In most business entities, employees perform not only the direct work function, because they also integral part The staff of many enterprises is also AUP - the decoding of this abbreviation is quite simple - this is administrative and managerial personnel. However, not all employers know who belongs to administrative and managerial personnel, what are their functions and what legislative regulation ensures the activities and control over the actions of these employees.
Administrative and managerial personnel - what is it
Before considering the very concept of APM and its decoding as administrative and managerial personnel, one should familiarize oneself with the basic principles of forming the structure of personnel in an organization. So, despite the fact that the personnel structure in many cases is developed individually, taking into account the characteristics of a particular business entity, all the same, employees of an enterprise can often be divided according to different criteria. The most popular separation technique now is the division of employees into two fundamental groups:
- Administrative and management personnel. It includes employees who are engaged in managerial activities or ensure the existence of the enterprise itself, solving key administrative functions as part of their work activities.
- Production personnel. This category includes the line staff of the organization - as qualified specialists, who are performers, and ordinary employees with a minimum level of qualification. At the same time, production personnel mainly include employees who provide direct profit to the enterprise, but lower-level service employees can also be attributed to it.
From the point of view of Russian legislation, such a division of employees is not reflected in any way in normative documents. The only indirectly considering this question documents can be the same qualification guides professions - they are divided into a directory of working professions and a directory of employees. And the administrative and managerial staff in most situations belongs precisely to the category of employees.
Since the legislation does not provide direct criteria for the separation of types of personnel, other options for dividing the personnel structure of an enterprise may be considered. For example, the division into administrative and production personnel may imply attribution specifically to the administrative staff of various support staff.
The legal regulation of the activities of administrative and managerial personnel, respectively, is left in the hands of the employer himself. It is he who can regulate the division of employees into different groups, the procedure for applying various remuneration systems in relation to employees, and also establish the rules of subordination in the enterprise, which are quite important for the administrative and managerial staff of the organization.
Who belongs to the administrative and managerial staff
As can be understood from the name, administrative and managerial personnel include employees who perform, respectively, administrative or managerial functions within the enterprise. To performers managerial function can be attributed directly management team organization, and he is part of the administrative and managerial staff, regardless of its importance and position in the vertical hierarchy of the organization.
The performers of the administrative function do not participate or take part in the management process, however, they are important employees for the activities of the entire organization. Accordingly, the administrative and managerial personnel in general include:
In most cases, belonging to the AUP is determined both by the presence or absence of a production function, and by the need for the employee's activity for the formal functioning of the organization. Thus, the absence of a security guard will not lead to the closure of the organization, and the absence of an accounting or personnel department and, accordingly, the absence of accounting and personnel reporting will definitely be illegal and will entail negative consequences.
Tasks of administrative and managerial personnel
The correct definition of the tasks of administrative and managerial personnel is the key to the effectiveness of any organization. The specific distribution of responsibilities and business processes is purely individual for individual business entities.
Managing the activities of the production system as a whole. They are built on the principle of hierarchy, which provides for the division of departments into higher and lower. The linear body of each stage performs the entire complex of functions of managing the corresponding object, which is the lower linear division; communication between divisions of different stages is carried out via one vertical channel. This type of structure most fully meets the principle of centralism and increases the responsibility of leadership and execution. The effectiveness of linear structures is significantly reduced with the complication of production systems, as the range of special issues for various management functions expands, which must be addressed by one manager, the linkage of the management structure increases, the danger of red tape increases due to the need to use only vertical connections. For driving modern enterprise the use of linear structures of the control apparatus in its pure form is practically impossible. However, linear bodies and communications are used in the construction of the structure of the enterprise and production association management apparatus.
Depending on the tasks and nature of the program, the organizational framework for its implementation (enterprise, association, industry, department), the types of program-target structures being created, the content of the functions of individual bodies can vary significantly, however, their distribution between the levels and main links of the management apparatus should be based on compliance with certain principles arising from the objective patterns of the implementation of organizational relationships in socio-economic systems.
