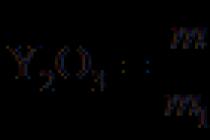Strategic planning forms a long-term plan (over 3-5 years, depending on the stability and uncertainty of the external environment) and determines the enterprise development strategy as the basic basis for a stable and sustainable long-term functioning of the company. In accordance with this, strategic planning identifies and takes into account economic patterns in the interaction of many internal and external economic processes, factors and phenomena.
The process of strategic planning in enterprises includes the following interrelated functions:
1) determination of the long-term perspective, the main ideals, goals and objectives of the development of the enterprise;
2) creation of conditions for reliable and stable long-term development of the enterprise;
3) formation of prerequisites for the effective operation of the enterprise based on the implementation of the strategy through a set of current and medium-term plans.
In accordance with this, in the process of strategic planning, justification is carried out:
The long-term goal of the development of the enterprise, its refinement, taking into account changes in the conditions of its activity;
Enterprise development strategy, which formulates the concept and main directions of development;
Plan for the long-term (strategic) development of the enterprise.
The strategic plan identifies the tasks that, in accordance with the concept, must be solved in order to achieve the goals at each stage of the enterprise development. It indicates the main parameters of development, enlarged quantitative and qualitative indicators. The strategic plan combines two aspects of planning - target and resource, that is, it links goals with the possibilities of achieving them, which implies internal consistency of its indicators and sections. Since resources can be limited at each stage of enterprise development, the strategic plan not only provides for the achievement of goals with their help, but also develops methods for expanding the types and increasing the volume of these resources.
Strategic planning allows you to turn the long-term, stable and competitive development of any enterprise into a controlled process of purposeful movement from the initial state of affairs (if it does not satisfy the management) to the intended goal. The trajectories of such a movement can be different, each of them corresponds to a certain development option, and the choice of the most effective option- one of the tasks of strategic planning.
The development of any plan is based on the definition of the initial and final states, on which attention is focused in the process of drawing up the plan.
In strategic planning, when determining the final state of the enterprise in the long term, two approaches are used: planning from the achieved level in accordance with the established patterns and trends in the development of the enterprise and planning from the final goals. In the first case, it is assumed that the current growth rates and the mechanism for managing the enterprise's activities do not change significantly during the planned period.
At the same time, resource opportunities, their expansion and qualitative improvement within the established rates and proportions are taken into account. An important task solved with this approach is to achieve the appropriate parameters of balance between resources (material, financial and labor) and the volume of the enterprise. Methodologically, this approach consists in the fact that, based on the expected resources, the growth rates of the volume of sales and production of goods and services, as well as the proportions of the development of the enterprise's divisions, are optimized. These procedures are completed by the development of measures to improve the efficiency of the use of the resource base. An approach that takes into account resource capabilities must be considered in conjunction with the target approach.
Planning from final goals involves:
Clarification of the purpose and objectives of the enterprise, taking into account forecast indicators related to the internal and external environment;
Substantiation of the desired (ideal) state of the enterprise in the long term, taking into account the external conditions of its functioning;
Analysis of the main conditions and features internal environment, analysis of the stages and patterns of development of the enterprise's activities in the future upon reaching desired level, assessment of the problems arising in this case, clarification of the degree of provision with the necessary material and labor resources of the target option for the development of the enterprise;
Clarification and interconnection of indicators of the strategic plan of the enterprise, taking into account resource constraints, possible changes in the behavior of competitors, as well as changes in the preferences of consumers of goods and services (by type of activity of the enterprise).
These two approaches involve the use of planning methods differentiated adequately by the procedures and the idea of a strategic plan.
In accordance with this, the following planning methods are used in the development of a strategic plan:
Extrapolations - planning from the achieved level based on trend models, multi-factor mathematical model;
Program-target - planning from the end goals based on a set of target standards and indicators that describe the ideal state of the enterprise in the future;
Simulation modeling - setting the maximum permissible parameters for the development of an enterprise, building a model of controlled and uncontrolled factors in order to study the degree of their influence on the development of an enterprise in the future taking into account factors of the internal and external environment);
Network planning is one of the forms of graphical reflection of the content of work and the duration of the implementation of strategic and long-term plans.
In the complex of methods, it is necessary to highlight the use of network planning, which contributes to the solution of the following tasks:
Synchronize the development of activities and divisions of the enterprise upon reaching the parameters of the strategic plan of the enterprise;
Reasonably choose the goals for the development of enterprise units, taking into account the planned final results, based on the breakdown of a set of goals and objectives to specific activities and determining their executors;
Set tasks for departments based on their relationship with the strategic plan of the enterprise;
Involve direct executors of the main stages of the planned work in the preparation of plans;
Predict the timeliness of the implementation of the main work focused on the critical path;
Determine the need for resources and coordinate their receipt and rational use;
Draw up network schedules for the performance of work, taking into account the formation of a single network schedule and schedules for the performance of work by departments.
Strategic planning helps the company to effectively use its existing advantages and create new potentials for successful activities in the future. The Strategic Planning Service acts as an internal advisor to managers, supplying the necessary information to make informed decisions.
The development of a strategic plan includes the following steps:
Formation of goals for the long-term development of the enterprise and their disaggregation to a set of tasks;
Justification of the concept of long-term development of the enterprise, ensuring the achievement of the goal;
Determination of long-term forecasts for the development of the enterprise with various options for changing the external environment and the possibility of changing the internal potential;
Substantiation of directions and indicators of the strategic plan for the development of the enterprise, including business plans for an investment or entrepreneurial project.
Let's take a closer look at each of these stages.
The 1st stage - the formation of the goals of the long-term development of the enterprise - is very important, since when substantiating the goal, the long-term results of the enterprise's activities are anticipated, the most general guidelines and mission for the development of the enterprise are formed.
Basic rules for justifying the goal:
Must be specific and understandable (measurable goal);
Must be achievable in the foreseeable future (realistic goal);
Can be broken down into a set of tasks that ensure the achievement of the goal, i.e., be able to build a "tree of goals" (comparability of goals and objectives);
It should formalize the mission (main functional purpose) of the enterprise in the long term (specificity of the goal).
The goal is formulated by top management and predetermines the concentration of efforts for its implementation. Goals are important because they:
They are the foundation for planning, management, organization, coordination and control;
Determine the prospects of doing business;
Serve as a guide in the formation of the image of the enterprise.
There are eight key spaces within which the enterprise defines goals:
1. Market position (share and competitiveness).
2. Innovative processes of production and sale of products and services.
3. Profitability of the enterprise.
4. Resource intensity of products and services and the possibility of additional attraction of resources.
5. Mobility management: organizational structures, forms and methods of interaction, motivation, etc.
6. Qualification composition of personnel and the possibility of its change.
7. Social Consequences changes and their impact on the level of development of the enterprise.
8. Ability to quantify the goal. The formulated goal is disaggregated through a set of tasks, then the tasks are detailed to measures that are concretized into target standards and indicators that determine the ideal future state of the enterprise.
2nd stage - substantiation of the concept of long-term development. The concept as a system of views on the prospects of the enterprise is based on future opportunities and risks, and also relies on the resource potential of the future (technology, equipment, personnel, etc.). Realization of the set goal involves taking into account three basic conditions in the justification of the concept:
Sustainability economic relations both within the enterprise and in the external environment;
The efficiency of the enterprise at all stages of its development;
Innovativeness of strategic directions.
These conditions for determining the concept of enterprise development are based on three main approaches:
Minimization of costs for the production and sale of products and services and the formation of competitive advantages on this basis is a very vulnerable strategy, especially for enterprises;
A high level of specialization and, on this basis, an increase in the quality characteristics of products and services - highlighting basic service or products with subsequent diversification of related and additional services providing the effect of "synergy" due to the complexity and mutual support of the system of production, promotion and sale of products and services;
Orientation to only one segment of the market with the study of its needs and specialization for their maximum satisfaction.
