and business liquidation.
Inspection plan
The work of the enterprise requires continuous monitoring of compliance with the specified indicators. To do this, an audit plan is drawn up for the organization as a whole, as well as for each unit separately. Similar documents are also drawn up by tax and other regulatory services. At the enterprise, inspections can be carried out both on their own and with the involvement of outsiders and organizations. This should also be written into the plan. 
Definition of a forward-looking strategy
Strategic planning is the process of determining the desired future state of an enterprise through analysis, forecasting and goal setting. We can say that this is a certain set of actions to create long-term prospects for the organization.
Strategic planning may include the following points:
- distribution of material and technical resources between departments of the organization;
- response to change external environment, as well as conquering your own niche in the market;
- possible future change organizational form enterprises;
- coordination of management actions in the internal environment;
- analysis of past experience in relation to future plans.
The strategy of the enterprise is developed by the top managers of the company. It must necessarily be supported by financial calculations based on a retrospective analysis. One of the main requirements for such plans is flexibility, because the external environment is quite unstable. Also, when developing a strategy, it is necessary to take into account the fact that the costs of its implementation must be fully justified by the expected results.

Enterprise development
The enterprise development plan implies cardinal changes both in the economic and in organizational system firms. At the same time, significant financial and technological growth should be observed. The central place is occupied by the increase in production volumes and, as a result, net profit.
A strategic plan for the development of an enterprise can be developed in the following main areas:
- improvement production program;
- introduction of achievements of scientific and technological progress;
- increasing the efficiency of production by increasing the indicators of labor productivity and material efficiency;
- a plan for the construction of new facilities, as well as the installation of new equipment;
- improvement of the personnel structure and composition;
- improvement social position workers;
- introduction of environmentally friendly production systems.

Perspective plans
Long-term plans are the most important component of the activities of managers, which largely determines the effectiveness of the company as a whole. During their development, not only specific goals should be specified, but also the resources that will be used to achieve them. In addition, the timing of the implementation of the planned activities should be determined. It can be said that it is necessary not only to determine the directions of activity, but also to foresee options for the development of the situation in the external environment.
Long-term plans are based on forecasts regarding the future economic situation both inside and outside the organization. The period of drawing up such a program can cover a period of time up to 15 years.
financial planning
The financial plan is inextricably linked with the development of economic and social issues. It reflects the use of material resources, as well as the planned cost finished products. Also when compiling this document should provide for the use of existing inventories and financial resources in order to improve the production process.
A financial plan is similar in form to a balance sheet. It should clearly spell out all the articles that relate to the revenue and expenditure parts. The income section displays transactions such as equity receipts, interest on deposit accounts, and so on. Speaking of costs, they note depreciation, repayment of debts, and so on.

Enterprise annual plan
Almost every production (and even non-production) enterprise considers it mandatory to draw up a work plan for the year. It prescribes such points as the cost of production of components and parts, as well as the cost of finished products, the revenue that is expected to be received, as well as the amount of mandatory payments.
The annual plan is something like a forecast. It is based on the development trends of the enterprise itself, as well as the industry and the market as a whole. These forecasts are made on the basis of data for previous periods, while taking into account possible deviations and unforeseen fluctuations in the economy.
On large enterprises it is not enough to draw up an annual plan only for the organization as a whole. Wanted financial calculations and detailed economic indicators for each division. At the same time, such plans should be linked to each other and not have contradictions.
Drawing up an operational plan
The operational work plan ensures that strategic goals enterprises. Unlike long-term plans, this type regulates the current activities of the company. Such a document may cover a period of up to three months.
- the organizational structure of the enterprise, which must undergo changes or remain in the same state;
- manipulations with the existing technological base or the acquisition of new equipment;
- efficiency improvement economic efficiency in general or its individual indicators;
- determination of the profitability of the coordinates of the enterprise itself or its main counterparties;
- improving the procedure for managing inventories in order to ensure their savings;
- improvement of product quality control processes at all stages of its manufacture;
- increasing the company's reputation among suppliers and customers by improving the image.
Planning process
Drawing up plans for the work of enterprises involves the passage of several successive stages:
- definition possible problems and risks that the company may face in the prospective period;
- determination of the goals of the enterprise, as well as their clear economic justification and assessment of the reality of their implementation;
- logistical and financial condition enterprises; assessment of the cost of resources that are necessary to achieve the goals;
- specification of goals by dividing them into separate specific tasks;
- development of measures to control the execution of plans, as well as the definition of their schedule.
