Customs authorities perform the following main functions:
1) carry out customs clearance And customs control, create conditions conducive to the acceleration of trade through customs border;
2) charge customs duties, taxes, anti-dumping, special and countervailing duties, customs duties control the correctness of the calculation and the timeliness of payment of the said duties, taxes and fees, take measures to enforce their collection;
3) ensure compliance with the procedure for the movement of goods and Vehicle across the customs border;
4) ensure compliance with the established in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on state regulation foreign trade activities and international treaties of the Russian Federation prohibitions and restrictions in respect of goods transported across the customs border;
5) ensure, within their competence, the protection of the rights intellectual property;
6) fight against smuggling and other crimes, administrative offenses in the field of customs, stop illegal circulation across the customs border of narcotic drugs, weapons, cultural property, radioactive substances, endangered species of animals and plants, their parts and derivatives, objects of intellectual property, other goods, as well as assist in the fight against international terrorism and the suppression of unlawful interference at the airports of the Russian Federation in the activities of international civil aviation;
7) carry out, within their competence, currency control of operations related to the movement of goods and vehicles across the customs border, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on currency regulation and currency control;
8) keep customs statistics of foreign trade;
9) ensure the fulfillment of the international obligations of the Russian Federation in the part related to customs, cooperate with customs and other competent authorities of foreign states, international organizations dealing with customs matters;
10) provide information and advice in the field of customs, provide in the prescribed manner government bodies, organizations and citizens with information on customs issues;
11) carry out research work in the field of customs.
End of work -
This topic belongs to:
Constitutional principles of justice
On the site site read: "constitutional principles of justice"
If you need additional material on this topic, or you did not find what you were looking for, we recommend using the search in our database of works:
What will we do with the received material:
If this material turned out to be useful for you, you can save it to your page on social networks:
| tweet |
All topics in this section:
Constitutional principles of justice
§ 1. The principle of the legality of justice. § 2. The principle of the administration of justice only by the court. § 3. The principle of ensuring the suspect, the accused and the defendant the right to defense.
The principle of the legality of justice
The general legal principle of legality is enshrined in the Constitution of the Russian Federation (clauses 2, 3, article 15). This principle is understood as a requirement of the state, addressed to the subjects of the process, to strictly and unswervingly observe and use
The principle of the administration of justice only by the court
According to the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the court is the only state body authorized to administer justice in criminal cases as a special function. state power. Right
Defense rights
According to the law, the suspect, accused or defendant is granted the right to defense. This right is exercised in two main forms: 1) through the personal exercise of the rights granted to them
The principle of equality of all before the law and the court
The Constitution of the Russian Federation (part 1, article 19) enshrines the principle of equality of all before the law and the courts (the principle of non-discrimination), which applies to citizens of the Russian Federation, foreign citizens, stateless persons (ap.
The principle of the state or national language of legal proceedings
The democratic principle of national equality is also reflected in the constitutional consolidation of the right of everyone to use their native language, to freely choose the language of communication, education,
The principle of independence of judges and their subordination only to the law
This essential principle implementation of the judiciary, which determines its status in the rule of law. Independence of judges, their subordination only to the Constitution of the Russian Federation and federal
The principle of publicity in the activities of the courts
The principle of publicity (openness), the publicity of the trial, is an important legal guarantee of fair and impartial resolution by the courts of civil, administrative, criminal
The principle of competitiveness and equality of the parties in the trial
The principle of competitiveness of the parties predetermines the special role and functions of the court in the administration of justice. This principle means such a construction of legal proceedings when the functions of the prosecution
The principle of immunity of judges
The immunity of judges is an essential guarantee of their independence. Since the judge resolves legal conflicts, he needs an increased level of security, in addition
The principle of the presumption (assumption) of innocence
The principle of the presumption of innocence, enshrined in Art. 49 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation, is one of the basic principles of justice. It is the court and only the court as an independent and independent body of the judiciary
The principle of citizen participation in the administration of justice
The Federal Constitutional Law “On the Judicial System of the Russian Federation” of 1996 (Part 1, Article 1) states that the judiciary in the Russian Federation is exercised only by courts represented by judges and
Justices of the peace and their powers in the field of legal proceedings
The Federal Constitutional Law “On the Judicial System of the Russian Federation” states that the judicial system of the Russian Federation includes federal and magistrate judges of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (Part 2, Article 4). Justice of the Peace
District (city) court as the first link of courts of general jurisdiction. Powers of the district (city) court
The Federal Law "On the Judicial System of the Russian Federation" determines the procedure for the creation and abolition of district courts. District courts are created in districts, cities that do not have district division, in districts (districts) of
Powers of the federal courts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation as middle-level courts
The courts of the subjects of the Russian Federation are: - The Supreme Courts of the republics within the Russian Federation; - regional (regional) courts; - court of a federal city;
Military courts in the system of courts of general jurisdiction
As part of the courts of general jurisdiction, military courts are specialized courts, and organizationally, like the general territorial courts, are closed to the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation. According
Supreme Court of the Russian Federation
The Supreme Court of the Russian Federation is the supreme judicial body in civil, criminal, administrative and other cases within the jurisdiction of courts of general jurisdiction. It carries out in the prescribed feda
Judicial Department under the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation
Judicial Department at Supreme Court of the Russian Federation carries out its activities on the basis of the Constitution of the Russian Federation, federal constitutional laws, Federal Law of 8
The legal basis for the activities of the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation and its tasks
The Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation is the federal executive body that conducts public policy and exercising management in the field of justice, as well as coordinating activities in this
The main functions of the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation
In accordance with the tasks assigned to the Ministry of Justice, this body performs a number of the following functions: 1) coordinates the rule-making activities of federal bodies
Powers of the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation
In accordance with paragraph 7 of the Regulation "On the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation", the Ministry of Justice of Russia, within its competence: 1) creates its own territorial bodies, approves their regulations, approves the state
Organization of the activities of the bailiff service and their tasks
Legal basis activities of bailiffs are: the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the Federal Law "On Bailiffs" of July 21, 1997, the Federal Law "On Enforcement Proceedings" of July 21
Types of bailiffs, their rights and obligations
Depending on the duties performed, bailiffs are divided into: - bailiffs who ensure the established procedure for the activities of courts (hereinafter referred to as judicial
Conditions and limits for the use of physical force, special means and firearms by a bailiff
The bailiff-provider of the established procedure for the activities of the courts may apply in necessary cases physical strength, special means and firearms, unless otherwise
And the principles of its activity
The Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation, acting as the guarantor of the rights and freedoms of citizens and organizations enshrined in the Constitution of the Russian Federation, occupies a special place in the judicial system of the Russian Federation. The
The structure of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation and its powers
The Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation consists of nineteen judges (appointed by the Federation Council on the proposal of the President of the Russian Federation) and two chambers, respectively, including ten
Status of a Judge of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation
A judge of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation may be a citizen of the Russian Federation who has reached the age of at least forty years by the date of appointment, with impeccable reputation with a law degree and experience in
Constitutional (charter) courts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation
In accordance with Art. 27 of the Federal Constitutional Law of December 31, 1996 "On the judicial system of the Russian Federation", the Constitutional (charter) court of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation may create
The system of arbitration courts of the Russian Federation and their powers
Arbitration courts occupy a special place in the judicial system of Russia. The system of arbitration courts is mainly built taking into account the federal and administrative-territorial structure of the Russian Federation.
