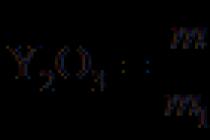Exists great amount classifications that define types of consumers. One of the approaches to this issue is associated with the name of Carl Ransom Rogers, an American psychologist, one of the most prominent figures of the 20th century. He is considered the creator of an important direction in psychology - humanistic. His merits are also known in the field of psychotherapy. It is the works of Rogers that marketers and advertisers use today, evaluating the types of consumers by the speed of product adoption, taking into account the psychological parameters of personal behavior.
The most common types, according to Rogers, are:
- o innovators;
- o quickly accepting;
- o early majority;
- o late majority;
- o Conservatives (belated).
The essence of different types of consumers is extremely important for understanding which advertising message to address to different groups, because each of them has its own characteristics.
The group of innovators, as a rule, is characterized by a strong desire for innovation and implementation, mobility and youth. In addition, those belonging to this group have long recognized the global nature of the world and, to some extent, are especially in relation to the world of goods and services that they are offered to use. Job-tori are receptive to advertising, respond to suggestions because of the desire to try, improve the conditions of their life or work. Innovators perceive advertising messages in all distribution channels. In recent years, it has been recorded that this group is more focused on information on the Internet. But traditional media - newspapers, magazines, radio and television - serve as important information sources for them. The core of the group of innovators is youth.
Example
A special term "youth marketing" has appeared, which is no longer exotic in Russia either. It has gone through a fast path of inevitable ideological adaptation in the last decade and continues to evolve within the framework of modern market economy. Indicative in this regard is the activity of trend-setters - people who adopt innovative ideas and carrying them "to the people". One of these ideas is good. Ki.ta conducted a 2007 study of the blogosphere. According to the study, bloggers are the most advanced and receptive part of society to everything new. Most of them are the conductors of fashion trends among the youth, active consumers. Most of the blog owners are in the age range of 15-35 years.
Group fast accepting characterized by high social status. Consumers of this group have already reached a certain position in society, many of them are opinion leaders in other groups. This group consists of young, but mostly middle-aged people who have clearly defined their life priorities. Advertising messages, like innovators, they perceive using all channels of information. But the purchase decision is made more meaningfully, more rationally, taking into account consumer characteristics, and not fashion, novelty, unusualness. The group of fast accepters is also characterized by autonomy and independence in making decisions about the purchase and use of the goods.
Group early majority, like the group of fast accepters, it has the status of middle and above average both in terms of the social hierarchy and in terms of income. However, this group is less independent in decision-making and most often perceives first the reaction of innovators and quick adopters, and only then makes its own decision. At the same time, the trial purchase made by the consumer of this group and the acceptance of the product itself can have a significant time gap. The group perceives advertising messages through the media and other distribution channels of advertising, but this requires additional sources, such as from sellers, members of other groups, or influencers, so that the advertised product is considered for purchase.
Group of consumers under the conditional name late majority has, as a rule, status and income below the average. A consumer of this type is very concerned about the opinions of others, needs the approval of his own kind. This audience is more difficult to reach through the media, it is important for them to navigate and see the goods on the shelves in the store, these people are influenced by other representatives of their own group.
And finally the group conservatives. The name already speaks for itself. Conservatives resist any changes and either do not perceive any new or unusual proposals at all, or perceive them with great doubt and distrust. Representatives of this group generally have a limited circle of social contacts and a low social status. It is believed that this is the most difficult audience in terms of perception of advertising.
When advertising various products and services, of course, these different types of consumers must be kept in mind. However, these groups cannot be fixed in immobility. Depending on the product, the consumer can behave either as a conservative or as an innovator. When introducing a new product to the market, the company is interested in the fastest possible adoption of it by various groups. The speed and degree of acceptance depends on the benefits that the new product provides to the buyer:
- about what newer product, the slower the adoption process goes, the more it needs to be advertised;
- o the more complex the product, the longer the approval process, the more carefully it is necessary to approach the creation of advertising messages that could simply and competently explain the features and benefits of this product;
- o The easier it is to test/test the product, the faster the acceptance process. A product that is on the shelf and displayed in many stores will be accepted faster, but still needs supportive advertising.
