STAGES OF REFORMING THE SYSTEM
AND DIRECTIONS OF ITS REFORMING
STANDARDIZATION IN THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SYSTEM
LECTURE 6
1. general characteristics standardization systems in Russian Federation and directions for its reform.
2. Bodies and services of standardization of the Russian Federation.
3. The concept of technical regulations.
4. The procedure for the development, adoption, modification and cancellation of technical regulations.
5. Types of national standards of the Russian Federation.
STANDARDIZATION SYSTEM OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION- this is a set of organizational, technical, legal and economic measures carried out under the control of the national standardization body and aimed at the development and application of regulatory documents in order to protect consumers and the state.
1. INITIAL STAGE ( 1992-2002 .)
State standardization system ( GSS) began to function in 1992 in connection with the formation of the state independence of Russia as a separate state after the collapse of the USSR in 1991
State management of standardization was carried out Gosstandart of Russia through local authorities Centers for Standardization and Metrology (CSM), there were more than 90 of them.
The basis of the GSS was a fund of laws, by-laws, regulations, which was four-tier system:
1 level - technical legislation, the basis of which was the Law of the Russian Federation "On Standardization", which became invalid from the date of entry into the Law of the Russian Federation "On Technical Regulation" in 2002.
2 level – documents of the all-Russian level: state standards of the Russian Federation ( GOST R); interstate standards; state standards of the former USSR ( GOST); rules, norms, recommendations on standardization, metrology, certification; all-Russian classifiers technical, economic and social information;
3 level- documents whose scope is limited specific industry National economy - industry standards ( OST) - or the field of activity - the standards of the scientific, technical and engineering communities ( ONE HUNDRED); the OST category was introduced in 1960, the STO category was introduced in 1992.
4th level- documents with limited scope within the organization (enterprise)- enterprise standards ( STP) And specifications (THAT).
2. TRANSITION STAGE (2003- 2010)
With the adoption in December 2002 of the Federal Law "On Technical Regulation", the next stage of reforming the standardization system of the Russian Federation began - a transitional one. According to the law, it is equal to seven years, i.e. until 2010
In 2006 developed The concept of development of the national standardization system (adopted by order Government of the Russian Federation No. 266-r dated February 26, 2006), according to which the State Standardization System ( GSS) should be converted to the National Standardization System ( NSS) with change legal status systems from state to voluntary.
The national standardization body instead of the State Standard of Russia approved in 2004 federal agency on technical regulation, metrology and standardization - Rostekhregulirovanie.
The basis of the NSS is a fund of laws, by-laws, regulations, which was three-tier system:
1 level – technical regulations of the Russian Federation (TR) that set mandatory requirements to the objects of technical regulation (products, buildings, structures and facilities, processes of life cycle)
2 level – national standards of the Russian Federation (NS) that set requirements on a voluntary basis to the objects of technical regulation (products, buildings, structures and facilities, processes of the life cycle program).
3 level – organization standards (STO).
From the date of entry into force of the Federal Law "On Technical Regulation" national recognized as operating at that time in the country state (GOST R) And interstate standards ( GOST).
The transitional stage of reforming the standardization system of the Russian Federation in accordance with the Federal Law "On Technical Regulation" was to end in 2010 d, when the current NSS had to finally acquire the form and content in accordance with the underlying idea - i.e. must run by a non-governmental organization the TR fund should be finally formed within 7 years from the date of entry into force of the Federal Law "On Technical Regulation", and in connection with the end of the formation of the TR fund, the NC will be documents of purely voluntary use.
Is product standardization.
Standard translated from English - this is the norm, measure, sample. The main task of standardization is the creation of a system of normative and technical documentation (NTD), which defines progressive requirements for products manufactured both for the needs of the national economy, the population, the defense of the country, and for export, as well as control over the correct use of this documentation.
Current system product standardization allows you to develop and maintain up to date:
- unified technical language;
- unified ranks of the most important specifications products (tolerances and fits, voltages, frequencies, etc.);
- size ranges and standard designs of products for general machine-building applications (bearings, fasteners, cutting tool and etc.);
- system of classifiers of technical and economic information;
- reliable reference data on the properties of materials and substances.
Standardization is based on a number of principles:
- repeatability- defines the range of objects to which things, processes, relations that have one common property- repeatability either in time or in space;
- variability- creation of a rational variety - provides a minimum of rational varieties of standard elements included in the standardized object;
- consistency- defines the standard as an element of the system and leads to the creation of systems of standards interconnected by the internal essence of specific objects of standardization;
- interchangeability- in relation to technology, it involves the assembly or replacement of identical parts manufactured in different time and at different points in space.
State standardization system
At present, the state standardization system of the Russian Federation (SSS) has been formed, which regulates the processes of building, presenting and distributing standards in the Russian Federation. GSS includes 5 fundamental standards:
- GOST R 1.0-92. State system of standardization of the Russian Federation. Basic provisions;
- GOST R 1.2-92. State system of standardization of the Russian Federation. The procedure for the development of state standards;
- GOST R 1.3-92. State system of standardization of the Russian Federation. The procedure for agreeing, approving and registering technical conditions;
- GOST R 1.4-92. State system of standardization of the Russian Federation. Enterprise standards. General provisions;
- GOST R 1.5-92. State system of standardization of the Russian Federation. General requirements for the construction, presentation, design and content of standards.