district arbitration courts
Arbitration courts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation constitute the first link in the system of arbitration courts in Russia. In the constituent entities of the Russian Federation there are arbitration courts of republics, territories, regions, cities of the federal level
Competence of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation and its structure
Higher Arbitration court The Russian Federation is the highest judicial body for resolving economic disputes and other cases considered by arbitration courts. Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation de
International commercial arbitration
International Commercial Arbitration is a body established to resolve disputes arising in the field of international trade. Its activities are regulated by the Law of the Russian Federation of July 7
Arbitration courts
Any dispute arising from civil legal relations may be submitted to the arbitration court by agreement of the parties to the arbitration proceedings (hereinafter referred to as the parties), unless otherwise provided by law. Dispute m
The system of bodies of the prosecutor's office of the Russian Federation
The activities of the prosecutor's office are regulated by the Federal Law of January 17, 1992 "On the Prosecutor's Office of the Russian Federation". The Prosecutor's Office of the Russian Federation is a single f
And investigators of the prosecutor's office
Prosecutors and investigators may be citizens of the Russian Federation with a higher legal education, possessing the necessary professional and moral qualities,
Prosecutorial supervision and its main directions
In order to ensure the rule of law, the unity and strengthening of the rule of law, the protection of the rights and freedoms of man and citizen, as well as the legally protected interests of society and the state,
Coordination of the activities of law enforcement agencies, as the most important task of the prosecutor's office
The Prosecutor General of the Russian Federation and the prosecutors subordinate to him coordinate the anti-crime activities of the internal affairs bodies, the federal security service
Concept and tasks of preliminary investigation
The preliminary investigation is an independent stage of the criminal process, at this stage the validity of the decision to initiate a criminal case is checked and evidence is collected.
Inquiry as a form of preliminary investigation. Bodies of inquiry
Inquiry is carried out by investigators of the internal affairs bodies of the Russian Federation, as well as other executive authorities vested in accordance with federal law with the authority to carry out operational
Preliminary investigation as a form of preliminary investigation. Bodies of preliminary investigation
The preliminary investigation is carried out by investigators: the prosecutor's office, the federal security service, the internal affairs bodies of the Russian Federation, the bodies for controlling the circulation of narcotic drugs
Activities and their powers
Operational-search activity is carried out openly and behind the scenes by operational units of state bodies authorized to do so by the Federal Law of August 12, 1995. "About promptly
The main tasks and functions of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation
The activities of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation are regulated by the Regulations on the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation, approved by Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of July 18, 1996. Min
Organ system of the Ministry of Internal Affairs
The Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation heads the system of internal affairs bodies, which includes: - ministries of internal affairs of the republics, - main departments, management
main activities
The Federal Security Service is a unified centralized system of bodies of the Federal Security Service and the Border Troops, which makes decisions within the limits of its powers
Combating crime and terrorist activities
The FSB bodies carry out operational-search measures to identify, prevent, suppress and disclose espionage, terrorist activities, organized crime, corruption, illegal
Bodies of the federal security service: tasks, basic rights and obligations
State protection is carried out on the basis of the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the Federal Law of May 27, 1996 No. “On State Protection” and other normative legal acts of the Russian Federation, as well as between
Bodies of the Federal Foreign Intelligence Service of the Russian Federation and their powers
Foreign intelligence of the Russian Federation is a set of foreign intelligence agencies of the Russian Federation specially created by the state, which are an integral part of the security forces of the Russian Federation and are called upon to
Federal Service of the Russian Federation for Control over the Circulation of Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, its bodies and tasks
The Federal Service of the Russian Federation for the Control of the Circulation of Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances is a federal executive body specially authorized to decide on
The system of customs authorities of the Russian Federation and the goals of customs policy
In accordance with the Constitution of the Russian Federation and the Customs Code of the Russian Federation of May 28, 2003, customs regulation consists in establishing the procedure and rules, subject to which persons exercise the right to transfer
Organization of advocacy and advocacy
Advocacy is qualified legal assistance provided on professional basis persons who have received the status of a lawyer, individuals and legal entities in
The status of a lawyer, his rights and obligations
The requirements for a candidate for the position of a lawyer are established by the Federal Law "On Advocacy and the Bar in the Russian Federation", these are: 1) cash
Powers of a notary
Notaries, according to Art. 1 of the Fundamentals of the Legislation of the Russian Federation on Notaries dated February 1, 1993, is designed to ensure the protection of the rights and legitimate interests of citizens and legal entities by committing
Rights and obligations of notaries
A citizen of the Russian Federation who has a higher legal education, who has completed an internship for a period of at least one year in a state notary office, can be appointed to the position of a notary.
and security activities
The main sources regulating the provision of private detective or security services are the Constitution of the Russian Federation and the Law of the Russian Federation of March 11, 1992 “On private detective and security activities”.
Private security activity
The provision of private security services is permitted only to enterprises specially established for their performance. The security activities of enterprises do not apply to facilities subject to state
The use of weapons and special means in the implementation of private detective and security activities
During the implementation of private detective activities, it is allowed to use special means, and in the implementation of private security activities - special means and firearms.
Legal service of the organization (legal work)
Legal work as a type of law enforcement activity is assigned to legal service organizations. This activity aimed at ensuring the normal functioning of the enterprise, namely
Foreign economic activity: a training course Makhovikova Galina Afanasievna
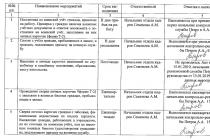
4.4. The structure of the customs authorities of the Russian Federation and their main functions
The customs business itself is conducted by a single system of customs authorities, which, being part of the executive branch, have specific formation goals, carry out state executive and administrative functions, are endowed with certain competence, are formed by higher authorities, are accountable and controlled by them and are responsible for their activities to the state and citizens. .