The presented consumer type classification model is one of many. There are also many others that can be seen in the specialized literature.
In general, the considered approaches to consumer segmentation give an idea of the main framework for dividing consumers into groups according to different type grounds. Nevertheless, it should be noted that specific features of each classification group may change over time depending on the development of the market and the consumers themselves, their movement in space and in hierarchical and social planes. However, there are some general psychological features of perception that are important to understand when developing advertising. It is in the sphere of general approaches that ways of influencing target audience, which will be discussed in more detail below.
The need to attract additional financial resources for institutions of culture, sports, education contributed to the emergence of Clubs of Friends, Boards of Trustees;
There is a creation and restoration of children's unions and organizations (scouts);
Arise professional associations, for example, the Association of University Graduates, territorial Associations (Unions) of psychologists, veterinarians, marketers;
There is an association of citizens on a territorial basis (Council of the microdistrict).
All these examples show that the activity public organizations is multifaceted and affects different aspects of public life, allows a person to fulfill himself, increases his self-awareness, gives him a sense of belonging, contributes to his professional growth, allows you to express your civic position, i.e., the activities of NGOs in many ways contribute to the socialization of the individual.
Considering the three main groups of consumers in territorial marketing It is important to note that different consumer groups have their own specific needs, desires and expectations. To assess the expectations of different groups of consumers, it is possible to decompose the territorial product, highlighting those characteristics (parameters) of the territorial product that are more significant for individuals, commercial organizations and non-profit public organizations (Table 3).
Table 3 - Expectations different groups consumers of the territorial product
| What would private individuals (residents) want to have? | What would businesses/entrepreneurs want to have? | What would you like to have non-profit organizations? | |
| In terms of territory resources | Certain parameters of climate, social and technological resources | Certain natural, / technological, property, human, financial resources territories | The actual presence of potential objects and subjects of activity of a public organization |
| From the point of view of the socio-economic state of the territory | Certain living conditions, high quality and standard of living | Maximum Income and minimum costs for the conduct of activities, including the solution of socio-economic problems of the development of the territory | A certain level of solving the main tasks that are the subject of the activity of a public organization |
| From the point of view of territory management | Receipt Guarantees public services certain quality | Stable rules of the game, reduction of unjustified interference in current affairs, assistance with business investments | Assistance or non-interference in the activities of a public organization |
The implementation of such a decomposition in territorial marketing makes it possible to evaluate the same component of a territorial product in different ways, for example, the specifics of assessing the achieved level of socio-economic development of a territory in the understanding of residents and businesses of the territory. On the other hand, one can raise the question of choosing priorities or finding compromises in an attempt to combine the interests of different segments regarding a particular territory resource. For example, can logging, which is significant for business, be combined with the preservation of the forest as an object of study, entertainment and recreation for the inhabitants of the territory?
After the analysis of enlarged groups of consumers in territorial marketing, it is possible to conduct microsegmentation.
Consumers are individuals and organizations that buy or acquire goods and services for personal consumption, resale or rental. Consumers are the central object of marketing. There are five types of consumers that differ in their behavioral strategies in the markets.
1. Individual consumers purchase goods solely for their own personal use. Individual consumers are interested, first of all, in the consumer properties of the product: usefulness, price, external data, internal packaging.
2. Families or households- the main type of consumer of food and non-food consumer goods.
3. Intermediaries, making purchases not for consumption, but for subsequent resale. They are not interested in the consumer qualities of the goods, but in their exchange characteristics - demand, absolute price, profitability, speed of circulation, transport packaging, shelf life.
4. Suppliers or company representatives. The buying process, from the recognition of the problem to the assessment of the performance of the supplier, is clearly formalized. This takes into account: the price and quality characteristics of each product, the promptness of deliveries and fare, completeness of the assortment, the reputation of the manufacturer, consultations and reference literature, the possibility of obtaining a loan.