Without drawing up clear and detailed plans, it is impossible to ensure the smooth and efficient functioning of the enterprise. Management must have a clear idea of the objectives of the activity, as well as the means that will be needed to achieve them. In addition, all types of plans provide an opportunity for the enterprise to mitigate the impact of economic fluctuations.
Like any activity, planning is characterized by methodology and organization.
Planning methodology - the choice of a set of principles, approaches, ways of organizing and planning methods for effective solution problems and achieve their goals.
Planning organization is a way of ordering certain actions in accordance with their composition, structure and characteristic features. The object of organization is the planning process itself. (the task of managers is to consciously choose and design a planning methodology).
Method in planning - methods, techniques, planning procedures that are essential and allow you to successfully solve a particular problem.
Planning methodology - a set of methods related by the generality of the problem being solved, performing the function of a methodological instruction.
The object of planning is various socio-economic systems (enterprises, its links, etc.)
The subject of planning is the activity itself and relations that cover individual elements of the system and its interaction with the external environment.
Planning principles: (A. Fayol, R. Ackoff)
The principle of unity (holism) - planning in an organization should be systematic;
The principle of participation;
The principle of continuity;
The principle of flexibility;
The principle of precision.
Classification of types of planning.
1. According to the degree of obligation to fulfill planned targets:
Directive planning - has a mandatory character in relation to planning objects;
2. According to the planning time horizon:
Long term planning(3 or more years);
medium term;
Short term (up to 1 year).
3. By type of planned decisions:
Strategic planning - covers not only the relationship between subsystems within the company, but also the relationship between the company as a whole and its business environment, with which the company directly interacts and on which it has a direct impact. Strategic planning is based on strategic decisions that: 1) are future-oriented and serve as the basis for making tactical and operational decisions; 2) are associated with significant uncertainty, since they take into account uncontrollable factors in the external environment of the business; 3) are associated with the attraction of significant investment resources, and therefore may have significant long-term consequences for the company.
Tactical planning - covers the relationship between the subsystems of the company, as well as between them and the company as a whole.
operational planning– choosing from traditional means of solving problems or those established by higher management and developing a process for their implementation.
4. According to the planning object:
Corporate;
Business planning;
Activity planning functional divisions;
Planning the activities of structural units;
Planning the activities of individual workers.
In accordance with the indicated types of planning, the following types of plans are distinguished: corporate plan; business plan; operational plans for the activities of structural units.
5. According to the degree of coverage of the planning object:
Partial.
6. On the subject of planning:
Production planning;
Supply, marketing, sales, finance, personnel, R&D.
7. According to the degree of repeatability:
systematic;
One-time.
8. According to the degree of adaptation:
Rigid;
9. In terms of detail:
Aggregated;
Detailed.
10. According to the form of coordination:
Sequential planning - plans are developed with a certain frequency and upon completion of one plan, another one is developed on its basis;
Synchronous planning when the content of plans for all years is determined simultaneously, taking into account their temporal interdependencies;
rolling planning;
Extra planning.
11. By orientation of planning ideas:
Reactive - orientation to the past development of the company;
inactive;
proactive;
The achievement of the goals of the organization is largely ensured by the actual practice of management based on planning. Let's consider this control function in more detail.
Planning- this is the process of determining the goals, objectives and indicators of the organization's activities for the future, as well as specific actions (activities) and the material and human resources necessary for their solution.
In fact, planning- this is the process of developing and making a decision to ensure the effective functioning and development of the organization in the future. In the narrow sense of the word, planning is reduced to the work of drawing up a special document - a plan that defines specific actions to achieve the goals set within the framework of the upcoming planning period.
Work plan- a document that defines the content, volume, sequence, timing of the implementation of activities and their performers.
In the process of planning the activities of the organization, the following main goals:
purposefulness of activity is provided;
organizational bases of activity management are created;
coordination of the efforts of all employees is ensured structural divisions in the course of activity;
the optimal variant of the management decision is developed;
a system of specific indicators is determined, with the help of which their implementation is monitored, an objective assessment of the activities of each employee, structural divisions and the organization of culture as a whole is given.
Planning as a process is implemented in the system of plans, in which the forecast is fixed from various positions organization development, intermediate and ultimate goals, tasks, mechanisms for fulfilling planned targets and using resources, deadlines for the implementation of certain activities and responsible persons.