The customs authority is a federal state executive body endowed with special competence in the field of customs and performing the task of promoting the development of foreign trade.
The customs authorities constitute a single federal centralized system, which includes:
1) Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation;
2) regional customs departments;
3) customs;
4) customs posts.
The customs system also includes institutions directly subordinated to the FCS (customs laboratories, educational establishments, computer centers, etc.). The FCS may have state unitary enterprises whose activities contribute to the solution of tasks assigned to the customs authorities.
All links of the system are federal and are not subordinate to the state authorities of the constituent entities of the Federation, bodies local government and public associations. Each lower customs authority is vertically subordinate only to the higher customs authorities that control its activities.
Locations of customs authorities are determined based on the volume of passenger and goods flows, transport organizations, the intensity of development foreign economic relations individual regions, the needs of exporters, importers, other participants in foreign economic activity, as well as other factors.
The Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation is the federal executive body directly managing the customs business in the Russian Federation. The FCS is under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Economic Development and Trade of the Russian Federation.
Creation, reorganization and liquidation of regional customs administrations, customs houses and customs posts, as well as the competence of specific customs authorities to implement specific functions, committing certain customs operations, as well as the region of activity of the customs authorities are determined by the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation.
The customs service has the right to create specialized customs authorities, the competence of which is limited by individual powers to perform certain functions assigned to the customs authorities, or to perform customs operations in relation to certain types goods.
Regional customs departments, customs offices and customs posts operate on the basis of regulations approved by the FCS.
The system of customs authorities also includes non-law enforcement institutions that are established by the FCS to support the activities of customs authorities.
The customs authorities of the Russian Federation perform the following main functions:
Carry out customs clearance and customs control, create conditions conducive to the acceleration of trade across the customs border;
Collect customs duties, taxes, anti-dumping, special and countervailing duties, customs fees, control the correctness of the calculation and timely payment of the said duties, taxes and fees, take measures to enforce their collection;
Ensure compliance with the procedure for the movement of goods and vehicles across the customs border;
Ensure compliance with the prohibitions and restrictions established in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on the state regulation of foreign trade activities and international treaties of the Russian Federation in relation to goods transported across the customs border;
Ensure, within their competence, the protection of intellectual property rights;
They fight against smuggling and other crimes, administrative offenses in the field of customs, stop illegal trafficking across the customs border of drugs, weapons, cultural property, radioactive substances, endangered species of animals and plants, their parts and derivatives, objects of intellectual property , other goods, as well as assist in the fight against international terrorism and the suppression of unlawful interference at the airports of the Russian Federation in the activities of international civil aviation;
Carry out, within their competence, currency control of operations related to the movement of goods and vehicles across the customs border, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on currency regulation and currency control;
Keep customs statistics of foreign trade;
Ensure the fulfillment of the international obligations of the Russian Federation in terms of customs affairs, cooperate with customs and other competent authorities of foreign states, international organizations dealing with customs matters;
Carry out informing and consulting in the field of customs affairs, provide state bodies, organizations and citizens with information on customs issues in the prescribed manner;
Carry out research work in the field of customs.
The Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation carries out its activities in cooperation with other federal executive authorities, executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and public associations. State bodies and their officials are obliged to assist the customs authorities of the Russian Federation in solving the tasks assigned to them, including by creating appropriate conditions for this.
This text is an introductory piece. From the book Money. Credit. Banks [Answers to exam tickets] author Varlamova Tatyana Petrovna118. Features banking system USA and its structure and functions Core credit system The United States is the Federal Reserve System (FRS), consisting of 1) 12 Federal Reserve Banks; 2) of a large number member banks. According to the Federal Reserve Act
From the book All taxes in Russia 2013 author From book Innovation management author7.2. The main functions of state bodies in the innovation sphere The role of the state in innovation activities manifests itself in its functions aimed at regulating all processes taking place in the innovation sphere. The most important state functions V
From the book All taxes in Russia 2012 author Semenikhin Vitaly ViktorovichSection III. Tax authorities. Customs. financial authorities. Internal affairs bodies. Investigative authorities. Responsibility of tax authorities, customs authorities, internal affairs authorities, investigating authorities, their officials Chapter 5. Tax authorities. Customs
From the book Finance of Organizations. cheat sheets author Zaritsky Alexander Evgenievich85. Functions and structure of money circulation Functions of money in circulation: 1) payment; 2) appeals; 3) accumulation. In the process of money movement, there are always stops, and it is during periods of temporary cessation of movement that the function of money as a means is realized.
From the book Money, credit, banks. cheat sheets author Obraztsova Ludmila Nikolaevna22. Functions and structure of money circulation Functions of money in circulation: 1) payment; 2) appeals; 3) accumulation. In the process of money movement, there are always stops, and it is during periods of temporary cessation of movement that the function of money as a means is realized.
From the book Tax Law. cheat sheets author Smirnov Pavel Yurievich40. Functions of the regional bodies of the Federal Tax Service in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation tax inspections By
From the book Banking: a cheat sheet author Shevchuk Denis AlexandrovichTopic 44. Financial market: structure, functions, participants Financial market - an organized or informal trading system financial instruments. In this market, money is exchanged, credit is granted, and capital is mobilized. Key role in financial
From the book State and municipal government author Sibikeev Konstantin40. The system and structure of local governments In any state, the ability of local governments to perform their task effectively depends largely on how they are organized. It is known that the organization of something has a structural and
From the book Economics of the Firm: Lecture Notes author Kotelnikova Ekaterina2. Functions and structure of the market The definition of the market given in the previous chapter requires an approach to its characterization as a complex object, consisting of a wide range of separate parts, elements. Such a variety of components and specificity
From book Economic theory: lecture notes author Dushenkina Elena Alekseevna1. Subject, structure, functions and methodology of economic theory The word "economics" (from the Greek oikonomike) means the art of conducting household, home economics. To say exactly what "economy" is in modern conditions, difficult. The economy is also a set
author Makhovikova Galina AfanasievnaLecture 6 Topic: MARKET RELATIONS: ESSENCE, FUNCTIONS, STRUCTURE This lecture examines the economic content of a market economy: the conditions for the emergence, role and functions of the market are considered; the role and place in the economy of households, firms and
From the book Economic Theory. author Makhovikova Galina Afanasievna6.1 Market: essence, role, functions and structure In the formation of a market economy, a number of stages can be distinguished: exchange, commodity circulation, market. The presence of a social division of labor leads to the need for an exchange of activities and products of labor. In that
From the book Economic Theory. author Makhovikova Galina Afanasievna18.3. Monetary system: structure and functions The credit system is a complex of monetary and financial institutions designed to regulate the economy by changing the amount of money in circulation. The modern monetary system consists of three
author Makhovikova Galina Afanasievna5.1. Market: essence, role, functions and structure In the history of the development of a market economy, a number of stages can be distinguished: exchange, commodity circulation, market. The presence of a social division of labor leads to the need for an exchange of activities and products of labor. IN
From the book Economic Theory: Textbook author Makhovikova Galina AfanasievnaLesson 8 Market: essence, role, functions, structure
The customs authorities of the Russian Federation are state bodies that directly carry out activities in the field of customs. Customs authorities are executive authorities. The executive activity of the customs authorities consists in the daily practical organization solving issues related to the customs business. The main activity of the customs authorities is the implementation of their functions and powers in the field of organizing the movement of goods across the customs border, customs clearance, placement of goods under certain customs regimes, implementation of special customs procedures, collection of customs payments.