5. Officials or responsible persons state and public institutions = generalists. Officials do not spend their own, but public funds, so the purchase procedure is formalized and bureaucratized.
In their attitude to new products, consumers are divided into 5 categories:
- superinnovators- 2.5%, people who are prone to risk and experiment, have a high social status, and belong to the upper group in terms of income;
- innovators- 13.5%, less inclined to take risks, more cautious in their actions;
- ordinary- 34% are thorough, try not to take risks, are active in public life;
- conservatives- 34%, do not approve of innovations, willingly imitate ordinary ones. Among them are many elderly and low-income people employed in low-prestige jobs;
Superconservatives - 16%, are against any changes, remain committed to the habits and fashions of their youth, are devoid of aesthetic flair and creative imagination.
Consumers are heterogeneous in their characteristics. consumer can be classified by highlighting various features, for example, according to the directions of use goods, psychological characteristics, attitude to price, etc.
Types consumers by direction of use goods
|
Characteristic |
|
|
Individual consumers |
People using wealth And services For reproduction life, for work or social activities, to ensure a certain style and lifestyle and spiritual culture. |
|
Mass consumers (legal entities) |
Organizations, institutions, companies, associations, etc., using material goods and services for their professional activities (but not for production or trade). |
|
Industrial consumers |
manufacturing enterprises, firms, cooperatives, trade enterprises and service industry enterprises using material goods and production services for production (including trade) purposes. |
Types consumers according to psychological characteristics
|
Characteristic |
|
|
movable need |
The people are poor; main need at least somehow ensure their everyday existence. |
|
Integrated Personalities |
Psychologically stable, self-asserted middle-aged people, well-educated, financially secure, with a sense of proportion, active in charity. |
|
Extroverts |
stable, conservative (workers and pensioners) imitators (average education and good income) reached a high position in society (leaders in business, in government) |
|
introverts |
egocentric (young, impulsive, often changeable) cheerleaders (active, have a good income, education) Self-aware members of society (interested in the environment, future, personal growth, have a decent income)- |
Types consumers in relation to the price
|
Typeconsumer |
Characteristic |
|
Economical |
Focused primarily on price level |
|
Apathetic |
The price is not important, the main thing is convenience, prestige or quality |
|
Rational |
Evaluates the purchase in terms of price and quality of the product |
|
personalized |
Product image is more important than price, but still it has an impact on the purchase |
Typesconsumers on the basissociability
Revealed type consumer in the target market companies, allows it marketing voi service to develop tools to influence the buyer, adapted to its characteristic features and behavior, which generally works to increase the level of sales.
Consumer groups - WHO is a consumer and receives satisfaction of their needs and desires
The main client groups are individuals and organizations, which, in accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, are divided into commercial and non-commercial. Non-profit organizations are non-profit-making, operate in the public interest, and may include both individuals and commercial organizations, or both. It turned out three main groups of consumers of the territorial product: individuals, commercial organizations and non-profit organizations. Let's consider each consumer group in more detail.
The first group of consumers are individuals. Individuals in modern Russia received much more rights and opportunities. Territorial authorities should take into account the fact that a modern Russian:
- has the ability to move freely throughout the country (there is no mandatory registration at the place of residence and problems with employment in the presence of citizenship);
- can acquire (rent) and sell housing in the primary/secondary market;
- expects to receive a certain level of quality of life for himself and would like to be sure of a worthy future for his children;
- has the right to compare different territories, and has a lot of information about how people live in other territories;
- tends to material well-being and correlates expected income and expenses when living in different territories;
- has the opportunity to actively search for a job after graduating from higher and secondary vocational educational institution(there is no mandatory "allocation" to work). It is necessary to recognize the high expectations and demands that a person makes to the conditions of life and to the quality of territorial management. A dissatisfied resident "votes with his feet", which means that the territory is left without its main - human resource. An adult leaves the territory with children, depriving the territory of the future, taking with him financial resources current and investment character. If the territory wants to develop successfully, then everything should be done so that people are satisfied with the quality and living conditions, and not prefer the competitor's territory.