The Chairman of the State Customs Committee 1) manages, on the principles of unity of command, the activities of the State Customs Committee, other customs authorities of the Russian Federation, customs laboratories and other subordinate enterprises, institutions and organizations 2) bears personal responsibility for the fulfillment of the tasks and functions assigned to the State Customs Committee 3) represents the State Customs Committee and ensures its interaction with other state bodies of the Russian Federation 4) distributes duties among the deputy chairmen of the State Customs Committee and establishes the degree of their responsibility 5) signs (approves) normative acts within the competence of the State Customs Committee, organizes verification of them 6) appoints and dismisses senior officials of the State Customs Committee, heads and chief accountants of regional customs departments and customs of the Russian Federation, heads of customs laboratories and other subordinate enterprises, institutions and organizations 7) establishes the powers of subordinate customs bodies of the Russian Federation to independently decide organizational, personnel , financial and other issues 8) approves regulations on the main departments and other structural subdivisions of the State Customs Committee, regional customs administrations, customs and customs posts of the Russian Federation, customs laboratories, as well as regulations (charters) of other subordinate enterprises, institutions and organizations 9) approves within the established the structure, staffing of the State Customs Committee, as well as the cost estimate for the maintenance of the management apparatus 10) assigns special ranks to employees within its powers subordinate institutions, in the prescribed manner, introduces ideas about the assignment special ranks of the highest commanding staff to officials of customs authorities and employees of institutions 11) awards badges and applies other forms of encouragement to employees of customs authorities, customs laboratories and other subordinate enterprises, institutions and organizations 12) submits, in accordance with the established procedure, especially distinguished employees for conferring honorary titles and awarding state awards of the Russian Federation 13) applies in full the measures of disciplinary action established by the legislation of the Russian Federation in in relation to employees of customs authorities, heads of customs laboratories and other subordinate enterprises, institutions and organizations 14) perform other functions and enjoy other rights in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
State organization is a general concept. These include government agencies and enterprises. The differences between enterprises and institutions are in their purpose, role in society, the content of the main activity. Enterprises are primarily engaged in production activities, institutions - management, social services population. At state enterprises, there is an administration (its bodies), but its functions are reduced to resolving issues internal management, and it does not act externally as a governing body. Exist different types enterprises by the nature of their activities (production, trade, etc.), by subordination and structure (state, municipal, joint-stock, unitary, etc.). State enterprises are not part of the state apparatus.
Expansion of functions of association. One of the main directions of increasing the efficiency of production is its concentration. In the oil industry, the main production unit should be a production association - a single territorial production complex a large number legally independent enterprises of drilling, production, ancillary services. The management body of the association (the apparatus of the association) already at the present time carries out a number of planning and distribution supply functions of management. rotting performs administrative functions, distributes production tasks among enterprises, ensures the sale of products, the implementation of funds, uninterrupted supply and systematic operation of enterprises, studies and generalizes the experience of their work, develops long-term plans for the development of the association as a whole and all its enterprises, etc. With the transition to a new production management structure, the functions of the association have expanded significantly, since most enterprises are directly subordinate to the association, bypassing intermediate management instances (trust, management). In the future, with the development of specialization and cooperation of labor, automation and mechanization of production, the introduction of automated control systems - oil, improvement
Production without proper management turns into complete chaos. As the enterprise grows, it becomes more complicated and acquires an official character and its management apparatus.
Traditionally, the organization and management of an enterprise is concentrated in three main areas of activity:
production,
financial activities.
R&D is added to these areas. It is on this approach that enterprise management apparatuses are created.
The management apparatus is a body of the organizational structure designed to implement the tasks of management by performing the functions of managing the forces of specialists to achieve the organization's goals.
Employees of the management system specialize in one of these areas, and manage this area.