The subject of the study is "Goals and objectives of the customs service". The purpose of the work is to consider the goals and objectives of the customs service. To achieve the goal, we have set the following tasks:
1. Consideration of the customs service of Russia.
2. Consideration of the goals, objectives and functions of the customs authorities.
3. Consideration of the development of the customs service.
1. Customs Service of Russia
Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of March 9, 2004 N 314 "On the system and structure of federal executive bodies" The State Customs Committee of the Russian Federation (SCC of Russia) was transformed into the Federal Customs Service (FCS of Russia). Its functions of adopting normative legal acts in the customs sphere have been transferred to the Ministry of Economic Development and Trade of the Russian Federation, and in terms of customs payments, to the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
The customs authorities of the Russian Federation are state bodies that directly carry out activities in the field of customs. Customs authorities are executive authorities. The executive activity of the customs authorities consists in the daily practical organization of solutions to issues related to the customs business.
The main activity of the customs authorities is the implementation of their functions and powers in the field of organizing the movement of goods across the customs border, customs clearance, placement of goods under certain customs regimes, implementation of special customs procedures, collection of customs payments.
Customs authorities carry out both executive and administrative activities. Both of these activities are closely related. At the same time, the administrative activities of the customs authorities are carried out strictly within the framework of the provisions determined by the customs law.
important hallmark customs authorities is that they are classified as law enforcement agencies by the current legislation.
As law enforcement agencies, the customs authorities protect the economic sovereignty and economic security of the Russian Federation, the rights and legitimate interests of individuals and legal entities. Customs authorities are fighting crimes and administrative offenses in the field of customs.
The customs authorities constitute a single federal centralized system. State authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, local governments, public associations cannot interfere in the activities of customs authorities in the exercise of their functions (Article 401 of the Labor Code).
In accordance with Article 402 of the Customs Code, the system of customs authorities includes:
1) the federal executive body authorized in the field of customs (currently it is the Federal Customs Service (FCS);
2) regional customs departments (RTU);
3) customs;
4) customs posts.
The central body exercising direct management of the customs business in the Russian Federation is the federal executive body authorized in the field of customs business - the Federal Customs Service of Russia. He is in charge of the main components, blocks and sections of the customs business, which he manages through the relevant departments, departments, services, other structural divisions of his apparatus, as well as through regional customs departments, customs, customs posts.
The legal status of the FCS of Russia in the system of customs authorities is determined by the Federal Law of June 29, 2004 N 58-FZ "On Amending Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation and Recognizing Some Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation as Invalid in Connection with the Implementation of Measures to Improve government controlled"and the Regulations on the FCS of Russia, approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 21, 2004 No.
The Federal Customs Service is a federal executive body that performs the following functions in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation:
1) on control and supervision in the field of customs;
2) a currency control agent;
3) special functions to combat smuggling, other crimes and administrative offenses.
At the same time, the customs service carries out:
1) maintaining registers of persons carrying out activities in the field of customs;
2) maintaining the Register of banks and other credit organizations that have the right to issue bank guarantees for the payment of customs duties;
3) maintenance of the customs register of objects of intellectual property;
4) cancellation of qualification certificates of customs clearance specialists;
5) issuance of licenses for the establishment of a free warehouse.
In addition to the above, the customs service:
Keeps customs statistics of foreign trade and special customs statistics;
Informs and advises on a gratuitous basis on customs issues of participants foreign economic activity;
Carries out, within its competence, currency control of operations related to the movement of goods and vehicles across the customs border of the Russian Federation;
Carries out proceedings on cases of administrative offenses and consideration of such cases in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on administrative offenses;
Carries out inquiry and production of urgent investigative actions in accordance with the criminal procedure legislation of the Russian Federation;
Carries out operational-search activities in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation;
Carries out in accordance with the established procedure the development and creation of information systems used by the customs authorities, information technologies and means of their provision;
Carries out the functions of the main manager and recipient of funds federal budget provided for the maintenance of the Service and the implementation of the functions assigned to it;
Ensures, within its competence, the protection of information constituting a state secret;
Considers complaints against decisions, actions (inaction) of customs authorities and their officials, etc.
In agreement with the Ministry of Economic Development of Trade of the Russian Federation, the Federal Customs Service has the right to:
Create, reorganize and liquidate customs posts, specialized customs authorities, the competence of which is limited by certain powers, to perform certain functions assigned to customs authorities, or to perform customs operations in relation to certain types of goods;
Determine the region of activity of customs authorities;
Approve general or individual regulations on customs authorities.
The Federal Customs Service is not entitled to carry out regulatory legal regulation in the established field of activity, except in cases established by federal laws, decrees of the President of the Russian Federation and resolutions of the Government of the Russian Federation, as well as the functions of managing state property and providing paid services.
2. Goals, objectives and functions of the customs authorities.
The main goals, tasks and functions of the customs authorities are determined in Chapter 39 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation.
The Customs Code defines the customs authorities as law enforcement and as an integral part of the forces for ensuring the economic security of the Russian Federation. They are designed to directly ensure compliance with customs legislation and other legislation, the control over the implementation of which is entrusted to the customs authorities.
Diverse in nature, the activities of the customs authorities are aimed at solving the following main tasks.
The solution of economic problems is achieved through the participation of customs authorities in ensuring, within their competence, the economic security and unity of the customs territory of Russia, as well as the collection of customs duties, taxes, anti-dumping, special and countervailing duties, customs fees when moving goods across the customs border of the Russian Federation.
The solution of the problems of regulation of the customs business is achieved through the organization of the application and improvement of the means of customs regulation, based on the priorities of the development of the economy of the Russian Federation. Among such means is making decisions on the classification of goods in accordance with the TN VED, on the country of origin of the goods, on the protection of intellectual property rights, on ensuring the uniform application of customs legislation by customs authorities, etc.