Based on this, four groups of basic conceptual strategies are distinguished:
Concentrated growth strategy - includes plans to strengthen market positions; search for new markets for existing goods and services; upgrading a product or service for sale in an existing market;
Growth strategy by increasing the number of structures (integrated growth), including horizontal mergers of enterprises of the same market segment, production or sales (creation of a network of enterprises of the same profile); vertical mergers along the chain of production-distribution-sales, carried out on different organizational and legal conditions; conglomerate mergers of enterprises from different sectors of the economy in order to diversify activities);
Diversified growth strategy through the production of new goods and services;
Downsizing strategy - includes a liquidation plan when the business is unable to maintain existing business, therefore, it sells all or part of its business.
In addition, enterprise strategies are divided into levels:
Corporate - involves the strengthening of positions in the market, the formation of corporate interests and goals, culture;
Business (business strategy) - is developed by types and areas of activity based on corporate strategy;
Functional - managerial, i.e. substantiation of approaches to ensure effective management for the implementation of business strategies;
Operational - includes the strategy of logistics, commerce, production, marketing, ensuring the implementation of the business business strategy.
3rd stage - development of forecasts for the long-term development of the enterprise (at least three options). Forecasting the development of an enterprise takes into account changes in the external environment, which implies:
Determining the potential of the market and its conjuncture;
Changing quality needs for products and services;
Growth of incomes of the population and directions of its use (as a growth factor);
Changing the internal environment:
Growth in production and sales of products and services;
Qualitative and quantitative change in resource potential;
Competitiveness and stability of the enterprise.
Forecasting can be carried out according to trend models, according to target standards, using economic-mathematical, simulation and network modeling.
The practical tasks of modeling are:
Analysis and forecasting of the economic situation within the enterprise and beyond;
Analysis and forecasting of sales markets and logistics;
Preparation of planned decisions regarding the subsequent activities of the enterprise.
Each of the methods gives its own version of the forecast, which are subsequently compared, analyzed, evaluated from the point of view of the possibility of developing the enterprise under different options, and the degree of controllability of the forecast indicators is determined. There should be at least three forecast options: minimum, maximum and most probable.
It is advisable to develop forecasts for periods exceeding the periods of a long-term (strategic) plan.
Stage 4 - the development of a long-term plan involves the evaluation and selection of the most effective and realistic forecast option, its concretization. In the long term, goals, strategies are expressed in planned indicators and tasks (in an enlarged form, sometimes in extreme values).
The range of strategic plans includes:
1. Company-wide consolidated strategic plan:
General corporate business portfolio, which defines the prospects for the types of business, areas of activity of the enterprise;
Strategies and key indicators development of the enterprise, taking into account the goals and forecast calculations;
Plan for strategic transformations (changing the types and objects of activity; creating a network of enterprises, etc.).
2. Plans by type of business:
Business portfolios by types of business and activities;
Key indicators of development of business types;
Plans for new products and technologies.
3. Strategic plans for the development of the functional areas of the enterprise:
Commercial activities;
production development;
Development of material and technical supply;
Development of complex functional areas of activity (marketing, personnel, etc.).
4. Plan for improving the organizational structure and legal form enterprises:
The plan for the reorganization of the enterprise as legal entity(taking into account changes in the tasks to be solved, volumes and structure of economic activity);
Reengineering (redesign) of the organizational structure of the enterprise:
5. Plans for improving the management system (management):
Arrangement and reserve of leading personnel;
staff development;
Improving the organizational structure of management;
Improving the personnel incentive system;
Development of information management system.
This indicative list strategic plans for each enterprise is specified taking into account the purpose and development strategy of the enterprise, as well as taking into account the completeness and reliability of information characterizing the future conditions of its activities.
Draft strategic plan submitted for discussion general meeting shareholders or other management bodies, where it is considered as a general direction in the activities of the enterprise. It is advisable to involve ordinary employees in the discussion to participate in the development of the most promising areas of activity. The strategic plan, approved by the supreme governing body, acquires a directive character and is implemented in stages, mainly through the inclusion strategic indicators into current plans and ensuring their implementation.
Current planning is a short-term strategy that implements a long-term (strategic) plan. The current plan is being developed by:
In the development of the strategic plan;
As a rule, at all levels of management;
For a shorter period of time compared to the strategic plan;
To determine the results of the implementation of the strategy in a shorter period of time.
In the system of plans (strategic and current), the implementation of the strategy means:
Determination of indicators of the current work plans of the enterprise, taking into account their strategic values;
Formation of procedures for the implementation of planned indicators with the definition of specific resources for them, justification of a set of tasks for each division of the enterprise;
Action planning and development calendar plans and charts;
Monitoring the implementation of strategic and current plans.
Thus, the implementation of strategic plans involves their interconnection with the current ones and the formation of a planning system at the enterprise with different time horizons.
The set of methods, or the methodology of strategic planning, is part of the methodology of strategic planning.
Under strategic planning method understand the specific method (technique) by which any planning problem is solved, the numerical values of indicators of forecasts, strategic programs and plans are calculated. Strategic planning methodology- this is a set of methods, techniques for developing, substantiating and analyzing forecasts, strategic programs and plans of all levels, as well as a system for calculating planned indicators and their interconnection.
Drawing up a plan involves, first of all, solving various problems that reveal differences between the actual and desired state of the planning object. Different planning methods are used depending on the nature of the problems.
There are the following planning problems:
- 1. Standard. Such problems are well structured, the connections are strictly defined, that is, a change in the cause leads to an unambiguous change in the result. An example of a problem is the calculation of the amount of materials for the production of goods on existing equipment with available human resources.
- 2. Structured. The correlation between the cause and the result in such problems is quite close, i.e., a change in the cause is reflected in the result, as a rule, with a certain interval “from and to” (an increase in labor productivity depending on the stock and power supply).
- 3. Weakly structured problems. In such problems, the relationship between cause and effect is weak, since other factors influence it. This is expressed in a change in the result in a very large range of values "from and to" (for example, the implementation of a demographic policy to increase the birth rate).
- 4. Unstructured. Connections in this case can only be established on the basis of logical analysis (an example is the development of science in the long term).
Differences in the degree of problem structuring cause differences in the applied methods of strategic planning. These include: expert (evaluative) methods, methods of social economic analysis, methods of direct engineering and economic calculations, balance method, economic and mathematical methods and models, methods system analysis and synthesis.
Expert (evaluative) methods also called heuristic, or methods of expert assessments. This is a complex of logical and mathematical procedures aimed at obtaining information from specialists, its analysis and generalization in order to prepare and develop rational decisions in planning and forecasting.
Methods of expert assessments can be divided into individual and collective. They differ in that in the first case, the individual opinion of all members is revealed. working group regardless of the others, and in the second, a collective decision is developed when working in a group.
1. Individual: methods of questionnaire survey, in-depth interviews and the Delphi method. The main advantage of individual methods is the possibility of deep study of the issue with each of the experts without pressure from their side. Their disadvantage is a subjective assessment.
Questionnaire- collecting opinions (orally or writing) in the form of answers to questions on a particular problem, followed by statistical processing of survey questionnaires by specialists.
In-Depth Interview- a method in which the questions asked do not require a simple answer "yes" or "no", but require a detailed answer. An in-depth interview is conducted according to a predetermined plan in the form of informal negotiations.
Delphi method(method of the Delphic oracle) involves an interactive polling procedure. At the same time, it is necessary to observe the absence of communication between experts and the anonymity of assessments. The procedure includes conducting several stages of questioning specialists with the provision of assessment results after each stage. The results of the survey are processed at each stage, common patterns and differences in the assessments are identified, and the transition to the next stage is carried out.
- 2. Collective. These are the methods: a) business games; b) meetings;
- V) brainstorming and d) courts. Their main advantage lies in the multilateral study of the problem. Their disadvantages: difficulties in organizing the procedure for obtaining an expert opinion and in forming a group opinion on individual judgments, as well as the danger of suppressing the authority of other members of the group.