The second group of consumers - commercial organizations. Most commercial organizations are privately owned (either individually or collectively). The owner determines the mission and goals of the enterprise, sets tasks in the field financial results activities, decides on participation or non-participation in solving social problems of a particular territory. in behavior commercial enterprises there are differences depending on whether these enterprises are already operating or just planning to start work in this territory. But even those enterprises that operate in the territory can:
- refuse to provide services if payment for these services is not made in a timely manner and in full, for example, for heat supply and heating of houses in a settlement;
- abandon the implementation of some previously adopted social programs for employees, if there is a need to solve the production problems of their enterprises;
- carry out a significant reorganization of production with the release of a large number workers;
- attract from another territory cheaper labor force despite the high level of unemployment among the local population;
- refuse to provide sponsorship to solve urban problems, etc.
But their "leaving" the territory, the transfer of business to another territory is associated with certain (often significant) financial losses. Such enterprises are ready to endure disrespect for their interests for a long time, are more likely to come to terms with the poor quality of territorial management, and try to somehow adapt to business conduct manager and style of work of employees of the executive authority.
Another group of commercial organizations are those that can potentially be established in the territory. Such enterprises do not yet risk anything and therefore can compare territories rationally, harshly, without having any moral obligations to the territory. Their assessment of the territory is complex. They are interested in the availability and quality of all resources (human, natural, material, financial, etc.). Special attention they pay to the quality of territorial management. What is business reputation the first person, how the work of the territorial authority is organized, whether there are local investor support programs, how long decisions are made, how corrupt the authorities are, how ready the employees of the authorities are to interact, how quickly information can be obtained - these and many other questions will be asked by the investor . If the answers to these questions do not satisfy the potential investor, he will prefer another territory where a similar analysis has given better results.
If the territory wants to receive benefits from commercial activities (jobs, taxes, participation in solving social problems, etc.), then you should learn to talk to business in a different way (“Give before you take”). It is necessary to understand what needs to be done so that the entrepreneur feels cared for, sees good prospects for his business activities, and is confident in tomorrow wanted to expand its activities. It is necessary to learn to listen and hear, understand the interests of business and be ready to contribute to the realization of these interests. Only then will business activities develop in the territory and financial and other resources will appear for the socio-economic development of the territory and improving the quality of life in the territory.
The third group of consumers - non-profit public organizations(NPO). Non-profit public organizations can unite both individuals and commercial organizations, or both at the same time. Activities on the territory of NPOs always create a good social background and, with properly organized interaction between NPOs and authorities, allow solving many social problems. One of the main features that distinguish the activities of NGOs is the association of caring, enterprising citizens who have an active life position. Members of NPOs are the “vanguard” of the community of citizens of a given territory, it is NPOs that are the first to designate difficult questions, ready to get involved in solving problems, will be persistent in achieving the goal. Each of the NPO participants acts "not out of fear, but out of conscience." The activities of NCOs make it possible to preserve the continuity of actions, public initiatives, even when specific persons are changed - heads of executive authorities and new deputies are elected.
There are a number of prerequisites for the active development of new NGOs:
Development of activities on the territory of Russia of international
public organizations ("Greenpeace") resulted in the creation
NPOs similar in terms of issues;
- new socially negative problems arose in society, which led to the creation of social movements and societies, such as No to Drugs;
- the growth of national self-consciousness and national self-identification led to the creation of societies of national culture, the activities of national communities;
- the expansion of the rights of territorial (especially regional) authorities found expression in the creation of inter-territorial public unions;
- liberation from a single ideology and the development of party movements led to the creation of primary cells of different parties, youth movements of political parties, which was reflected in the nominal funds of political leaders (Gorbachev Foundation);
- the emergence of fundamentally new social groups of citizens and new tasks entailed, for example, the creation of NGOs to support small businesses;
- the need to attract additional resources for institutions of culture, sports, education contributed to the creation of clubs of friends, boards of trustees;
- new children's unions and organizations (scouts) began to appear and to be restored;
- new professional associations have emerged, for example, an association of university graduates, territorial associations (unions) of psychologists, veterinarians, marketers;
- new associations of citizens have emerged on a territorial basis, for example, the public council of the microdistrict, TOS, etc.