The solution of law enforcement tasks is achieved by identifying facts of violation of the rules, prohibitions and restrictions established by the customs legislation, performing urgent investigative actions and inquiries in criminal cases and proceedings in cases of administrative offenses on the facts of customs offenses.
The activity of the customs authorities is expressed in the performance of numerous functions by them. They reveal the essence and content of the executive, control and supervisory activities at all levels of customs management and are a reflection of the distribution of responsibilities between individual bodies that make up single system customs authorities.
Classifying the functions of customs authorities, they can be divided into basic and providing.
The main functions reveal the essence of the management activities of the customs authorities. The list of the main functions of the customs authorities is enshrined in Article 403 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
Implementation of customs clearance and customs control, creation of conditions conducive to the acceleration of trade across the customs border;
Collection of customs duties, taxes, anti-dumping, special and countervailing duties, customs fees, control over the correctness of calculation and timeliness of payment of the said duties, taxes and fees, taking measures for their enforcement;
Ensuring compliance with the procedure for the movement of goods and vehicles across the customs border;
Ensuring compliance with the prohibitions and restrictions established in accordance with Russian legislation on state regulation of foreign trade activities and international treaties of the Russian Federation in relation to goods transported across the customs border;
Ensuring, within its competence, the protection of intellectual property rights;
Combating smuggling and other crimes, administrative offenses in the field of customs, suppression of illicit trafficking across the customs border of narcotic drugs, weapons, cultural property, radioactive substances, endangered species of animals and plants, their parts and derivatives, objects of intellectual property, other goods, as well as assistance in the fight against international terrorism and the suppression of unlawful interference at Russian airports in the activities of international civil aviation;
Implementation, within its competence, of currency control of operations related to the movement of goods and vehicles across the customs border, in accordance with Russian legislation on currency regulation and currency control;
Maintenance of customs statistics of foreign trade;
Ensuring the fulfillment of the international obligations of the Russian Federation in the part related to customs, cooperation with customs and other competent authorities of foreign states, international organizations dealing with customs matters;
Implementation of informing and consulting in the field of customs affairs, providing state bodies, organizations and citizens with information on customs issues in the prescribed manner;
Holding competitions and concluding state contracts for the implementation of research work in the field of customs.
The supporting functions of the customs authorities include all types of administrative and economic activities:
Personnel activities;
Financial, accounting activities;
Psychological and educational activities and social security;
Logistics;
Development of customs infrastructure, capital construction, etc.
The list of functions of the customs authorities is concretized and detailed in the Regulations on the federal executive body authorized in the field of customs affairs, and in general provisions about other customs authorities.
Customs bodies carry out their functions both independently and in cooperation with other state bodies. This applies primarily to financial and tax authorities, the border service, transport authorities and other authorities directly related functionally with the customs authorities.
3. Prospects for the development of the customs service
The target program determines the strategic goal of developing the customs service to implement national tasks in the field of customs and ensure unconditional and full compliance with the customs legislation of the Russian Federation for the economic prosperity and social well-being of the nation.
The strategic goal will be achieved by solving the following tasks.
Task 1. All-round assistance in the development of trade, acceleration of trade and expansion of Russia's foreign trade relations.
Task 2. Filling the revenue part of the federal budget of the Russian Federation.
Objective 3. Reducing potential threats to the state caused by the movement of goods prohibited, restricted for import (export) into the territory of the Russian Federation or the illegal movement of goods across the customs border of the Russian Federation, as well as illegal foreign exchange transactions that can harm society or undermine the country's economy. Improving the management system of customs authorities.
The listed tasks correspond to the functions of the Federal Customs Service, which are enshrined in Article 403 of the Customs Code of the Russian Federation and the Regulations on the Federal Customs Service.
To solve the tasks defined by the Target Program, comprehensive measures have been developed that will be implemented through the implementation of three departmental budget programs.
1. Departmental budget program "Customs border. Improving customs control at checkpoints across the border of the Russian Federation". This program will allow:
Ensure the necessary and sufficient level of control over goods and vehicles moving across the border;
Create conditions for speeding up customs procedures;
Ensure the use of the latest information and customs technologies in the activities of customs posts and customs at the border; to strengthen the customs infrastructure on the State Border of the Russian Federation through the construction, reconstruction and operation of automobile checkpoints and other customs infrastructure facilities;
Ensure the detection and suppression of crimes and other offenses when moving goods across the border;
Strengthen the personnel potential of customs posts (customs clearance and customs control departments) located at checkpoints;
Raise the level of logistical and information support border customs authorities.
2. Departmental budget target program "Administration and control over compliance with international trade agreements. Customs clearance and customs control in the territories of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation". This program will allow:
Ensure the fulfillment of the planned tasks of the Government of the Russian Federation for the transfer of customs payments to the federal budget;
Ensure the necessary and sufficient level of control over goods and vehicles at the places of customs clearance;
Create conditions for accelerating the process of customs clearance and customs control of goods and vehicles at the places of customs clearance;
Ensure the use of the latest information and customs technologies in the activities of customs posts and customs in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation;
Ensure the detection and suppression of crimes and other offenses in the field of customs and currency legislation in the field of foreign trade activities;
Strengthen the customs infrastructure of customs posts located within the country through the construction, reconstruction and operation of administrative buildings (office premises), the creation of temporary storage warehouses and customs warehouses established by customs authorities;
Strengthen the personnel potential of customs posts located within the country (departments of customs clearance and customs control);
To raise the level of material, technical and information support of customs posts and customs houses in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
3. Departmental budget target program "Institutional development and formation of the information and technical potential of customs authorities. Organization of the implementation of the customs legislation of the Russian Federation and international treaties of the Russian Federation". This program will allow:
To improve the efficiency of the customs administration system;
Ensure the organization of customs clearance and control processes;
Modernize the information system of customs authorities;
To increase the effectiveness of ongoing measures to combat smuggling and violations customs regulations;
Expand and strengthen international cooperation;
Strengthen the system of departmental control;
Provide training, retraining and advanced training of personnel;
Provide medical care and social guarantees customs officials;
Raise the level of material and technical, legal, financial, personnel, information support of customs authorities.
Thus, the activity of the customs authorities is universal and specific, it has no analogues. Its versatility is manifested in the variety of social functions performed by the customs authorities. Fundamental changes in the economy, the demonopolization of foreign economic activity, the separation of customs authorities into an independent state structure, and many other factors led to the fact that more than 20 ministries and departments of Russia transferred part of their powers and functions to the customs authorities: economic, statistical, environmental, etc. functions has become an integral element of the competence of the customs authorities of the Russian Federation.