Business game method based on simulation of functioning social system management when performing operations aimed at achieving the goal. Unlike other collective methods, business games involve the active work of an expert group, each member of which is assigned a certain duty in accordance with pre-compiled rules and a program.
Meeting method(commissions, round table) involves holding a meeting or discussion to develop a common opinion or decision on the problem. During the meeting, members of the working group can not only express their opinion, but also criticize the opinions of others.
brainstorming method(brainstorming) is based on the collective generation of ideas, i.e., expressing opinions free from criticism about solving a problem, followed by selecting the most valuable ones and developing an appropriate solution.
court method is a kind of meeting method and is implemented by analogy with the trial. Chosen solutions act as defendants, decision makers act as judges, members of the expert group act as prosecutors and defense lawyers. When conducting such a "trial", certain decisions are rejected or adopted.
It is advisable to use expert methods in solving predominantly unstructured and semi-structured problems.
Method of socio-economic analysis is a comprehensive study of socio-economic reality, internal connections between phenomena and their mutual dependence in order to determine progressive development trends and production opportunities, as well as social relations.
The analysis uses such working methods as comparison, selective study of the work of large objects of strategic planning, grouping, chain statements, calculation of balance differences, indices, calculation of regression and correlation coefficients, principal component method, etc. Methods of socio-economic analysis are used in solving problems for all classes.
Methods of direct engineering and economic calculations are used in the design of production growth at enterprises - calculations of market needs for a given type of product and the possibilities of its production. At industrial enterprises, such calculations cover: improving the use of production capacities, raw materials, materials, fuel, energy, labor resources (personnel); reducing the cost of production, etc.
A special place among the engineering and economic calculations used in strategic planning is occupied by calculations economic efficiency production, investments, profitability of securities, used credit resources, currency conversion and accrual of interest (simple and compound), etc.
Engineering and economic calculations are often based on a system of norms. It uses:
- 1. Norms for the use of fixed production assets.
- 2. Terms of use working capital(raw materials, materials).
- 3. Norms of labor costs and labor intensity of products (rates of production, norms for the use of working time).
- 4. Norms of organization production processes(time spent on repairing equipment, the formation of stocks of raw materials, materials, etc.).
- 5. Product quality standards (the content of useful substances in the product, indicators of reliability and durability, etc.).
- 6. Specific investment. Rates of return on capital expenditures, etc.
- 7. Norms of production and circulation costs, profitability rates.
Methods of engineering and economic calculations are widely used in solving standard and structured problems.
Under balance method strategic planning refers to a set of techniques used to ensure the linkage and harmonization of interdependent indicators. The purpose of these techniques is to achieve a balance (balance) between indicators.
The balance method is an important tool for analyzing and forecasting the development of the national economy. With its help, you can identify the direction of movement of material and financial flows in the country, determine the material and cost proportions in the economy, model their quantitative parameters for the future, get an idea of the state of equilibrium of the socio-economic system, calculate the necessary increase in various factors of production in order to create material basis to meet the needs of the market in material wealth and services. The balances used by the firm make it possible to judge its available production capacities, their dynamics in the forecast period, the degree of use; plan the production of the company's products in marketing monitoring; get a clear idea of the resources of the fund of operating time of equipment and production capacities and its (equipment) use in production, as well as of the fund of working hours of personnel, its structure and directions for saving; prepare the planned budget of the company; solve other problems.
It is a mistake to confuse the balance method with the development of only one balance. The system of balances covers all sections of programs and plans. When compiling them, both balance and other methods of strategic planning are used. The balance method is widely used in solving problems of all types of structuredness.
Economic and mathematical methods are specific techniques for analyzing social economic systems, equilibrium of the economy, forecasting economic growth. Of great importance for the practice of strategic planning are economic and mathematical models. The most important economic and mathematical models used in strategic planning are: the system of national accounts, the balance sheet "Costs - output", the intersectoral balance of production and distribution of products and services, the balance of financial resources and costs, matrix models of the technical and industrial financial plan, network models, etc. .
Economic-mathematical methods and models are applicable for solving standard and structured problems. With the help of linear programming, the problems of production planning are successfully solved: 1) drawing up an optimal program for the production of products for given labor and material resources; 2) optimal loading of equipment.
A special group is made up of the problems of rational cutting of industrial materials and the problems of formulating mixtures that are used in many industries (metallurgical, oil refining, chemical, food, etc.).
Great opportunities are opened up by the use of linear programming in planning agricultural production - for solving problems of distributing sown areas between different crops, rational planning of crop rotations, calculating the optimal combination of agricultural production sectors, determining the best herd structure, the most effective livestock feeding rations, etc.
The vast majority of dependencies in the economy are non-linear. Therefore, other types of programming have also been developed: non-linear, dynamic, stochastic.
Specificity method of system analysis and synthesis consists in the dismemberment, decomposition of economic systems and the processes occurring in them into component parts and the identification on this basis of the leading links, bottlenecks, key problems of long-term development.
The solution of complex problems associated with the development of strategic plans for the development of production systems at various levels is provided by a promising integrated analysis.
Increasing the complexity of the analysis is associated with its direction not only on the functioning of production systems, but also on the achieved level of their structural development.
Based on the analysis of the state of the organization (considered as a result and as an activity aimed at improving the efficiency of production systems), the initial positions of the new plan are determined.
A comprehensive analysis is inseparable from the synthesis of the problems of long-term development. Analysis and synthesis are a single methodological whole. The method of system analysis and synthesis can be used in solving all problems of strategic planning.
Strategic planning toolkit depends on the object and the planning horizon. The following strategic planning tools are available:
- 1. Mind map method.
- 2. Porter's five forces model. Structural logic method.
- 3. Strategic analysis:
- 1) analysis of the external environment of the organization;
- - SWOT-analysis;
- 2) analysis of the internal environment of the organization;
- - SNW analysis;
- - portfolio analysis;
- - scenario planning, etc.
Mind map method(mind map). This technique, developed by T. Buzan, is a special case of a goal tree. The technique is interesting primarily because it allows you to structure the thought process and stimulate step-by-step thinking. This method is almost universal, it can be used in most different situations: to clarify any issue, collect information, make a decision. It is best used when new ideas need to be structured, at the planning stage. The basis of the methodology is the process of radiant thinking, when the main problem is taken and from it, as from a tree trunk, various ideas related to it branch off.
Porter's Five Forces Model is a methodology for analyzing industries and developing a business strategy, developed by M. Porter at Harvard Business School in 1979. The methodology identifies five forces that determine the level of competition, and, consequently, the attractiveness of doing business in a particular industry. The attractiveness of the industry in this context is expressed in its profitability. Accordingly, an unattractive industry is one in which the combination of forces reduces profitability. The most unattractive is the industry, the market situation in which is close to " perfect competition". Porter's 5 forces analysis includes three forces of horizontal competition - the threat of substitute products, the threat of new players, the level of competition - and two forces of vertical competition - the bargaining power of suppliers and the bargaining power of consumers.
Strategic analysis. Analysis of the external environment of the organization should be carried out constantly, as its result is to obtain information on the basis of which estimates of the current position of the company are given. This type of analysis gives the organization time to: a) anticipate opportunities; b) drawing up a contingency plan; c) development of an early warning system in case of possible threats; d) developing strategies that can turn past threats into profitable opportunities. There are seven areas of threats and opportunities that an organization typically faces. These are economics, politics, market, technology, legal regulation, international position and social behavior.
The state of the economy can influence the goals of the organization. Some factors (including those identified above as threats and opportunities) in the economic environment must be constantly diagnosed and assessed.
SWOT analysis. For analysis environment organizations use the so-called SWOT analysis, i.e. an analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of the organization, as well as the opportunities and threats emanating from the environment. The same matrices are made for competitors. First, a general SWOT analysis matrix is compiled (Table I). Then the so-called auxiliary matrices are compiled. The information presented in the auxiliary matrices is transferred to the main one and used to summarize the results of the analysis. There are two such matrices - the matrix of opportunities and the matrix of threats.