It is advisable to consider the formation of the management apparatus in the genesis of the enterprise from small business before big company, which will give the key to understanding the structure of the control apparatus and its functional purpose.
A. Owner-managed firm.
According to the experience of the United States and the study of the activities of Russian companies by the author, the owner, manager himself can perform all management functions (as long as the number of employees in the company is up to 30-50 people and does not have a complex more than 2 levels of hierarchical structure.
- 1). He plans the work of the company,
- 2). Dealing with supplies
- 3). Controls the production process
- 4). Engaged in sales
- 5). Solves financial issues.
At best, he is helped by masters or assistants (the difference between Russian firms, as a rule, an entrepreneur hires an accountant due to his unprofessionalism in this matter and the complexity of reporting and tax system). Thus, the management apparatus of this type of enterprise is the head (see diagram 1.1.)
Scheme 1.1 Control apparatus (shoe repair shop)
B. Growing firm
The expansion of the company begins with the fact that the owner hires two new employees: to perform sales functions; for financial activities. The owner and two new specialists make up the management apparatus, see diagram 1.2.
Scheme 1.2. Control apparatus (shoe repair and sewing workshop)

With this structure of the apparatus, a number of functions, sales and finances are transferred from the head to his subordinates, thereby reducing his function.
If the enterprise continues to grow, then soon a production manager is added to the three employees of the management apparatus, who is equated with sales and finance specialists, see diagram 1.3.
Scheme 1.3 Management apparatus of Catalunya House LLC, Khabarovsk

The manager at this stage of development of the management apparatus continues to answer and perform "compact" and "stable" management functions.
The former are understood as: decision-making, giving orders, organizing production, motivating employees, and communicating in the organization.
Under the second: planning, collecting information, coordinating activities, monitoring and accounting, consulting, clerical work. As the enterprise grows, the management apparatus becomes more complicated: 1) the emergence of hierarchical levels of management, 2) the division of activities into “command” (linear) and “headquarters”. Specialists directly responsible for the functions of production, marketing, finance, R&D are line managers and are engaged in "team" activities. Technical and clerical specialists who are not directly involved in the management of these types of activities are paid specialists and collect information, calculate, account and control, develop standards, etc., see diagram 1.4.
Scheme 1.4. Management apparatus of JV Mirmetall, Khabarovsk



At this enterprise, the management apparatus has a functional division by type of activity (sales, production, finance + legal activity, security), and by type of activity line managers (general director, chief engineer, commercial director, chief accountant, managers 3 and 4 level) and staff specialists (assistant to the general director, lawyer, head of the KhCh, head of security), as well as staff specialists of the 2nd level of management (chief mechanic, chief power engineer, dispatcher, controllers, marketer). Together with him, the general director continues to combine "command" and "staff" functions, this concerns the issues of planning the activities of the enterprise, developing the structure of the company, etc.
In the conditions of a large company, the creation of headquarters units is a condition successful management enterprise. The growth of the enterprise makes it necessary to organize it in the form of a system of coordinating structural divisions. The apparatus must ensure the achievement of the main goal of the enterprise - making a profit.
B. Large enterprise.
The main interrelated tasks of the enterprise are production, research and development, marketing, financial activities. Therefore, this is how the control apparatus is created, based on these functions. Separation of functions in order to perform each of the tasks, splitting each function into subfunctions, correct distribution work force, the use of material resources - this is the basis of an organized plan.
Building a management apparatus on this approach ensures the achievement of goals. At the same time, the combination of command and staff functions leads to a decrease in the effective activity of the control apparatus. Therefore, their differentiation becomes a necessity.
There are two approaches: staff-oriented specialists of the first level of management are decentralized (see "Mirmetal"), or as, for example, on large American companies centralized i.e. merged into one department. The company "Radon" has chosen this path, see Scheme 1.5.