The activity of the customs authorities as executive authorities is expressed in the performance of the functions assigned to them by the state.
Conclusion.
A special place among the subjects of customs law is occupied by state customs officers working both in customs authorities and in other organizations subordinate to the State Customs Committee of Russia, directly involved in the implementation of customs affairs in the country.
The concept of "customs service" like many others legal categories can be considered in the broad and narrow sense of the word. In a broad sense, the customs service should be understood as the totality of customs authorities and other organizations of the State Customs Committee of Russia, directly involved in the implementation of customs affairs, the legal status of customs officials, as well as the procedure and conditions for passing public service in the customs authorities and organizations of the customs service. The customs service in the narrow sense is a type of professional activity to ensure the powers of the customs authorities.
A state customs officer is a citizen of the Russian Federation who, in accordance with the procedure established by law, performs the duties of his position in the customs bodies and organizations of the customs service for a monetary reward paid from the federal budget, and who, in the manner prescribed by law, has been awarded a special rank.
The position should be understood as a separate and fixed in official documents part of the organizational structure of the customs authority with the corresponding part of the competence of this customs authority, granted to a person - a civil servant for the purpose of its practical implementation. The position determines the range of duties, the rights and limits of responsibility of the state customs officer, the requirements for his professional and qualification training. It reflects the content of the work performed by the customs officer and determines his legal position in the general system of the state customs service.
The content of the activities of the customs authorities is the performance of their functions to implement the tasks of the customs business in the country. There are many ways to implement these functions, so the form of activity must be characterized, first of all, as a part, more precisely, one of the parts into which the activities of the customs authorities for the implementation of the functions assigned to them can be divided. Moreover, this part of the activity, firstly, must be objectively expressed in some way, and secondly, it must differ from other forms of similar activity.
Legality is one of the basic principles of the state customs service. It has a constitutional basis and means that all the activities of the customs authorities and their officials must be carried out on the basis of strict and unswerving compliance with the requirements of the current Russian legislation. Strict service discipline must also be observed in each customs authority or organization of the customs service.
The implementation of general supervision over the activities of customs authorities and their officials is within the competence of the prosecutor's office, whose activities are regulated by the law of the Russian Federation. In case of detection of violations in the activities of customs authorities and their officials, the prosecutor is obliged to respond appropriately: bringing a protest, making a presentation and issuing an appropriate decision.
List of used literature:
2. Federal Law No. 164-FZ of December 8, 2003 "On the Fundamentals of State Regulation of Foreign Trade Activities" (as amended on February 2, 2006)
3. Federal law in the Russian Federation "On currency regulation and currency control" dated 10.12.2003 173-FZ (as amended on 2207.2008)
4. Legal support of the new organization and activities of customs authorities: the state and tasks of further improvement (A.F. Nozdrachev, "Legislation and Economics", N 2, 3, 4, February, March, April 2008)
5. Stages of customs clearance (Berator "Practical encyclopedia of an accountant. Currency. Export. Import") (as amended in November 2007)
6. Control of customs value in the system of state regulation of foreign economic activity (A.V. Agapova, "Financial Bulletin: Finance, Taxes, Insurance, Accounting", N 1, January 2008)
7. Order Federal Service on technical and export control of April 4, 2008. N 79 "On approval of the Administrative Regulations of the Federal Service for Technical and Export Control for the performance of the state function of issuing opinions on the application of non-tariff regulation measures in the implementation of foreign economic activity"
8. Order of the Ministry of Industry and Energy of the Russian Federation dated February 27, 2008. N 79 "On approval of the Recommendations on the organization of work on the collection and processing of information for the preparation of schedules for the transportation of oil outside the customs territory of the Russian Federation and the transit of oil of the CIS member states through the customs territory of the Russian Federation "
9. Gabrichidze B.N. Customs law. 2nd ed., corrected. and additional - L.: Law and Law, 2007. - 500 p.
10. Khalipov S.V. Customs law (Customs regulation of foreign economic activity). 2nd ed., corrected. and additional - M.: IKD Zertsalo, 2008. - 276 p.
The functions of the customs authorities are the main activities of the customs authorities. From this point of view, a special role is played by the importance of customs authorities from the standpoint of the economic development of the Russian Federation and the growth of trade between Russia and foreign countries. The role of customs authorities in the foreign policy activities of the Russian Federation determines a special “set” of functions of customs authorities, but at the same time, the relationship with the implementation of the most important socio-economic and foreign policy programs does not limit the diversity of functions of customs authorities.
The customs authorities of the Russian Federation are federal executive bodies, links in the system of state administration. Customs authorities are classified as executive authorities in accordance with the structure of federal executive authorities approved by the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated March 9, 2004. Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of March 9, 2004 No. 314 “On the system and structure of federal executive bodies” СЗ of the Russian Federation of March 15, 2004 N 11 Article 945 Based on the understanding of the executive power as an activity consisting in the practical organization and implementation of norms and provisions of the Constitution, federal laws and other norms and provisions of the Constitution, federal laws and other legal acts, it can be said that the customs authorities, as executive authorities, carry out executive and administrative activities in the field of customs.
The executive activity of these bodies consists in the daily practical organization and implementation of customs affairs.
Customs authorities, using a variety of forms and methods, exercise their functions and powers in the field of organizing the movement of goods and vehicles across the customs border; collection of customs payments; customs clearance and control, etc. These areas are the main ones in the activities of the customs authorities.
Note that in these areas of activity, the customs authorities act as administrative and executive bodies.
Customs authorities carry out both administrative and executive-organizational activities. Both of these activities are closely interrelated and together form a single whole. At the same time, the administrative activity of the customs authorities has its own characteristics, the most important of which is its normative nature.
It is manifested in the adoption by the customs authorities of the relevant legal acts. Executive (organizational-executive) activity can be carried out in other forms. These are, in particular, working meetings of employees of departments, departments and sectors of customs authorities; meetings for the exchange of experience and in the process of retraining customs personnel; scientific and methodological, practical conferences and seminars for customs officials.
An important distinguishing feature of the customs authorities is that they are classified as law enforcement agencies by the current legislation. This characterization requires further explanation. In the broad sense of the word, any state body can be considered law enforcement. However, there is and is generally accepted a narrower understanding of the term "law enforcement agencies": they usually include judicial and prosecutorial bodies, the bar, notaries, internal affairs bodies, etc. See. more details: Gabrichidze B.N. and etc. Law enforcement Russian Federation. Moscow, 2002, pp. 8-96.