The activities of NPOs affect various aspects of public life, allow a person to fulfill himself, increase his self-awareness, give him a sense of belonging, contribute to his professional growth, and allow him to express his civic position, i.e. The activities of NGOs in many ways contribute to the socialization of the individual.
Russia is gradually expanding cooperation territorial bodies authorities with NGOs, because they unite active citizens who are not indifferent to how the territory will develop and how people will live in this territory. The tasks solved by the authorities and NGOs are in many respects similar and involve the achievement of a complex social effect both in the short and long term.
Having considered the three main groups of consumers in territorial marketing, we note that different groups of consumers have their own special needs, desires and expectations. To assess the expectations of different consumer groups, it is possible to decompose the territorial product by highlighting those characteristics (parameters) of the territorial product that are more significant for individuals, commercial organizations and non-profit public organizations (Table 4.2).
Table 4.2
Expectations of different groups of consumers of the territorial product
|
Component territorial product |
Customer needs |
||
|
What would you like have individuals (residents)? |
What would you like to have commercial business enterprises? |
What would non-profit organizations like to have? |
|
|
In terms of resources of the territory |
Certain options climate, social and technological resources |
Certain natural, technological, property, human, financial resources of the territory |
The actual presence of potential objects and subjects of activity of a public organization |
|
socio-economic states territories |
Certain living conditions high quality and standard of living |
Maximum income and minimum costs to conduct business, including number to decide socio-economic tasks of the development of the territory |
Certain level of decision main tasks being object of activity of a public organization |
|
From a management point of view territories |
Guarantees for the receipt of public goods, services of a certain quality |
Stable "rules of the game" reduction of unjustified interference in current business, help when investing in business |
Help or non-intervention in the activities of a public organization |
The implementation of such a decomposition in territorial marketing allows you to evaluate the same component of the territorial product in different ways, for example, the specifics of assessing the achieved level of socio-economic development of the territory
in the understanding of residents and businesses of the territory. At the same time, one can raise the question of choosing priorities or finding compromises in an attempt to combine the interests of different segments regarding a particular resource of the territory.
Worries, needs, desires individual to a large extent may coincide with the target setting of the activities of NGOs (environmental cleanliness, healthy lifestyle life, social well-being of certain groups of citizens, etc.). At the same time, NCOs may have some special needs that are different from the needs of individuals. The target setting of NPO activities is not only the achievement of a greater result by combining private efforts, but it is also the desire for a different quality of the result due to synergistic effect. The activities of NGOs, as a rule, are aimed at achieving social, environmental and other effects not only in the short term (sometimes for this reason, for example, residents who are interested in working now agree to the development of a mineral deposit, and NGOs, worrying about the future of the territory, are actively against). The results and effects of the activities of NPOs can be extended to a wider range of potential users of benefits - "beneficiaries".
Unfortunately, the needs, needs and desires of individuals and commercial organizations in many cases differ, so different elements and characteristics of the territorial product can be significant. For most commercial organizations, the quality of life in this area is almost never a criterion for choosing a location for an enterprise, while for an individual it is the main criterion. Targets for activities can vary considerably. For example, a commercial organization has the goal of making a profit through the extraction of minerals and seeks to reduce production costs by bringing it closer to places of residence, roads, communications, power grids, etc., without worrying about solving the social problems of this territory (while social responsibility Russian business small). The development of a quarry can be carried out close to the settlement, and the export of rock is organized through the settlement, and as a result, local residents live in constant noise, local roads “break” and houses are destroyed, there is an increase in diseases of the respiratory system, people lose their place of traditional gathering of wild plants, etc.).