Table 1
SWOT matrix
In the process of performing a SWOT analysis, it is also recommended to draw up an environment profile, i.e. a table in which environmental factors that have or may have a significant impact on the organization should be noted. Then, for each factor, the degree of its importance for the industry, the degree of influence on the organization, the direction of this influence are determined, and the total degree of impact for each factor and in general is calculated.
Analysis of the internal environment of the organization reveals those opportunities and the potential that a company can count on in a competitive struggle in the process of achieving its goals. It also allows you to better understand the goals of the organization, to formulate the mission more precisely, that is, to determine the meaning of the company's activities and its direction. At the same time, it must be remembered that the organization not only produces products for consumers, but also employs its employees, provides them with the opportunity to participate in profits, provides social guarantees, etc.
Analysis of the internal environment of the company is carried out in the following areas:
- - personnel, their potential, qualifications, interests, etc.;
- - organization of management;
- - production, its organizational, operational and technical and technological characteristics, as well as research and development;
- - finance;
- - marketing;
- - organizational culture.
SNW analysis - this is an analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of the organization, the internal environment is evaluated by three values: Strength (strength), Neutral (neutral side) and Weakness (weak side). As practice has shown, in a situation of strategic analysis of the internal environment of an organization, it is best to fix the average market state for this particular situation as a neutral position. Typically, SNW analysis is used to study the internal environment of an organization in more depth after conducting a SWOT analysis.
Portfolio analysis - is a tool by which the management of the enterprise identifies and evaluates its economic activity for the purpose of investing in the most profitable or promising areas and stopping investments in inefficient projects. At the same time, the relative attractiveness of the markets and the competitiveness of the enterprise in each of these markets are evaluated. It is assumed that the company's portfolio should be balanced, that is, the right combination of products that need capital for further development should be ensured with business units that have some excess capital. The purpose of portfolio analysis is to harmonize business strategies and allocate financial resources between business units of the company. Portfolio analysis in general is carried out according to the following scheme:
- 1. All activities of the organization (product range) are broken down into strategic business units and levels are selected to analyze the portfolio of businesses.
- 2. The relative competitiveness of individual business units and the development prospects of the respective markets are determined. Data collection and analysis in this case are carried out in the following areas:
- - the attractiveness of the industry;
- - competitive position;
- - Opportunities and threats to the firm;
- - resources and qualifications of personnel.
- 3. Portfolio matrices (strategic planning matrices) are built and analyzed and the desired portfolio of businesses and the desired competitive position are determined.
- 4. A strategy is developed for each business unit, and business units with similar strategies are combined into homogeneous groups.
Next, management evaluates the strategies of all divisions in terms of their alignment with the corporate strategy, commensurate the profit and resources required by each division, using portfolio analysis matrices. At the same time, business portfolio analysis matrices are not in themselves a decision-making tool. They only show the state of the business portfolio, which should be taken into account by management when making a decision.
Scenario planning - a part of strategic planning related to tools and technologies that allow you to manage the uncertainty of the future. The essence of the method is to study the external environment of the organization in order to identify predetermined elements (predetermined elements) and key uncertainties (key uncertainties) and combine them to formulate alternative scenarios for the future.
Predetermined elements are often demographic factors (for example, the number of adolescents aged 10 to 15 in 10 years is predetermined, since many of them have already been born), as well as political, technological and geographical factors.
Any elements of the external environment that are important for a given organization (for example, the level of the government deficit or the size of the market) can act as key uncertainties.
All alternative scenarios must combine the full set of predefined elements and the various outcomes of key uncertainties. Scenario planning considers all scenarios as equally possible in the future.
- An enterprise portfolio, or a corporate portfolio, is a set of relatively independent business units (strategic business units) owned by one owner.
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Similar Documents
Stages of the strategic planning process. The main features of strategic planning. Differences between strategic management and tactical and operational management. The concept and main types of goals. Strategy and goals. Tools for analyzing the external and internal environment.
presentation, added 01/05/2016
Concepts of strategic management, evolution of its theories, characteristic features and principles. Stages of strategic management. The concept of strategic planning, its functions and structure. Advantages and disadvantages of strategic planning.
term paper, added 10/11/2010
The concept and main objects of study of strategic management, its purpose is the stages of implementation in the enterprise. Features and principles of the classical model of strategic analysis and planning ADL / LC. Maturity stages of the industry and opportunities to work in it.
test, added 11/15/2009
Concept, essence, types, tasks, functions, principles, objects and methods of planning. The concept of strategic planning, goals and stages, as well as features of its application in various fields activities of the enterprise, proposals for its improvement.
term paper, added 03/05/2010
Essence, principles and methods of planning. Brief description, analysis of technical and economic indicators and strategic planning of OAO "Kommash". Choice of the priority direction of strategic planning based on the method of analysis of hierarchies.
term paper, added 03/01/2012
Improvement of the strategic planning system. Models and methods of strategic management and project management. Classification and ranking of problems in the project of improving the strategic planning system of "Technical equipment" LLC.
term paper, added 01/14/2015
The subject of strategic planning; school of strategic management. The formation of strategic management as an independent research area and management practice. Definitions, main stages of the process of strategic management.
term paper, added 01/16/2010
Basic approaches in strategic planning and forecasting. Organizational and economic characteristics of Yandex. Problems in the company's strategic management system. Improving the efficiency of strategic planning at the enterprise.
thesis, added 01/31/2018
In the strategic planning of the enterprise, as domestic and foreign experience shows, a wide variety of methods and models are used.
The methodology of strategic planning is a set of methods, techniques for developing, substantiating and analyzing forecasts, strategic programs and plans of all levels and time horizons, a system for calculating planned indicators, and their mutual linking. The strategic planning method is understood as a specific method, a technique by which any planning problem is solved, numerical values of indicators of forecasts, strategic programs and plans are calculated.
There are the following methods of strategic planning:
- - settlement and analytical, which include balance sheet, regulatory, engineering and economic, etc.;
- - graph-analytical, for example, extrapolation (trend), network, regression-analytical, methods of correlation trends, etc.;
- - economic and mathematical, including methods of linear, non-linear and dynamic programming, game theory models and theory queuing and etc.;
- - heuristic, which include methods of peer review (individual, collective, systematic, mass, etc.), scenario method, etc.
The balance method is a set of techniques, ways to identify and ensure proportions and relationships through the development of interrelated balances. This method is designed to link the volume and structure of social needs with material, labor and financial resources and coordination of all sections and indicators of the plan for both economic and social development. The application of this method makes it possible to identify and link natural-material and cost proportions in the development of the economy.
Balances developed in the planning process can be classified according to the following criteria:
- - on the basis of the planning stage (forecast, planned and reporting balances)
- - by validity period (current, prospective)
- - on the basis of purpose (material, labor, financial)
The balances used at the level of the company make it possible to judge its available production capacities, their dynamics in the forecast period, the degree of use, to plan the production of the company's products in marketing monitoring; get a clear idea of the resources of the equipment and production facilities operating time fund and its use in production, as well as the staff working time fund, its structure and areas of savings; prepare the planned budget of the company, solve other tasks facing it.
It is a mistake to confuse the balance method with the development of only one balance. The system of balances covers all sections of programs and plans; both the balance method and all other methods of strategic planning are used in their preparation.
The normative method is based on the definition and application of norms and standards. Norms and standards for a certain set of indicators are interrelated. A norm is a scientifically based measure necessary costs resources for the manufacture of a unit of output of a given quality. The standard is a scientifically justified ratio in proportions, the simplest quantitative expression of socio-economic ties, which covers two quantities: the consumption of materials per unit of production and the consumed products per capita. All standards used in planning must be progressive and realistic, taking into account the achievements scientific and technological progress, organizational, technological and socio-economic limitations of a particular period.