This planning system includes various kinds.
In terms of decision level:
plans of higher authorities;
own organization's plans;
plans of structural divisions;
individual employee plans.
Depending on the obligation to perform:
forecast plans (give orientation, concept of development);
directive (contain clear indicators, specific activities, deadlines and responsible persons).
Direction:
thematic;
complex (software).
Depending on the period (length of the period) for which they are developed:
prospective (which can be long-term or strategic, medium-term and short-term);
current (for a month, a quarter);
operational (for a week, a decade).
Consider the most important species planning the activities of the organization more specifically.
forward planning This activity can be carried out for a period of 1 to 5 years or more.
In the long-term planning of the organization's activities, such a variety as programming is of particular relevance.
Programming is a process of preparing goals and objectives for the development of an organization, designed for a long period. Program is a set of organizational, economic, economic activities with unified management, vertical and horizontal connections coordinated in time, resources and performers See: Chizhikov V.M., Chizhikov V.V. Introduction to Socio-Cultural Management: Textbook. - M.: MGUKI, 2003. - S. 118 ..
Purpose of programming- to combine the efforts of all real and potential subjects of activity to achieve its goals. Thus, programming integrates the activities of not so much one organization separately, but the entire set of subjects of this activity, united by territorial, sectoral, object and other criteria, it solves the problem of development as a whole, determines the main directions and types of activities, their final and intermediate goals, deadlines and performers. Therefore, programming can and should be carried out by management entities at the territorial, multi-industry levels, and then used and specified in the lower structures of the organization.
forward planning organizations is determined by the mission and common strategic goals. Their long-term plans differ significantly from the plans of other organizations, because they do not associate their future with profit indicators.
Long-term plans define the actions that the organization intends to take to achieve the strategic goals, the direction of the allocation of resources, development creativity, equipment, increasing the number of visitors and users of cultural services.
tactical planning is aimed at the implementation of tactical goals, has a shorter planning period (usually a quarter, a month). In organizations tactical plans determine specific activities with an indication of the time of their implementation and performers.
Operational plans are developed in the structural divisions of the organization. They determine the sequence of actions to achieve operational goals, the solution of intermediate tactical tasks and are aimed at the implementation of tactical plans.
On the basis of operational plans, the activities of specialists and structural units are built. Operational plans can be developed in the form of schedules or network plans, which are sequentially performed operations and works tied to a calendar.
The technology of planning the organization's activities involves focusing on a certain system of principles.
Scientific principle focuses on the use of the findings and recommendations of science in the planning process.
The principle of purposefulness and continuity requires clarity in the development of goals and the implementation of planned activities as a permanent and continuous process. Continuity also requires that all plans be developed taking into account the prospects and results of the implementation of previous plans, as a system of long-term and current plans.
The principle of concreteness focuses on the clarity and clarity of the wording of tasks, activities, responsible persons and deadlines.
reality principle involves taking into account the conditions and real opportunities plan implementation, security necessary resources, availability of time and other factors.
Principle of connection with life, the state of the surrounding social environment.
Establishment principle personal responsibility allows to provide control of performance and to give an objective assessment of the activities of specialists and structural divisions.
Flexibility. The implementation of this principle is achieved by adjusting plans in the process of activity, taking into account changes in conditions, tasks and other circumstances.
Profitability. The essence of this principle is that the costs of planned activities do not exceed the efficiency expected from it.
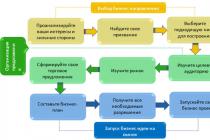
Activity planning technology involves the allocation several stages.
Organizational and preparatory stage.
Stage of development of the draft plan.
Stage of coordination and approval of the plan.
On first stage organizational and methodological prerequisites for successful planned activities are created and the following issues are resolved.
Identification of responsible developers of the draft plan (usually this task is assigned to the most qualified employees or a group of employees).
Determining the timing of the development and approval of the plan.
Organization of methodological support (a meeting of all participants in the planning process is held, the goals and objectives of planning, its methodology and other issues are explained).
Information support, the essence of which is to provide participants in planning activities with the information necessary for planning.
On second stage(stage of development of the draft plan) the following issues are resolved.
Editing goals and objectives of socio-cultural activities.
Choice of the form and structure of the work plan. It should be noted that there are no standard requirements on this issue, however common sense and work experience show that the structure of the plan (its sections) should correspond to the system of tasks of the organization.