The law enforcement nature of the activities of the customs authorities is largely due to the very structure of the customs business, as well as the fact that all the main tasks and powers in the field of customs affairs are carried out by the customs authorities taking into account the interests of the country, strengthening, its economic sovereignty and economic security.
Since both general and specific tasks and functions of the customs authorities are determined in the customs legislation, the core of which is the Customs Code, it is appropriate in this case to refer to its preamble: "The Code is aimed at protecting the economic sovereignty and economic security of the Russian Federation ... ensuring the protection of the rights of citizens, economic entities and state bodies and their observance of their duties in the field of customs”. In this case, state bodies are understood as a wide range of state bodies (and not just customs authorities) that, in accordance with the law, have duties in the field of customs. It can be concluded that the customs business itself and the customs authorities initially, due to the specific nature and structure of the customs business, are law enforcement in nature and in most cases act in this capacity.
The law enforcement nature of the activities of the customs authorities also has more specific specific manifestations, which are clearly visible when analyzing the structure of the customs business, as well as a number of individual powers of these authorities. Article 408 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation The complex nature of the customs business predetermines the presence of heterogeneous elements in it, including law enforcement, and the corresponding activities of the customs authorities. In accordance with these articles, the customs authorities are bodies of inquiry in cases of smuggling and a number of other crimes in the field of customs (Articles 151, 157 of the Criminal Procedure Code of the Russian Federation), in cases specified by the Labor Code, these bodies carry out operational-search activities.
The code establishes two goals for the implementation of operational-search activities by customs authorities:
1) detection, prevention, suppression and disclosure of crimes, the production of urgent investigative actions and inquiries on which the criminal procedural legislation of the Russian Federation is assigned to the jurisdiction of the customs authorities ( art.151, 157 Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation), identification and identification of persons who prepare them, commit or have committed them;
2) ensuring their own security.
To achieve these goals, the customs authorities have the right to carry out operational-search measures, the list of which is enshrined in Article 6 Federal Law "On operational-search activity" and is exhaustive: survey; making inquiries, collecting samples for comparative research; test purchase; research of objects and documents; observation; identification of the person; inspection of premises, buildings, structures, terrain and vehicles; control postal items, telegraphic and other messages; listening telephone conversations; removal of information from technical communication channels; operational implementation; controlled delivery; operational experiment. The bulk of the work in connection with the proceedings on cases of violations of customs rules and their consideration is assigned to the customs authorities and their officials.
In view of the special managerial, consolidating and organizing role, the specific nature of the tasks and functions performed by the FCS of Russia, the leading role of this central body in the implementation of the Labor Code and the allocation of its place in the Code itself, as well as the practical organization of its customs activities Let's analyze it in more detail. legal status, composition, structure and fundamental issues of application of the provisions and norms of the Labor Code. Unfortunately, in the Code itself, the status and functions of the Federal Customs Service of Russia are formulated very schematically and concisely: in essence, there is no detailed description of the legal and functional organization of the FCS.
The Federal Customs Service is a federal executive body exercising, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, the functions of control and supervision in the field of customs affairs, as well as the functions of a currency control agent and special functions to combat smuggling, other crimes and administrative offenses. The Federal Customs Service is under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Economic Development and Trade of the Russian Federation.
Today, the Federal Customs Service carries out following features: See attachments
issues qualification certificates for customs clearance specialists;
provides metrological support for the activities of customs authorities.
The Federal Customs Service carries out the following powers in the established field of activity:
1. collects customs duties, taxes, anti-dumping, special and countervailing duties, customs fees, controls the correct calculation and timely payment of the said duties, taxes and fees, takes measures to enforce their collection;
2. ensures compliance with the prohibitions and restrictions established in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on state regulation of foreign trade activities and international treaties of the Russian Federation in relation to goods transported across the customs border of the Russian Federation;
3. ensures the uniform application by the customs authorities of the customs legislation of the Russian Federation;
4. carries out customs clearance and customs control;
5. makes decisions on the classification of goods in accordance with the Commodity Nomenclature for Foreign Economic Activity and ensures the publication of such decisions;
6. ensures, within its competence, the protection of intellectual property rights;
7. takes, in accordance with the established procedure, preliminary decisions on the classification of goods in accordance with the Commodity Nomenclature for Foreign Economic Activity, on the origin of goods from a particular country (country of origin of goods);
8. carries out:
8.1. maintenance of registers of persons carrying out activities in the field of customs;
8.2. maintaining a register of banks and other credit institutions having the right to issue bank guarantees for the payment of customs duties;
8.3. maintenance of the customs register of objects of intellectual property;
8.4. cancellation of qualification certificates of customs clearance specialists;
8.5. issuance of licenses for the establishment of a free warehouse;
9. keeps customs statistics of foreign trade and special customs statistics;
10. informs and advises, free of charge, on customs issues of participants in foreign economic activity;
11. carries out, within its competence, currency control of operations related to the movement of goods and vehicles across the customs border of the Russian Federation;
12. carries out proceedings on cases of administrative offenses and consideration of such cases in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on administrative offenses;
13. carry out inquiry and conduct urgent investigative actions in accordance with the criminal procedure legislation of the Russian Federation;
14. carry out operational-investigative activities in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation;
15. Carries out in accordance with the established procedure the development and creation of documents used by the customs authorities information systems, information technologies and means of their provision;
16. performs the functions of the main manager and recipient of federal budget funds provided for the maintenance of the Service and the implementation of the functions assigned to it;
17. ensures, within its competence, the protection of information constituting a state secret;
18. Consider complaints against decisions, actions (inaction) of customs authorities and their officials;
19. organizes the reception of citizens, ensures timely and complete consideration of citizens' appeals, makes decisions on them and sends answers to applicants within the period established by the legislation of the Russian Federation;
20. ensures the mobilization training of the Service, as well as control and coordination of the activities of organizations under its jurisdiction for mobilization training;
21. organize vocational training customs officials, their retraining, advanced training and internships;
22. carries out, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, work on the acquisition, storage, accounting and use of archival documents formed in the course of the activities of the Service;
23. interacts in accordance with the established procedure with state authorities of foreign states and international organizations in the established field of activity, including representing, on behalf of the Government of the Russian Federation, the interests of the Russian Federation in the World Customs Organization (Customs Cooperation Council) and other international organizations;
24. holds competitions in accordance with the established procedure and concludes government contracts to place orders for the supply of goods, performance of work, provision of services for the needs of the Service, as well as for the conduct of research work for state needs in the established field of activity;
25. performs the functions of a customer for the construction of customs, customs checkpoints and other facilities necessary for the development of customs infrastructure;
26. performs the functions of the customer for the development of sketches and the production of excise stamps for marking alcoholic products, tobacco and tobacco products imported into the customs territory of the Russian Federation;
27. implements programs for the development of customs in the Russian Federation.
and other functions within its competence.