All technical, economic and balance calculations are based on norms and standards. An indispensable condition for the progressiveness of the norms is their revision, in connection with the changing conditions of production. In planning the activities of an enterprise, the standards of the following indicators are usually used: stock standards and unit costs raw materials, materials, fuel, electricity, as well as norms for specific capital investments, financial costs per unit of output, depreciation rates, transport tariffs, rental rates, interest rates on loans, natural loss material resources.
Expert (evaluative) or heuristic methods. They are based on the use of indirect and incomplete information, the experience of specialist experts, and intuition. Expert assessments are defined as the collective opinion of a group of specialist experts. The scope of expert assessments is determined depending on the limitations associated with the difficulties or impossibility of collecting information in the usual way (reporting, continuous or sample surveys, etc.). Special methods have been developed for obtaining expert assessments and checking their reliability. The most famous are the Delphi method, the brainstorming method, synectics and others. A simplified version of expert assessments is market meetings. The quality of expert assessments is largely determined by the professional experience of experts.
With the help of linear programming, the problems of production planning are successfully solved: drawing up - an optimal program for the production of products for given labor and material resources, optimal loading of equipment. A special group is made up of the tasks of rational cutting of industrial materials and the tasks of preparing mixtures that are used in many industries (metallurgical, oil refining, chemical, food, etc.).
The vast majority of dependencies in the economy are non-linear. Therefore, other types of programming have also been developed: non-linear (numerical, parametric), dynamic, stochastic.
The group of economic and mathematical methods of planning differs in that it provides the possibility of optimizing planning decisions. Economic and mathematical methods in planning make it possible to evaluate and take into account the effect of certain actions of employees to achieve the goal, including:
- - it is possible to make calculations for individual labor operations of employees, taking into account labor productivity and equipment productivity;
- - it is possible to extrapolate trends in labor efficiency in the past for the coming period.
The graphic-analytical method makes it possible to depict the results of economic analysis by graphic means. With the help of graphs, a quantitative relationship is revealed between related indicators, for example, between the rate of change in capital productivity, capital-labor ratio and labor productivity. Network graphs are a kind of graphic-analytical methods. With their help, parallel execution of work in space and time on complex objects is simulated, for example, the reconstruction of a workshop, the development and mastering of new equipment, etc.
The break method is widely used. The main task This method is to determine the discrepancy or gap between the goals of the enterprise and its capabilities. If such a gap exists, then it is advisable to establish how to fill it.
The break method can be used to:
- - clarification of the real capabilities of the enterprise in terms of situational analysis the current and expected future state of the environment;
- - determination of specific indicators of the strategic plan corresponding to the main goals of the enterprise;
- - establishing the deviation of the possibilities of the real situation of the enterprise from the indicators of the strategic plan;
- - development of special programs to fill the gap (growth in productivity, improvement in the organization of production, etc.).
Also in strategic planning methods of strategic analysis are widely used. At the heart of the development of the strategy we lay the mandatory method of strategic analysis - it is the strategic analysis that precedes the formation of the strategic plan.
Strategic analysis is the most important element of the procedure for the formation of a strategic plan for the development of an enterprise. Strategic analysis is “the stage of pre-planned research, at which the factors of the external, business environment and the resource potential of the enterprise are systematically analyzed to identify conditions for its further development. successful development in a market economy".
Thanks to strategic analysis, the necessary information base is created that allows the process of goal-setting and selection of alternatives to be carried out in the most efficient way.
Let's consider the main directions of the analysis of external and internal factors influencing the position of the company.
Analysis of the external environment (external analysis) is a set of actions designed to study the macro-environment and the competitive environment. The strength of the impact and the degree of significance of specific factors of the macro-environment are not the same and depend on the geographical location of the enterprise, the nature of its activities, on the current legislative acts and regulations of the local, national and international levels, the degree of availability of qualified labor force, as well as the size of the enterprise.
In order to facilitate the identification of the external environment of the organization and its impact on the activities of enterprises, the external environment can be divided into economic, technological, social, political and ethical.
The economic external environment includes the labor market, price levels, productivity, highly skilled entrepreneurs and managers, financial and tax policies of the state, buyers.
The technological environment implies the following. Technology is one of the most important factors not only in designing products and services, improving the way they are developed, but also in creating organizational structures. In this regard, any enterprise striving for success in the market must be aware of the latest advances in technology.
The social external environment is made up of the views, expectations, desires, degree of intelligence and education, beliefs and customs of people in a given group of society. In each state, views, beliefs and values, expectations, level of education, etc. do not match, so these issues should be taken into account without fail. The social environment is closely related to the ethical environment, which includes sets of generally accepted, applied in practice standards of personal behavior.
The political external environment is a complex consisting of laws, regulations, activities of government agencies that affects all types of organizations. It includes the Laws of the Republic of Belarus, regulating the activities of the enterprise; Resolutions of the Council of Ministers, departmental resolutions; government measures (privatization, social protection and so on). All of the above defines the “rules of the game” that every organization in the Republic of Belarus must follow.
After the analysis of the external environment, an analysis of the internal factors inherent in the organization is carried out. The internal environment includes goals, structure, tasks, technology, people.
One of the most common methods for analyzing and evaluating internal and external factors that affect the position of an organization is a SWOT analysis. In addition to it, PEST analysis is also used, which is the construction of economic, sociopolitical and technological forecasts to determine the long-term capabilities of an enterprise in the face of predictable environmental disturbances. PEST analysis got its name from the capital letters of the four directions of external factors that affect the organization: political, economic, social and technological factors. The PEST analysis is a table presented in Appendix A.
"Assessing the strengths and weaknesses of an organization and its external opportunities and threats is commonly referred to as a SWOT analysis".
The SWOT method is aimed at analyzing the external and internal environment and is designed to identify lines of communication between the strengths and weaknesses inherent in the organization, as well as between the threats and opportunities of the organization. The method is based on the initial fixation (in the form of a list) of strengths and weaknesses, threats and opportunities, and then - in identifying the chains of communication between them. The method got its name from the first letters of English words: S (Strengths) - strengths of the company; W (weaknesses) - weaknesses of the company; O (opportunities) - chances, opportunities available in the external environment; T (threats) - threats lurking in the external environment. General principle The analysis says: “when developing a strategy, it is necessary to ensure that the internal capabilities of the organization correspond to the external situation”, since the development strategy of the enterprise should be aimed at the most efficient use of the resources available to the organization, the use of market opportunities and the avoidance of threats.
Thus, by analyzing the internal environment, the organization analyzes and identifies strengths and weaknesses. As a rule, to strengths organizations include: a reputation for a solid, reliable, financially stable production structure, flexibility to respond to changes, concentration of efforts on the production of promising products, a diversified nature of production, versatility, dispersal of functioning capital, the presence of a product portfolio (such “reserve” goods for the production of which the organization can apply in case of a drop in interest in the products produced in this moment goods), high quality goods, high level normative profit, the availability of flexible technological lines used, the presence of an external market for the sale of products, the availability of highly qualified managerial and executive personnel, and others. The weaknesses of the organization are: poor product quality, high costs, fragile market positions, lack of an effective strategy, insufficient professionalism of employees, limited resources and access to them, lack of equity, lack of strong partnerships and so on.
Analyzing the external environment, the organization identifies the following opportunities for itself: high purchasing power of the population, insufficient degree of customer satisfaction, identification of promising markets, access to sources borrowed money, the presence of a highly skilled labor market and others . In addition, the organization identifies the following threats to its existence (dangers that lie in wait for the company): strong competitors, the impossibility of a radical improvement in the quality of goods, the unpredictability of the actions of powerful public institutions, the crisis situation in the economy, inflation with little predictable rates, and so on.
The meaning and purpose of analysis based on the SWOT method is to find a stable competitive advantage organization (which is already inherent in it or desirable for consolidation). Such an advantage, from the manager's point of view, is that feature of the organization he leads, which can be managed and which can be used in such a way as to get more profit than competitors.
Based on the identified strengths and weaknesses, as well as opportunities and threats, a SWOT matrix is compiled, which is shown in Figure 1.1.