Definition of forms and methods of activity. This task is solved taking into account the capabilities of the organization and the availability of material, financial, human and other resources.
Determining the timing (time) of events and their performers. In the decision this issue it is advisable to use the calendar form of the working document. Planned events are first signed in a calendar form, by day (and even numbers). This avoids overlaps and inconsistencies in time and performers.
Registration of the draft plan in accordance with the requirements for documents set forth in state standards.
On third stage the task of coordinating and approving the plan is being solved. The plan must be agreed with all stakeholders.
Planning in the activities of the organization
In an organization, planning is carried out at several levels: strategic, tactical and operational. On strategic level the management of the organization develops long-term goals and directions of activity. The development of such plans is possible only on the basis of forecasting the development of the organization in the future. In this regard, the organization needs a variety of forecasts.
On tactical level planning goals and objectives are specified in line with the adopted strategies.
The basis of planning in an organization is operational planning, which establishes a list of specific works, actions necessary to achieve the goals, as well as deadlines and responsible persons.
All types of planning in the organization form a single system. The technology of planning work is quite complex and creative process. It involves the allocation of certain stages of work, which can be universal, but the methods of planning and forecasting differ significantly.
Planning is the initial development and subsequent establishment by the management of the company of a system of quality and quantitative indicators its development, which determine the proportions, pace, and development trends of this enterprise not only in the current period of time, but also in the future.
Various types of planning are the main link in the economic management mechanism, as well as the regulation of any production. Administrative management, planning and control over the work of the enterprise in foreign practice are defined by a single concept - "management".
How does it happen?
There are different types of planning:
- Balance.
- Calculation and analytical.
- Economic and mathematical.
- Program target.
- Graphoanalytical.
balance sheet
Balance types of planning provide a direct connection between the needs of the company's resources, as well as the sources of their coverage and sections of the plan. For example, the use of this technology involves linking the production program with the capacities of a particular enterprise, and the labor intensity of the selected production program with the number of employees. Qualified employees who are assigned different kinds planning, should be a balance of working time, production capacity, as well as energy, financial, material and many others.
Settlement and analytical

Such planning is used to calculate in detail the characteristics of the plan, as well as to analyze their dynamics and factors that ensure the required quantitative level. within the borders this method the initial basic level of the most important indicators of the plan is determined, as well as their possible changes during the course of the planning period due to the quantitative influence of the main factors. In addition, the calculation of indices of changes in planned indicators in comparison with the baseline is also carried out.
Economics and Mathematics
Such types of planning provide an opportunity to develop in detail economic models the dependence of certain indicators, based on determining the change in their various quantitative parameters in comparison with the most important factors, and also make it possible to prepare several options for the plan, from which the most optimal one will subsequently be selected.
Graphoanalytical

This method provides an opportunity to present the results of the economic analysis using graphic tools. Using these types of financial planning, you can determine the quantitative relationship between various related indicators. For example, the relationship between the rate of change in capital-labor ratio, capital productivity, and labor productivity is determined in this way.
network
Network types of financial planning are a separate type of graph-analytical. With the help of specialized network charts you can simulate the parallel execution of work in time and space on various complex objects. For example, this may include the development and development of new technologies, the reconstruction of a particular workshop, and much more.
Program-targeted

Program-target types of work planning provide the opportunity to draw up a plan in the form separate program, that is, a certain set of activities and tasks that are united by a single goal and are timed to certain dates. A characteristic feature of the program in this case is that it is aimed at achieving certain final results, and the core of the program is the main goal, which is specified in a number of tasks and subgoals. The goals are already being achieved by specific executors who are provided with the necessary resources.
Based on the ranking of goals, a “tree of goals” type graph is already being formed, which will then be used as an initial base for the further formation of a system of program indicators, as well as a separate organizational management structure.
Timing differences
It is worth noting that there are also several varieties of planning, depending on the timing:
- Current.
- Promising.
- Operational production.
promising
Forward planning is entirely based on the construction of forecasts. Using this technology, you can determine the possible future need for any new types of products, as well as the product and sales strategy of the company in various markets. Among other things, promising types of training planning and other options for its implementation are divided into medium-term and long-term, depending on what specific period of time the forecast is made.