The Federal Customs Service, in order to exercise its powers in the established field of activity, has the right:
1. in agreement with the Ministry of Economic Development and Trade of the Russian Federation:
create, reorganize and liquidate customs posts, specialized customs authorities, the competence of which is limited by individual powers to perform certain functions assigned to customs authorities, or to perform customs operations in relation to certain types of goods; determine the region of activity of customs authorities;
approve general or individual regulations on customs authorities;
2. organize the conduct of the necessary research, testing, expertise, analyzes and evaluations, as well as scientific research in the established field of activity;
3. request information necessary for making decisions on issues related to the established field of activity;
4. give legal and individuals clarifications on issues related to the established field of activity;
5. exercise control, including financial control, over the activities of customs authorities and representative offices of the Service abroad;
6. to involve, in accordance with the established procedure, scientific and other organizations, as well as scientists and specialists, for the study of issues related to the established field of activity;
7. apply restrictive, preventive and preventive measures provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation, aimed at preventing and (or) suppressing violations legal entities and citizens mandatory requirements in the established field of activity, as well as measures to eliminate the consequences of these violations;
8. create advisory and expert bodies (councils, commissions, groups, colleges) in the established field of activity;
9. develop and approve samples of service certificates and the procedure for wearing uniforms.
7. The Federal Customs Service is not entitled to carry out regulatory legal regulation in the established area of activity, except for cases established by federal laws, decrees of the President of the Russian Federation and decrees of the Government of the Russian Federation, as well as the functions of managing state property and providing paid services. For example, these restrictions do not apply to the powers of the head of the Service for managing property assigned to the Service on the basis of operational management, resolving personnel issues and organizing the activities of the Service.
The FCS of Russia carries out its activities in cooperation with other federal executive authorities, authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and public associations.
In the system of government bodies for foreign economic activity (hereinafter referred to as foreign economic activity), a special role is assigned to the customs service of the Russian Federation, which is currently undergoing a new stage of its development and reform.
The Law of the Russian Federation No. 61-FZ dated May 28, 2003 adopted a new Customs Code of the Russian Federation. This was already the second codified regulatory legal act in the field of customs legislation, which entered into force on January 1, 2004.
In accordance with Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of March 9, 2004 No. 314 on the system and structure of federal executive bodies, the State Customs Committee of the Russian Federation was transformed into the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation (clause 15), which is under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Economic Development and Trade of the Russian Federation.
In pursuance of this by-law legal act The Minister of Economic Development and Trade of the Russian Federation adopted Order No. 190 dated July 5, 2004 “On organizational measures to transform the State Customs Committee of Russia into a federal customs service. Not published in official sources. On August 21, 2004, the Regulations on the Federal Customs Service were approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation.
The purpose of the customs authorities of the Russian Federation is to implement customs regulation through the most efficient use of customs control tools and regulation of commodity exchange, participation in the implementation of tasks to promote foreign trade, stimulating the development of the national economy and a number of other goals.
The main tasks of the customs authorities of the Russian Federation:
- - collection of customs payments in full and their transfer to the federal budget;
- - exercising state control over compliance by participants in foreign economic activity with prohibitions and restrictions when moving goods across the customs border of the Russian Federation;
- - control over the implementation of foreign economic activity using the means of tariff and non-tariff regulation;
- - detection, prevention, suppression and disclosure of crimes and administrative offenses in the customs sphere;
- - implementation of the search for persons hiding from the preliminary investigation bodies and the court, evading criminal punishment, as well as the search for missing persons;
- - obtaining information about events or actions that pose a threat to the state, military, economic or environmental security of Russia.
According to Art. 403 of the Customs Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), customs authorities perform the following main functions:
- - carry out customs clearance and customs control, create conditions conducive to the acceleration of the exchange of goods across the customs border of the Russian Federation;
- - levy customs duties, taxes, duties, customs fees, control the correctness of the calculation and timeliness of payment of the said duties, taxes, fees, take measures to enforce their collection;
- - ensure compliance with the procedure for the movement of goods and vehicles across the customs border;
- - ensure compliance with the prohibitions and restrictions established in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on the state regulation of foreign trade activities and international treaties of the Russian Federation in relation to goods transported across the customs border;
- - ensure, within their competence, the protection of intellectual property rights;
- - fight against smuggling and other crimes, administrative offenses in the field of customs, stop illegal circulation of narcotic drugs, weapons, cultural values, radioactive substances, endangered species of animals and plants, objects of intellectual property, other goods across the customs border, as well as assist in the fight against international terrorism and the suppression of unlawful interference at the airports of the Russian Federation in the activities of international civil aviation;
- - carry out, within their competence, currency control of operations related to the movement of goods and vehicles across the customs border, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on currency regulation and currency control;
- - conduct customs statistics of foreign trade;
- - ensure the fulfillment of the international obligations of the Russian Federation in terms of customs affairs, cooperate with customs and other competent authorities of foreign states, international organizations;
- - carry out informing and consulting in the field of customs, provide state bodies, organizations and citizens with information on customs issues in the prescribed manner;
- - carry out research work on customs matters.
The Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation (FTS of Russia) is the central body that directly manages the customs business. It has the right to create institutions that are part of the system of customs authorities, but do not carry out law enforcement. In accordance with Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 429 of August 21, 2004, the FCS, as one of its powers, “carries out proceedings on cases of administrative offenses.”
Regional customs departments of the Russian Federation (RTU) are an intermediate link between the FCS of Russia and customs. RTUs are included in the unified system of customs authorities of the Republic of Vietnam and carry out operational management of customs affairs on the territory of subordinate regions under the direct supervision of the Federal Customs Service of Russia.
Customs directly implement the bulk of the tasks of customs in their area of responsibility and manage the activities of subordinate customs posts. They, depending on their territorial distribution, are divided into border and internal.
Border customs include customs offices and customs posts located at the points of intersection of transport routes of the border of the Russian Federation, as well as at airports, seaports. These include points of transition (pass) for all types of vehicles across the border of the Russian Federation. As a rule, they record the passage of goods and vehicles across the border and report this to internal customs carry out customs control.
Internal include customs and customs posts located in the places of concentration of participants in foreign economic activity (recipients and senders of goods) in the customs territory of the Russian Federation. They carry out customs clearance of goods and control over their delivery, collection of due customs payments and other customs procedures directly on the spot.