Let us consider the combination of different interests and needs of individuals interested in the conservation of the forest as an object of study, entertainment and recreation for the inhabitants of the territory, and commercial organizations involved in the harvesting and processing of wood, using the example of the reasonable functioning of specially protected natural areas (hereinafter - 00PT).
In a number foreign countries(Canada, Australia, EU countries) has accumulated successful experience of involving 00PT in the regional and municipal socio-economic space. It took long time to stop considering the creation of protected areas as a "withdrawal" of natural resources from the process of use and thereby reducing the economic capital of the territory in the traditional sense and to see new opportunities for increasing economic capital, as well as a significant increase in the cultural, social and symbolic capital of the territory when creating protected areas. It is important to emphasize that the cultural, social and symbolic capitals of protected areas differ from the corresponding parameters of an urbanized area. The periodic and (or) limited nature of visiting and (or) living in PAs gives these territories a special charm of underdeveloped, intact territories, which creates interest in the territory and in people living or visiting this territory, increases the attractiveness of the territory for guests (scientists). , tourists).
specially protected natural areas is a unique multifunctional system that has a great ecological, scientific, cultural, aesthetic, recreational significance and can become a "growth point" for a given municipality and (or) the region as a whole. But for this, it is necessary that the employees of the local and regional authorities be ready to organize the process territorial administration subject to special legal status and multifunctional nature of the activities of protected areas. By preserving unique natural resources, it is possible to carefully involve them in their use, especially if the SPNT has the status of a biosphere reserve, in the buffer and peripheral zones of which the population lives and limited activities are allowed, for example:
- harvesting forest gifts (berries, mushrooms, medicinal herbs), catching and processing fish;
- production of handicrafts of the indigenous inhabitants of this area;
- providing guests of protected areas with hospitality and related services (food, transport, entertainment and leisure, etc.);
- work with children and adults on issues of ecology and environmental protection;
- professional training and retraining of the adult population, including for the purpose of preserving and developing local trades and crafts;
- activities to preserve both material cultural objects (repair of buildings, structures on the territory) and non-material culture (songs, rituals, etc.);
- training of new 00PT employees from among the residents settlements;
- formation of funds of local museums, holding exhibitions, and together with a cultural institution - preparation of local holidays (ethnic, event, etc.);
- training of local residents in the restoration (construction) of residential and utility buildings and create on their basis in compliance with all necessary requirements guest houses and other places of rest and food for guests of the park. The cooperation of executive authorities, local activists, institutions, NGOs, entrepreneurs with the management and employees of 00PT allows solving many complex tasks of the socio-economic development of the territory of a rural settlement, municipal district. Activation of activities in the field Agriculture, fishing and hunting, the procurement and processing of agricultural raw materials and wild plants is developing, enterprises are being created for the production of environmentally friendly food products. There are prerequisites for the development of various forms and types of tourism (recreational, rural, educational, etc.). There are new opportunities for the implementation of federal, regional and local programs for the development of small businesses and self-employment of the population.
If the territory of 00PT covers several municipalities or parts of municipalities in different regions, inter-territorial cooperation should be developed (development of roadside infrastructure, common social and educational projects, etc.). In addition, it is possible to develop cooperation between different ministries and state committees regional governments (economic development, construction, culture, education, nature management and ecology, agriculture, fisheries and hunting, labor and employment, local self-government development, youth affairs, physical education, sports and tourism, etc.). The result of interdepartmental cooperation can be both the development of settlements within the boundaries of protected areas, and the solution of some issues of the activities of protected areas (provision of personnel, implementation of projects for the restoration, reconstruction of objects of material culture (residential and outbuildings, chapels, etc.). Thus, properly organized cooperation between the authorities and the administration of protected areas makes it possible, if not to remove completely, then to significantly reduce the intensity of the discussion “to preserve or use” unique natural resources.