Such a plan is distinguished by a program-targeted nature, that is, it determines the economic strategy of the company for a sufficiently long period of time, taking into account the boundaries of existing sales markets, as well as the possible development of other markets. The number of indicators in this plan is limited, and its objectives and goals are more specifically specified in the medium term plan.
The objects for the definition of which the main types of planning activities are used are most often organizational structures, capital investments, production capacity, the need for certain financial resources, market share and many others. To date, the deadlines for the implementation of plans do not have any binding character, and a fairly large number of companies are developing long-term plans for a period of 5 years, while medium-term plans are built approximately for a period of 2 to 3 years.
Current

The current types of calendar-thematic planning are being developed as a medium-term plan with a detailed specification of its indicators. In this case, both the structure and indicators of annual planning may differ depending on which object is being considered, as a result of which they are divided into shop, brigade and factory.
Operational and production
This type of planning provides for the specification of the assignment of the annual plan for shorter periods of time, as well as the distribution of the goal among various production units. Such a plan is used as a means of ensuring the rhythmic release of products, as well as the implementation of a uniform operation of the enterprise, and ultimately brings the planned targets to their direct executors. Operational and production planning is also divided into dispatching, intrashop and intershop. As the final stage, the so-called shift-daily planning is used.
Classification
Is there enough a large number of signs by which various planning methods differ in forms, terms, types, as well as many other signs. From the point of view of the mandatory adoption and subsequent implementation of plan targets, planning can be divided into two types - indicative and directive.
Directive

Directive types of activity planning are distinguished by the obligatory acceptance, as well as the subsequent fulfillment of plan targets, which are determined by the parent company for those enterprises that are subordinate to it. Directive planning for a long time completely permeated every level of the socialist central planning system, and also limited the initiative of each individual company, but in the modern market economy it is used at the level of enterprises and is applied in order to develop their current plans.
indicative
Indicative planning is a separate form of state regulation of production by changing tariffs and prices, tax rates, bank interest rates, the minimum possible level wages, as well as a number of other indicators. Thus, it is possible to enumerate a sufficiently large number of characteristics that determine indicative planning. Types of plans of this type include tasks, which are called indicators.
Indicators are parameters in accordance with which the state and subsequent direction of the development of the economy are characterized and which are developed directly by the authorities government controlled. As part of such a plan, there may also be a variety of mandatory tasks, but their number is rather limited, as a result of which such a plan is more guiding and recommendatory. The use of this planning today is found in enterprises in the process of developing long-term plans.
promising
As mentioned above, the main types of planning of this type are entirely based on forecasting, that is, it is the basis, the foundation of this planning technology, and in contrast to it, it is entirely based on foresight, which is based on probabilistic, economic-mathematical, as well as scientifically based analysis. various prospects for the development of the company in the near future.
strategic
Strategic planning sets long-term goals, and also provides for the allocation of funds to achieve them and determines the most important directions further development companies. Also, no less important, such planning provides for the formation of the main mission of the enterprise, aimed at achieving its common purpose. The mission details the status of the enterprise, and provides precise direction and orientation in order to define precise goals and strategies at different levels of development.
tactical

Tactical planning, unlike the two above, covers the medium and short-term periods, and is also aimed at the most efficient and rapid implementation of these plans, specified in the complex of plans for the company's socio-economic development.
Bite-mining
These species scheduling represent a kind of technical and economic, but in the conditions of modern market economy its functions were able to expand significantly, as a result of which it turned into a completely independent type of planning. There are also a number of classifications of types and forms of planning, including reactive, interactive, preactive, inactive, and many others.
Features of financial planning
Financial planning includes the determination of all income and expenditure directions of the company's finances to ensure its further development. As main goals this process one can note the establishment of a correspondence between the presence of financial resources in the company, as well as the need for their availability. Besides, financial planning ensures the choice of the most effective sources of obtaining financial resources and the most profitable opportunities for their use.
Financial planning is carried out through the formation of a wide variety of financial plans, the content and purpose of which will directly depend on what tasks planning sets itself and in relation to which objects it is carried out. The financial plan should be considered as one of the real forms of manifestation of the distributive nature of the finances of a particular company, while it is worth noting that the financial plan acts in the form of balance sheets, grouping income and expense items in them, which are planned to be received and financed in a certain period of time.
The degree of detail of the plan will directly depend on the form of documents adopted by the company, while the form financial plan together with the technology of compiling and the technology of developing indicators is not identical to the balance sheet.