Scheme 1.5. The structure of the management apparatus of the enterprise "Radon"

Scheme 1.6. Apparatus structure executive director"Radon"

This approach determines the coordination and interaction of all headquarters structures of the 1st level under a single leadership and the main difference is the creation of a body responsible for planning the activities of the enterprise as a whole. The creation of an administrative service along with production, marketing, financial provides large enterprise more opportunities to achieve goals. At the same time, there are no right answers in management and this approach can be considered as an alternative one.
The approach itself is important in creating the structure of the administrative apparatus, proceeding both from the types of activity (production, marketing, finance) and from the nature of the activity (line management, headquarters directorates).
Staff employees influence the decisions made by line managers, but are not responsible for the process of managing line services and do not have the right to interfere in their activities. It is important to note that, as a rule, the problems of interaction between line and staff structures on small and large firms no, on the first they are inseparable and are carried out by the leader; on the second, there is a direct need to distinguish them. On average, everything depends on the understanding of this issue (for example, if a quality control specialist is subordinate to the shop manager, then his meaning is lost, if the production director, control is more valid), see diagram 1.7.

Thus, the management apparatus is the management of the enterprise to achieve the goals of the enterprise through the performance of management functions, creating for this purpose the structure of the apparatus, which provide a solution to the problems of production, research and development, marketing, financial activities and administrative activities.
The structure of the management apparatus depends on the tasks facing the enterprise, the size, the category of management on the structure of the apparatus.
When forming the management apparatus, it is advisable to take into account the following factors:
Analysis of the activities performed by specialists and ways of coordinating with others.
Decision-making level and the role of specialists in decision-making.
The manager's contribution to achieving the final result.
Determination of the allowable scope of assigned duties and the number of subordinates.
Calculation of working time, methods of labor organization.
Formation of the structure according to goals and objectives, and not according to other criteria.
The formation of departments depends on the features underlying them, among them are:
Divide by group size.
On a functional basis (production, marketing, finance, etc.).
On a territorial basis (all functions are entrusted to the territorial department).
Based on manufactured products (usually in large enterprises).
Based on consumer interests.
Practice shows that there is a combination of the use of these features, see Scheme 1.8.
Scheme 1.8. Manadgement Department
(combination of functional and territorial features)

The effectiveness of the management apparatus long time associated with economic indicators enterprises. The achievement of advanced companies indicates that it is advisable to introduce a strategic variable in this matter - an increase in the cost of a device today can, with effective strategic planning bring a significant effect. Evidence of this, the introduction of administrative services in the United States in the 1960s was compared to a revolution in management.
The functions of managing the activities of the enterprise are implemented by departments of the management apparatus and individual workers which at the same time enter into economic, organizational, social, psychological and other relations with each other. Organizational Relations, developing between divisions and employees of the enterprise management apparatus, determine its organizational structure.
The organizational structure of enterprise management is understood as the composition (or list) of departments, services and divisions in the management apparatus, their system organization, the nature of subordination and accountability to each other and to the supreme management body of the enterprise, as well as a set of coordination and information links, the procedure for distributing management functions according to different levels and divisions of the management hierarchy.
The organizational management structure of ER-Telecom CJSC is built taking into account 2 levels of management:
First level:
The supreme management body of ER-Telecom CJSC is the meeting of shareholders, consisting of the shareholders of the company or their authorized representatives, acting by making decisions on issues referred to its competence by this Charter. Once a year, the company holds a general meeting of shareholders. To exclusive competence general meeting shareholders include the following:
- - changes and additions to authorized capital organizations;
- - reorganization of the enterprise;
- - liquidation of the enterprise, appointment of a liquidation commission and approval of interim and final liquidation balance sheets;
- - determination of the number of members of the Board of Directors, election of its members and early termination of their powers;
- - determination of the maximum amount of declared shares;
- - statement annual reports, balance sheets, profit and loss accounts of the enterprise, distribution of profits and losses;
- - approval of the regulation on the procedure for preparing and conducting the general meeting of shareholders, determining the procedure for conducting the meeting.