Figure 1.1 - Final SWOT Analysis Matrix
A feature of the analysis of external factors is the fact that opportunities can quite easily turn into threats: if an organization does not take advantage of any opportunity, then a competitor will take advantage of it. To carry out a deeper analysis of external opportunities and threats, the construction of auxiliary matrix forms is used - the matrix of opportunities and the matrix of threats.
Table 1.1 presents the most common opportunities and threats identified by Thompson A.A. in Strategic Management.
Table 1.1 - Opportunities and threats to the organization in a competitive environment
|
External capabilities of the organization |
External threats to the organization |
|
Serving new customer groups or entering new geographic markets or product segments |
The threat of new competitors entering the market |
|
Expansion of the range to serve the new needs of customers |
Growth in sales of substitute products |
|
Using the organization's own technology and know-how to produce new products or start a new business |
Increasing competition from new Internet organizations implementing e-commerce strategies |
|
Use of Internet and e-commerce technologies to radically reduce costs and further increase sales. |
Increasing competition among incumbent organizations leading to lower profits |
|
Vertical integration |
Technological changes or innovations that lead to a drop in demand for the same products |
|
Reducing trade barriers in attractive overseas markets |
Market slowdown |
|
New opportunities to gain market share of competitors |
Adverse changes in foreign exchange rates or trade policies in other countries |
|
Opportunity for rapid growth due to sharp growth demand in one or more market segments |
Introduction of new regulatory requirements that increase the costs of the organization |
|
Acquisition of competing or advanced knowledge and technology organizations |
Growing pressure from consumer and supplier organizations |
|
Opportunity to exploit new technologies |
Decreased demand for the organization's products due to changing needs and tastes of customers |
|
Opportunity to spread the brand of the organization to new geographic markets, strengthening the company's reputation |
Adverse demographic changes causing a reduction in demand for the organization's products |
First of all, the impact of opportunities on the organization is determined, and then the probability of realizing the opportunities is determined. Thus, it can be said that the organization determines the risk of the realization of opportunities.
In addition to the matrix methods of SWOT analysis, under conditions of uncertainty and the risk associated with it, decisions are made using various rules based on the probability of certain environmental conditions occurring and on the principle of mathematical expectation (Bayes principle). This principle requires that the action alternative be chosen that shows the highest value of expectation related to the extent to which the goal is achieved. At the same time, the mathematical expectation is understood as the sum of all degrees of achieving the goal, aimed at the probability of their implementation. Such decision-making methods under risk conditions are based on mathematical expectation, such as the minimax rule, the maximax rule, the Gurvich rule, the Savage-Niehans rule, the Laplace rule, and so on.
Thus, the most important preliminary stage strategy development is a strategic analysis that provides the initial information for making an informed decision on the optimal strategy for the development of an enterprise using modern applied strategy development techniques.
The economy is changing so fast that only strategic planning at the enterprise can help build a formal forecast of potential risks and opportunities. It is this method that helps the management or the owner to set long-term goals, create a plan for their implementation, minimizing risks and including the tasks of the company's divisions.
What are the features of tactical, operational and strategic planning in the enterprise
Those who are seriously involved in business usually put some kind of strategic goal. It, in turn, consists of several subgoals, which include tasks. That is, the process of fulfilling the set plans in the company is carried out from setting the largest and most significant goal to the implementation of small everyday tasks.
To optimize the planning process, it is divided into several types:
- tactical;
- operational;
- strategic.
Strategic planning
The most common type of planning is strategic. It should not be compared with the long term. Developing a company strategy is setting a more global goal. For example, L. Mittal, adhering to the strategy of saving to the maximum, became one of the richest people in the world. The strategy was to reduce costs to the limit on the main parameters of activity (personnel, raw materials, resources, etc.).
It is the manager or owner who is engaged in strategic planning.
tactical planning
IN Soviet time medium-term plans were established at the enterprises. Tactical planning is somewhat similar to this practice, but there are significant differences. At the same time, although the plans are limited in time, this is the time allocated for the implementation of the goals set. Tactical planning is a consequence of strategic planning. L. Mittal set such tactical goals at his enterprise as to optimize the staff, acquire coal deposits to produce their own raw materials, automate business processes and production processes.
Typically, the development tactical plan handled by department heads. If we are talking O small company, this task is included in the range of duties directly to the head of the entire organization.
operational planning
Operational plans are created on the basis of a short time period. Based on the circumstances, it can be planning the actions of one day, several days, a week. However, it will be better for the staff and you if a list of tasks is defined for each day, which easily changes depending on the situation. operational planning allows you to record the results and exercise control.
In some areas of activity, it is more convenient for enterprises to form different types of plans of all three types. Eg, financial planning, marketing or investment is carried out at the operational and tactical levels.
Different planning methods will allow you to organize work as efficiently as possible, select the right performers, and monitor the implementation of tasks.
How to draw up a strategic development plan
Many managers mistakenly believe that long-term strategic plans can be successfully replaced by sales plans. The development of companies headed by such leaders is hampered by top management's misunderstanding of the business goals, and therefore, the failure to use funds to achieve these goals.
In order for an enterprise not to get bogged down in a routine, it needs a strategic plan. Download example algorithm for the development and implementation of a strategic plan you can in the article electronic journal"CEO".
The main goals of strategic planning in the enterprise
Determination with strategic plans in the firm is also to form and communicate to the designated official such a measure of responsibility and authority that will allow him to fully manage the company during the entire period of his tenure. Strategic planning has the following objectives:
1. Creating and displaying an enterprise model in perspective regarding its field of activity, mission, development.
2. Setting goals general manager or manager for the entire period of his activity in accordance with the concluded contract.
When deploying the goals and objectives of the company's strategic plan, it is worth remembering the possible problems that impede movement forward. These problems must be identified and ways to solve them must be found. The most important tasks in this type of planning are the following:
- analysis of the growth process of the company's activities from the very beginning, as well as compliance with the planned strategic plans;
- assessment of the external and internal development of the company today;
- adjustment of the mission and vision of the company in its field of activity;
- setting common development goals;
- analysis of the main problem in enterprise management and development of a method of elimination;
- development of the concept of the enterprise;
- search for opportunities and ways to implement them to transfer the company to the active sphere of TO-BE;
- creation and distribution of initiative actions for the implementation of the strategic plan;
- refinement of certain nuances and provisions in the areas of the company's activities that depend on strategic planning: investments, finance, marketing, etc.
Strategic planning of the enterprise: advantages and disadvantages
Strategic planning in an enterprise is the formulation and formulation of strategically important tasks on the basis of forecasts of the company's activities in the face of changing external factors, as well as the identification of the most important areas of development and the selection of ways to complete tasks.
This type of planning is based on the immediate application of innovative ideas, as well as proactive actions to minimize risks and accelerate the development of the company.
The strategic method of planning differs from the tactical one in the following ways:
- The forecast of future processes and results is made based on a strategic analysis of the enterprise's activities, risks, opportunities to change the situation in its favor, etc., and not by observing existing trends.
- This is a more time-consuming and resource-consuming method, but it gives more accurate and complete information in the end.
The process of carrying out this planning in the company is carried out using the following actions:
- Determination of the most important long-term tasks and goals.
- Organization of strategically significant departments in the company.
- Setting goals when conducting research activities in the marketing field.
- Analysis current situation and determining the vector of development in the economic sphere.
- Planning for increasing production, developing a marketing strategy for the company as a whole.
- Definition of a set of tools to achieve the goals.
- Carrying out control measures with adjustment of the strategy, if necessary.
Strategic planning has its own characteristics:
- it is characterized by a constant analysis of external activities to identify potential risks, problems that may affect the work, as well as trends, development alternatives, etc.;
- the economic activity of the enterprise easily adapts to changing circumstances;
- all the time there is a process of optimization of tasks;
- it is focused on the most important formed goals and stages of development of the company;
- planning in the company is optimally distributed from higher to lower positions;
- there is a constant correlation of tactical and strategic plans.
The advantages of this type of planning are as follows:
- Plans are based on reasonable probabilities and event forecasts.