Fundamentals of planning in an organization
Planning- this is the process of scientific development and implementation of a set of measures that determine the direction and pace of development of the organization, ensuring its compliance with the needs of the market and, on the basis of this, an increase in sales and profit maximization.
The main tasks resolved in the planning process are:
1. identification of development directions consumer demand for products manufactured by the enterprise;
2. increase in the volume of sales of the company's products, profits and profitability of production;
3. increasing the competitiveness of products by improving their quality, mastering new types of products and their prices;
4. cost reduction based on improved use of the enterprise's production resources;
5. Creation of new jobs to ensure social stability
Planning functions:
1. Statement before the team of the enterprise production tasks and determining ways to solve them
2. Formation of the needs of the enterprise, its divisions and services of labor, material, financial resources
3. Coordination of the activities of individual services and divisions of the enterprise, etc.
Types of planning:
1. Technical and economic planning provides for the development of a system of indicators for the development of technology and the economy of the organization. In the course of this planning, optimal production volumes are substantiated, the necessary production resources are selected and rational norms for their use are established, and final financial and economic performance indicators are determined.
2. Operational and production planning involves the subsequent detailing of the technical and economic plans of the organization. It provides for the establishment of current production targets for various structural units and the adjustment of planned targets in the production process.
3. operational planning represents a choice of means for solving problems that are defined by higher management.
4. tactical planning involves justifying the tasks and means necessary to achieve strategic goals (for example, gaining a leading position in the market, etc.). Tactical planning can cover the short and medium term.
5. Strategic planning focused on the development of the overall strategy of the organization and the establishment of its main goals, the management of strategically important factors of activity, the definition marketing strategy in the market of individual goods, identifying strategic prospects for financing capital investments, etc. .d. The duration of the planning period, which covers strategic planning, is usually 10-15 years
6. Regulatory Planning provides for a reasonable choice of means, tasks and goals of the organization and has no established time limits.
7. Market planning is based on the interaction of demand, supply and prices for goods and services produced.
8. indicative planning represents state regulation prices and tariffs, effective types and rates of taxes, minimum wages.
9. Centralized (directive) provides for the establishment by a higher management body of a subordinate organization of plans for indicators of natural volumes of production, nomenclature and delivery times
10. short term planning carried out for a period of 1 to 3 years. Its peculiarity lies in the fact that the indicators of the next year are adjusted quarterly, and the second and third years - every six months or annually. Short-term planning is the basis of the current one, in which indicators are set for the year, broken down by quarters. As part of this planning, a program for the movement of the product and all factors of production is developed, indicating specific dates and services responsible for a particular type of activity.
11. Medium term planning covers a period of 3 to 5 years and specifies the milestones defined by the long-term plan.
12. Long term planning (5-10 years) creates the foundations for business case development of a business entity for a certain period, and its result is the plans of the enterprise for various aspects of its activities (production, sales, costs, finance, etc.).
Planning principles.
To provide effective work organization and reduce the possibility of negative planning results, it should be based on the following principles:
The principle of necessity planning provides for the mandatory application of plans in the implementation of any kind labor activity. Compliance is in line with the requirements rational use limited resources in all organizations.
Continuity principle lies in the fact that in every organization the planning processes must be carried out constantly and the plans developed must continuously replace each other.
Unity principle involves the development of a general or consolidated plan for the socio-economic development of the organization (the plans of individual structural units must be linked to each other and to a single plan for socio-economic development).
Principle of Flexibility involves the possibility of adjusting already developed planned indicators.
The principle of accuracy is determined by the influence of various internal and external factors, therefore, plans should be specified and detailed to the extent that the conditions for the functioning of a business entity allow it.
Principle of optimality based on the choice the best option of several possible at all stages of planning.
Participation principle involves the active influence of personnel on the planning process.
The Principle of Efficiency requires the development of such a variant of the plan, which, given the existing limitations of the resources used, provides the greatest economic effect.
Planning Methods
The implementation of the principles of planning is carried out through the use of various methods:
ü balance,
ü normative,
ü system-analytical,
ü network,
ü program-target,
ü economic and mathematical, etc.
Graphic method can have various forms: network, linear (which is compiled in coordinate axes, where x is the time of work, y is the type of work), etc.
Program-target method developed during the development complex projects where many performers participate.
Economic and mathematical models are used in planning in various modifications: a model is compiled from a number of indicators and coefficients.