The meeting of shareholders is chaired by the branch director of ER-Telecom CJSC. At this level, there is a board of directors who, in the period between meetings, manage the company. The board of directors carries out general management of the company's activities, with the exception of resolving issues that fall within the competence of the meeting of shareholders of the enterprise.
The exclusive competence of the board of directors of the enterprise includes the following issues:
- - determination of priority directions of the enterprise's activity;
- - convocation of the annual and extraordinary general meeting of shareholders of the enterprise;
- - acquisition of shares, bonds and other valuable papers in cases provided by law;
- - use of reserve and other funds of the organization;
- - approval of internal documents that determine the procedure for the activities of the management bodies of the organization, with the exception of documents, the adoption of which is within the competence of the general meeting of shareholders;
- - creation of branches and opening of representative offices of the enterprise;
- - conclusion of transactions in which there is an interest, etc.
Second level:
The executive management body is the director of the branch.
The director of the branch, on the basis of the charter of the organization, acts on behalf of the organization and represents the interests of the organization, making transactions, approving the staff, issuing orders, giving instructions that are binding on all employees of the organization, in accordance with the competence defined by this charter.
The rights and obligations of the director of the branch to manage the current activities of the enterprise are determined legal acts of the Russian Federation, the charter of the organization, regulations and the director of the branch, approved by the board of directors.
Activities of the branch manager:
- - organizes the current activities of the organization;
- - resolves issues related to the functioning of structural divisions of the organization;
- - organizes rational use real estate and other property owned by the organization;
- - manages the property of the organization by concluding agreements and other transactions and legal actions;
- - organizes accounting and reporting;
- - Approves contractual prices for services.
The administrative and managerial staff of ER-Telecom CJSC consists of: the director of the branch, the head of the sales department, the head subscriber department, head of department technical support, head of marketing department, financial director, head of the security service.
The branch director is elected by the general meeting of shareholders of the company. According to the charter of the organization, the competence of the director of the branch includes all issues of managing the current activities of the enterprise, he has full power, is responsible for the daily activities of the enterprise. The director of the branch without a power of attorney acts on behalf of joint-stock company, including representing his interests, making transactions on his behalf, staffing, issues orders and gives instructions that are binding on all employees of the enterprise. In addition, the director of the branch ensures the implementation of decisions of the general meeting of shareholders and the board of directors, manages the property of the company, determines the organizational structure of the company, approves the rules, procedures and other internal documents of the company, hires and dismisses employees, including appointing and dismissing deputies, chief accountant, heads of departments, representative offices, encourages employees and imposes penalties on them, opens currency and settlement accounts in banks, concludes contracts and makes transactions.
The head of the sales department performs all functions CEO during his absence. In addition, it controls the workflow, that is, the main unit. In his submission are a senior specialist of the sales department, senior managers, a leader of promotions, employees of the corporate department. He is also responsible for the work of the sales department and reports to the director of the branch for its progress.
The head of the subscriber department is responsible to the head of the sales department for the work of his department, and also controls the work of dispatchers.
The head of the technical support department supervises the employees of this department and is responsible for the smooth operation of the Internet and cable TV connections.
CFO - Chief Accountant- deals with the execution of loan agreements with banks, analyzes the production and economic activity enterprises, monitors the implementation of the plan for the production and sale of services, reports to the director of the branch (and in his absence to the head of the sales department) on the economic condition of the enterprise, on the work of the accounting department and the planning and economic department, on the financial operations of the organization.
Services and departments
Services and departments are functional divisions providing life of the entire organization.
In ER-Telecom CJSC these include:
- - accounting;
- - security service.