- The company's management has the ability to set long-term goals.
- It is possible to make decisions based on the set strategic plans.
- At the same time, the risk in making one or another decision is reduced.
- Unites the set goals and their performers.
However, in addition to the benefits, there are a number of shortcomings.
Strategic planning does not, by virtue of its nature, give a clear description of the future. The result of this type of planning will be the creation of a model of potential behavior and the desired market position of the company in the future, but it remains unclear whether the company will remain afloat until then.
Strategic planning does not have a clear algorithm for drawing up and implementing a plan. Goals are set and achieved through the following actions:
- the company constantly monitors external activity;
- Goal setting staff have O a greater degree of professionalism and creative thinking;
- the company is actively innovating;
- All employees are involved in the implementation of the goals.
Strategic planning needs to invest a lot of resources, financial and time. Traditional planning does not require such efforts.
The consequences of non-fulfillment of strategic plans are usually much more serious than with conventional planning.
Planning alone will not produce results. Mechanisms for the implementation of the tasks set should be prepared.
The process of strategic planning in the enterprise is necessary to identify potential development options in the economic and social spheres the state as a whole. The company and government agencies should cooperate on the exchange of information on a voluntary basis.
What is the system of strategic planning in the enterprise
The concept of strategic planning today consists of the following points "decision - change - control". That is, it can be said that this species planning is based on three elements: deciding to do something, making certain changes after that, and monitoring the result. Each element represents an organized process.
Strategic planning is provided thanks to various subsystems of the enterprise: personnel, methodological, information and analytical. In other words, strategic planning can be represented as a set of subsystems that, when interacting, make it possible to achieve the set goals.
Subsystem for making strategic decisions
This element consists of methods for identifying company problems, analyzing effective ways to eliminate them, and making decisions that improve the organization's performance in the future. The subsystem includes a certain circle of people dealing with the identified problems, as well as a set of actions to analyze and find optimal solutions.
Change management subsystem
This element is a set of tools that allows you to develop plans and prepare projects for making the necessary changes to the structure or functional activity companies.
However, no plans will arise, and no programs will materialize on their own. This requires proactive people. It is these people who, together with managers, carry out the processes of strategizing, planning and business modeling.
- In strategizing, management works out a vision of the company's future place in the external economy, its activities and the means by which this position will be achieved.
- With the help of planning, alternative activities of the company in a given situation are discussed, fact-based assumptions are made about what awaits it in the future;
- In business modeling, models of a company's business behavior are built or modified based on long-term goals and a defined mission.
Strategic control subsystem
This element allows you to evaluate how the chosen strategy is being implemented, what changes are taking place within the company and in its external activities, how the goals set correspond to the developed plans, and also allows you to change the scenario for the development of the strategic plan if necessary.
They control the already completed part of previously planned programs and projects. The results should be summed up necessarily, to motivate leaders. The reports should include not only the results obtained, but also the strategic problems that have occurred or are likely to occur.
Information and analytical subsystem
With the help of this element, all direct participants in the strategic planning process are provided with the latest and most relevant information about events taking place inside and outside the company.
This subsystem is aimed at the full implementation of the set strategic tasks through the use of information sources and technologies.
That is, it does not just inform participants about everyday processes. In addition to daily formal reporting, it has tasks of a more global level.
Methodological subsystem
This subsystem is created to carry out the process of full information support of the enterprise during the development of a strategic plan. Information is obtained, analyzed and applied.
The methodological aspect of the company's activity consists of various methods of collecting and applying strategically important information in the process of management, setting strategic goals and monitoring their implementation. It also represents the tools for the implementation of the strategic objectives.
Organizational and personnel subsystem
The specified element represents an interaction organizational activities And personnel policy. With competent leadership, they organize special forms of interaction in the enterprise, which are used in the formulation and implementation of strategic plans.
Strategic planning management subsystem
This subsystem is used to carry out strategies and developed plans, the management process and control over it, as well as to find out how effective the ongoing processes are and whether there is a need to improve them.
The implementation of the activity of this subsystem occurs with the help of a specially organized autonomous unit. It is engaged in the implementation of the developed strategies, organizes the processes necessary for this, controls their implementation and results. All this is done with the support of the regulatory and methodological framework and on the basis of official documents.
Phased organization of strategic planning at the enterprise
The setting of strategic goals at the enterprise goes through the following stages:
Stage 1. Defining the mission of the enterprise
The process of identifying the mission involves an answer to the question why the enterprise exists, what is its role and place in the foreign economic sphere. The establishment of a strategic mission is significant for the implementation of the enterprise, both internal and external activities. In internal activities, a clear defined role helps staff feel unity, adhere to a culture of behavior.
In external activities, a clearly stated mission helps to establish a single image of the company in the market, only its own image, tells about the role of the enterprise in the economic and social spheres, as well as how it should be perceived by customers.
The mission statement consists of four elements:
- study of the history of the emergence and activities of the company;
- study of the field of activity;
- definition of the main goals;
- strategic aspirations of the company.
Stage 2. Formulation of goals and objectives of the functioning of the enterprise
The goals set do not just show the state that the company will reach after achieving them, they should also motivate employees to achieve them.
Therefore, goals must meet the following parameters:
- functionality - it is important to determine the functions of the set goals, since the manager must be able to adapt the goal and delegate it in a suitable form;
- selectivity - certain resources are always attracted to achieve the goal. But in case of their insufficiency, some specific goals should be allocated, on which it is necessary to concentrate, and for the achievement of which resources and efforts are used. That is, there is a kind of selectivity of goals;
- plurality - goals and objectives are set for all important areas in the activities of the enterprise;
- achievable, realistic – goals must be realistic. Employees must see that even though achieving the goal will require very hard work, in the end it is possible to achieve them, they lie within the possibilities. Setting unrealistic, unattainable goals demotivates, negatively affects the activities of employees and, as a result, the company as a whole;
- flexibility - it should be possible to change the goal or means of achieving it in the process of working on its implementation, if this is required by factors in the external or internal activities of the company;
- measurability - the goal should be measurable both in quantitative and qualitative terms, and not only at the time of setting, but also during work on its implementation;
- compatibility - all goals set in the company must be combined with each other. That is, long-term goals should meet the requirements of the company's mission, and goals for a shorter time period should stem from long-term goals;
- acceptability - at the time of goal setting, the interests of business owners, managers, company employees, partners, customers, etc. should be taken into account;
- Specific – The goal must be clearly stated. From it it should be clear in what key the company will act, what will happen when the goal is achieved, what the results will be, who is involved in its implementation and for how long.
The structure of goals in setting plans is revealed in two ways. The first is centralization. It represents the setting of goals by the management of the company. The second approach is decentralization. In this case, both management and employees at all levels are involved in goal setting.
The structure of goals is determined through the sequential passage of four stages:
- processing data on the external activities of the enterprise;
- setting clear global goals;
- alignment of goals in order of importance;
- setting specific goals for certain events.
Stage 3. Analysis and assessment of the external environment
When analyzing external activity and the environment, two components are taken into account: the macro environment and the micro environment:
When studying the macro environment, the following elements are analyzed:
- economic activity and its level of development;
- legal support;
- social and cultural spheres of life;
- the level of technical and scientific development;
- infrastructure level;
- the political state of society;
- the level of resources, the state of the environment.
The microenvironment of the company includes those firms that are in direct interaction with the company, that is, the enterprises that are constantly in contact with it are studied. These include:
- supplier firms;
- firms-consumers of manufactured products;
- intermediary organizations, including between the company under study and the state ( tax service, insurance companies, etc.);
- competing enterprises;
- various companies, commercial and not, that influence the formed public image of the company (for example, the media, the Consumer Rights Protection Society, etc.).
Stage 4. Analysis and evaluation of the internal structure of the enterprise
The study of the internal environment of the enterprise helps to understand what resources and potential opportunities are available for the company when moving towards its goals.