In general, the analysis of different groups of customers allows us to conclude that depending on the group of consumers, not only expectations and needs change, but also many factors that determine the behavior of different groups of customers. For example, the behavior of a private person is always largely subject to emotional assessments, and a commercial organization - to rational ones. An individual will pay much more attention to the social environment, while a commercial organization can create and cultivate its own organizational culture and their internal rules and rules that may differ from those in the public environment. This is especially noticeable when a foreign investor comes to the territory with their own national and business culture, and the locals find it extremely difficult to “fit” into these foreign rules, finding themselves “in a foreign monastery”, where your “charter” does not apply. So, despite the close historical and cultural ties between Finland and the Republic of Karelia, it was extremely difficult for the inhabitants of Karelia to get used to the rules and norms of employee behavior at enterprises created by Finnish entrepreneurs. The lack of a canteen was unusual (there is a dining room, sinks, kettles, microwave ovens, etc., i.e. the employee has the opportunity to warm up and eat what he brought with him), as Finnish entrepreneurs consider the canteen as a “cost center »; surprised that the norm good behavior it is considered to “warn” the employer about the poor quality of work of some employee, etc. Russian entrepreneurs and those who directly work at enterprises also note certain difficulties in finding understanding, for example, with Chinese partners. Finally, there is an awareness of the need to pay more attention to the national specifics of business behavior and business etiquette when working with foreign investors.
Differences in the needs and behaviors of different groups of customers become more understandable if we build a three-dimensional macro-segmentation matrix (Fig. 4.2).
Rice. 4.2.
Macro-segmentation can be carried out taking into account all three components, for example, what free services are received by a commercial organization operating in the territory on a permanent basis (perhaps, for such commercial organizations, executive authorities have developed a number of additional services for example, free inclusion of information about the activities of these enterprises in a regional information booklet). It is necessary to identify the level of awareness of commercial organizations working on an ongoing basis about free services, determine the desired list and highlight quality criteria. free service and promote these services to increase the investment attractiveness of the territory.
It is possible to decompose according to two components of macrosegmentation, for example, along the axes WHO the consumer and WHAT the consumer expects from the territorial product (Table 4.3).
Thus, macrosegmentation allows you to clearly structure information about consumers (WHAT, HOW, WHO), carry out the necessary decomposition to deepen the analysis and is the basis for a more detailed study of consumers in territorial marketing. After the analysis of enlarged groups of consumers in territorial marketing, it is possible to conduct microsegmentation.
Decomposition of a consumer group and consumption goals
territorial product
Table 4.3
|
product |
Consumer groups |
||
|
Private individuals |
Commercial organizations |
||
|
permanent residence |
Private individuals constantly reside in the territory, interested in improving the quality of life |
permanent residents, that are owners and (or) employees of commercial organizations, the purpose of the activity is profit when high level social responsibility |
Permanently resident residents are members of NCOs of their territories who are ready to decide socially significant tasks strive for self-realization and self-development |
|
Temporary |
Private individuals of the territory have a variety of purposes of visiting, interested in selected quality of life parameters |
Commercial organizations of the territory, which are hired as shift workers method of residents of another territory, have commercial purpose of visit |
Representatives NPO, scientific organizations and other territories have development goals cooperation, professional |
|
Continuous business |
Private individuals constantly operate for receipt of income and expenditures (growing solvent demand of the territory), are often small businesses |
Commercial enterprises are constantly conduct commercial activities in the territory, may be non-residents of the territory, aimed at long-term commercial results, the level of social responsibility is different |
NGOs constantly lead commercial activity in this area, well know and express interests and needs of local residents and entrepreneurs, the goals of activities are diverse (health, ecology, sports, children, business rights) |
The end of the table. 4.3
|
The goals of the consumption of the territorial product |
Consumer groups |
||
|
Private individuals |
Commercial organizations |
||
|
Temporary wild) |
Private individuals sporadically operate for receiving wages(shift workers), growth of effective demand of this territory almost not |
Commercial enterprises occasionally conduct commercial activities in the territory (temporary workers), low social responsibility |
NGOs in other territories occasionally conduct non-commercial activity in this area, often as participants and other partners projects |