The accounting department maintains accounting and tax records of the property and obligations of the organization, is engaged in the preparation of accounting and tax reporting enterprises and the provision of this reporting to higher authorities within the time frame corresponding to the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The security and fire service ensures the protection of the production area, the safety of the employees of the enterprise, monitors compliance with the access system
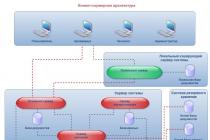
Structure and functions of the control apparatus.
The structure refers to the composition and functions of the governing bodies, their subordination and interconnection. The structure and management must meet the following requirements: provide conditions for the prompt and comprehensive high-quality implementation of enterprise management functions based on management principles; have a minimum number of links; be flexible, simple and economical.
Management of the railway car repair enterprise is carried out at two levels. At the first level, the issues of managing car repair plants are resolved by the apparatus of the Ministry of Railways, that is, a management system is organized in which the control object is the car repair plant, and the control body is the apparatus of the Main Directorate for the Repair of Rolling Stock and the Production of Spare Parts (TsTVR). The composition of this management apparatus includes the main managers and functional bodies - departments and sectors. They manage enterprises and design and technology bureaus (PKTB TsTVR) that are subordinate to this department.
At the second level, issues related to the management of car repair production within an industrial enterprise are resolved. Here, the object of management is the workshops, production sites, services and other divisions of the car repair plant, and the management body is the plant management apparatus of the enterprise.
The structure of the enterprise management apparatus is built on the basis of the differentiation of its functions into separate administrative divisions- management bodies, taking into account the degree of specialization, the level of technical equipment, the type and scale of production. The number of divisions of the management apparatus and the form of the organizational structure are chosen so that the coordinated and accurate work of the entire apparatus of the enterprise is ensured and the costs of production management are systematically reduced.
The management of an industrial enterprise is based on linear and functional principles.
The linear principle of management is characterized by the fact that each performer receives a task from only one higher manager and reports directly to him. The linear principle of management is based on a rational quantitative ratio of managers and subordinates.
The functional principle of management involves the distribution of managerial responsibilities among several performers within their specialization. In practice, the structure of the administrative apparatus is a combination of functional and line management, forming the so-called linear-functional management structure.
The functions of enterprise management are diverse, but all of them are subordinated to the main task - to ensure the implementation of the established plan for all indicators with minimal expenditure of public funds.
On fig. 3 shown organizational structure car repair plant management apparatus. The company is headed by the head of the plant - confidant state responsible for all aspects of the enterprise. He manages the entire production, economic and financial activities enterprises on the basis of unity of command, ensures the implementation of the state plan by the enterprise and bears full responsibility to the state for the production and economic activities of the plant. Responsibilities for the functional management of individual units are distributed among his deputies.
The first deputy head of the plant is the chief engineer, who is the technical manager of the enterprise. He is primarily responsible for pursuing a correct technical policy, for improving engineering, technology and the organization of production. Chief Engineer directly manages the work of the technical services of the enterprise, laboratories and experimental workshop. As the first deputy chief, he also manages the activities of the main production shops and, together with them, bears full responsibility for the correct production and technical management of the enterprise.
At large car repair enterprises there is a chief economist with the rights of deputy head of the plant. He coordinates all the economic work of the enterprise, systematically analyzes economic activity and outlines ways to improve it. Administrative and economic work and supply is managed by the Deputy Chief for Commercial and Economic Affairs.
To help the management of the enterprise, a management apparatus was created - the plant management, which unites a number of departments, each of which is specialized in performing certain duties.
The plant management includes departments of economic planning, chief accounting, production, chief designer, chief technologist, technical control, chief mechanic and chief power engineer, logistics and sales, labor and wages, personnel, administrative and economic, etc. Of great importance is a clear division of functions between these departments, excluding duplication in the management process.
Planning and Economic Department carries out technical and economic planning, develops long-term and current plans (technical and industrial financial plans) of the entire plant and workshops for a year, quarter, month, monitors their implementation, maintains statistical records and analyzes the production and economic activities of workshops and the plant as a whole, organizes internal plant cost accounting.