At the same time, analysis and study is carried out in the following areas:
- marketing;
- production;
- research and innovation;
- product distribution;
- resource opportunities.
Analytical work in this case involves the study of potential risks for the company's activities, as well as to determine the positive and negative features inherent in the company.
Studies of external and internal factors are carried out using the following matrix methods:
- Stickland and Thompson;
- Boston Advisory Group;
- SWOT analysis.
Stage 5. Development and analysis of strategic alternatives
Alternatives are worked out to determine ways to achieve the goals and objectives defined in the mission of the organization. The scenario will depend on the current position of the company.
At the same time, when working out a strategic alternative, you need to decide on three points:
- what activities are being liquidated;
- what activities are ongoing;
- in which business direction to start a new activity.
The strategy is developed on the basis of the following areas:
- reaching the level of a leader in the position of reducing production costs;
- permanent presence and development of activities in a certain area of the market;
- constant and high-quality production of the established assortment.
Stage 6. Choosing a strategy
In order to choose the most effective strategy, you need to rely on a clearly built and coordinated system of the company's activities. The choice of strategy should be clear and unambiguous. That is, one direction should be chosen, which is most suitable for the activities of this company. The stages at which the strategy is developed and the form in which it is communicated to the team have a generalized form and may change depending on the activities of the company.
Stage 7. Implementation of the strategy
This process is a very important link in the company's activities. After all, if successful, it will lead to the full implementation of the set strategic plans. Implementation is carried out using a set of actions: various programs and procedures are developed, from which plans are made for long and short periods. For a complete implementation, perform the following steps:
- familiarize employees of the company with the goals set so that they take part in the process of achieving them;
- the company always provides the resources necessary for successful implementation, prepares a plan for its implementation;
- in carrying out activities to achieve the set goals, managers at each level act in accordance with their authority and assigned tasks.
Stage 8. Evaluation of the chosen (implemented) strategy
The strategy is evaluated by the answer to the question - will the company be able to achieve the goals? If the developed strategy gives a positive answer to this question, then it is further analyzed according to the following parameters:
- how it correlates with the demands of external activity;
- how it correlates with the development potential of the company;
- how acceptable is the level of risk in this strategy.
The implementation of the strategy is evaluated. Feedback helps to control this process and make changes if necessary.
Methods of strategic planning in the enterprise
There is a classification of strategic planning methods in the enterprise, depending on the point in time they are applied.
Method 1. SWOT analysis
This type of analysis was created to determine the effectiveness / inefficiency of the company's activities in the foreign market. This is a kind of quintessence of a large analytical volume of information that allows you to understand and draw a conclusion about the next steps of the enterprise. Where should he move, how to develop, how to distribute resources. As a result of this analysis, a marketing strategy or intended behavior is created in order to test it.
The classic SWOT analysis method works by comparing the company with the most significant competitors. Based on the results obtained, the pros and cons of the enterprise, risks and possible successes are identified.
Method 2. "Tree of goals"
This method involves dividing the most global goal into smaller tasks, which are also divided into even smaller ones. The method is very important for the study of various management systems, because it is possible to represent the activities of the company in the form of a consistent implementation of the goals and objectives. The “tree of goals” method should be used, if only because it allows you to create a backbone, a stable framework that will remain unchanged under changing factors and circumstances.
Method 3. BCG matrix
This tool is also called Matrix BCG. It is used for strategic analysis of the company and its products in the economic and commercial field of activity. For analysis, data are taken on the volume of the market share of this enterprise and its growth. This method is quite simple, but at the same time very effective. Therefore, it is used not only in the economic, but also in the marketing and management spheres. Using the matrix, you can see the most successful and the most illiquid products or departments of the company. With its help, a marketer or manager will understand which product or department of the company should be allocated resources to develop, and which should be reduced or removed altogether.
Method 4. McKinsey Matrix
This kind of matrix as a planning tool was developed by a specially created McKinsey department. The order for the development was given by General Electric. The method is an improved BCG matrix. However, in comparison with the latter, it allows more floating funding for the strategy being pursued. For example, if on the basis of the analysis it is found that the company is weak as a competitor in the market, and the dynamics of market growth is not visible, then the financing of activities in this area can still be continued. Since there is a possibility of reducing the risk in this area or the occurrence of a synergy effect due to more effective work in other areas of activity.
Method 5. Ansoff matrix
This type of matrix is a method of analysis in strategic management, invented by Igor Ansoff. It is also called the product-market matrix.
This matrix can be represented as a coordinate field, where the company's products (existing and new) will be located on the horizontal axis, and the markets in which the company is present (already used and potential new ones) will be located on the vertical axis. The intersection of the axes gives four points.
The resulting matrix provides 4 options for marketing strategies to increase sales volume and / or to maintain existing volume: reaching new markets, developing in the current sales market, developing the range, expanding markets and product range.
The appropriate option is chosen based on how often the company can update the range and how saturated the market is at the moment. You can combine two or more options.
- Coverage of new markets - entering new markets with an existing product. At the same time, markets are assumed to be of different scales - international, regional, national;
- Development in the current sales market - holding various events from marketing sphere in order to strengthen the position of the product in the market;
- Development of the product range – offering new products to existing market in order to strengthen the position of the company;
- Diversification - expanding sales markets, attracting new markets, as well as expanding the range of products. However, one should be wary of dispersing efforts.
Scenario planning- not so long ago appeared a tool for setting strategic plans for the enterprise. With its help, alternative scenarios for the future of the company are developed. This method analyzes the external activities of the organization and combines both the known actual information and the assumed important points in the formation of the scenario. The developed alternatives necessarily combine predeterminations (which simply exist at the moment) and still undefined options for the development of important moments of activity. The enterprise strategy for strategic planning, developed on the basis of the scenario method, is characterized by flexibility and allows the company to successfully operate in different situations.
Method 6. SADT Method
Another method called Structured Analysis and Design Technique (abbreviated as SADT) is a set of actions that build a model of a specific object in a specific area. It is a method of analyzing and creating projections. With its help, the functional structure of the object is determined, in other words, the connection between the actions it performs and the analysis of the actions themselves.
Method 7. IDEF0
As a continuation of the previous one, the IDEF0 method was developed, the essence of which is to build a model and graph of the object's functionality. It describes business processes with an indication of the subordinate relationship of objects, and also formalizes them. The method explores the logical connection of works, but not their temporal sequence. The received information can be represented as a "black box" with holes for inputs and outputs, mechanisms inside, the outlines of which gradually appear up to the desired level. With the help of IDEF0, projects are organized to model various processes (for example, organizational, administrative, etc.).
- How to find inspiration for solving strategic problems
What are the problems associated with strategic planning of enterprise development
Today there is a sad tendency to reject the method of global strategic planning by a layer key managers. And it makes you wonder why. And was there even a period when strategic management was popular and used everywhere? It can be concluded that the "golden formula", which they tried to derive and apply, did not work, and this happened due to several factors. Here are some of the reasons that influenced the current businessmen's assessment of the current situation in the field of strategic planning.
- One of the main reasons is that the link "enterprise strategy - underlying projects and activities", even with the help of BSC, is very cumbersome. Real events show that correlation is needed, for example, for corporate cards, but this is unprofitable due to the lack of free resources.
- Today, strategic planning and its methods are too static, mechanistic, do not have the necessary flexibility. Therefore, at certain stages, the constructed model turns out to be irrelevant. Here, scenario modeling could be called upon to help create models of various versions of the current business, but this would require additional funding for the organization. special structure for planning.
- The third reason is purely Russian problem, which lies in the fact that the basis of strategic planning in business is capital gains and profits. And on the one hand, this is a worthy goal, especially from the point of view of a business owner. But in our country, this position allows the number of investors-speculators to grow above the number of conscientious key shareholders. Moreover, the attitude to the strategic tasks set by these two sides usually differs radically. The first type, in the end, wants to sell his block of shares as profitably as possible, so capital gains are important to him. A strategy developed under the influence of such a message can be said to devalue the very fact of setting strategic goals.