State standards of the Russian Federation include:
- mandatory requirements for the quality of products, works and services that ensure safety for life, health and property, environmental protection, mandatory requirements for safety and industrial sanitation;
- mandatory requirements for compatibility and interchangeability of products;
- mandatory methods of control, requirements for the quality of products, works and services that ensure their safety for life, health of people and property, protection environment, compatibility and interchangeability of products;
- parametric series and standard design of products;
- basic consumer and operational properties of products, requirements for packaging, labeling, transportation and storage, as well as disposal of products;
- provisions that ensure technical unity in the development, production, operation of products and the provision of services, rules for drawing up technical documentation, tolerances and fit, general rules ensure product quality, safety and rational use all types of resources, terms, definitions and designations, metrological and other general technical rules and norms.
In the Russian Federation, regulatory documents on standardization are divided into the following categories:
- state standards of the Russian Federation (GOST RF);
- industry standards (OST);
- technical conditions (TU);
- standards of enterprises and associations of enterprises (unions, associations, concerns, joint-stock companies, intersectoral, regional and other associations (STP);
- standards of scientific and technical societies and engineering (unions, associations and other public associations) (ONE HUNDRED).
Depending on the object of standardization, its specifics and the content of the requirements developed for it, standards are divided into the following types:
- fundamental standards;
- standards for products, services;
- process standards;
- standards for methods of control, testing, measurement, analysis.
Standardization system - a set of rules for performing work on standardization, the composition of its participants, the rules for the functioning of the system as a whole.
It is obvious from the definition that a standardization system, like any management system(quality system, certification system), consists of a subject and an object. Cast subjects are the participants in standardization work, the key of which are standardization bodies and services, and as objects - documents in the field of standardization (DS) as carriers of the rules of procedures for its implementation.
One of the most important provisions The Federal Law on technical regulation (1.1) is establishing unified system documentation on standardization: national standards, all-Russian classifiers (including the rules for their development and application), codes of practice, standards of organizations, standards of foreign countries, etc. (see Subsection 1.2).
As of January 1, 2012, the fund of documents of the national standardization system included more than 25,000 documents.
More precisely: GOST - 18200; GOST R - 5956 documents; rules and recommendations - 1004.
The key documents are the standards of the "Standardization in the Russian Federation" complex. It includes (as of 01.01.13) 16 national standards (GOST R), including the fundamental standard GOST R. 0-2004 (2.6), which defines the main provisions of the standardization system in the country.
IN major countries In Europe, it is about the same in terms of volume: in Germany - 27,179, Great Britain - 22,589, France - 26,544 units. But the fund of ND operating in Russia is not limited only by national standards. It is necessary to take into account the norms of the federal executive authorities mentioned above (SanPiNs, SNiPs, etc.)
In the future (presumably after 2020), the current standardization system will finally acquire the form and content that correspond to the idea inherent in the entire organization, and foreign practice. It will be led by a non-governmental organization. In connection with the end of the formation of the TP fund, national standards will become documents of purely voluntary application.
Changing the status of the system does not mean that the state will not participate in the activities of the national system. Its regulatory role is laid down in Art. 11-17 FZ on technical regulation. In particular, it manifests itself in the regulation of the goals and principles of standardization, the tasks of the national body of the Russian Federation for standardization, the rules for the development and approval of national standards.
In the future, the functions of the national standardization body are assumed taking into account foreign experience hand over non-governmental organization- "non-profit partnership".
In the industrialized countries - EU members, primarily the UK, Germany, France, there are such national standardization bodies as the British Standards Institute - BSI; German Standards Institute - DIN; French Association for Standardization - AFNOR. All named foreign organizations are non-commercial in nature. Membership is unlimited: this includes representatives government organizations and firms, developers and consumers of regulatory documents. For example, BS1 has rallied over 15 thousand specialists, AFNOR - more than 3 thousand, DIN - about 2 thousand.
Participation of the state in the activities of these organizations is regulated by relevant documents (memorandum, agreement).
Bodies and services of standardization of the Russian Federation
Standardization bodies and services - organizations, institutions, associations and their subdivisions, the main activity of which is the implementation of standardization work or the performance of certain standardization functions.
Organs By standardization- these are bodies recognized at a certain level, the main function of which is to guide standardization work.
The Constitution of the Russian Federation (clause "r" article 71) refers the standards to issues of the exclusive jurisdiction of the Russian Federation. Since maintaining standards is a function of the state, the Federal Law on technical regulation (Article 14) establishes that the Government of the Russian Federation determines the body authorized to perform the functions of a national body. Authorized body must be a federal executive body that acts on behalf of the national body. Government Decree (1.5) establishes that the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology performs the functions of a national standardization body.
The national standardization body carries out the whole range of standardization activities, from the development of national standards to their publication and distribution. The national standardization body participates in the development of international and regional standards and represents the Russian Federation 1! international organizations carrying out activities in the field of standardization.
Rosstandart performs its functions directly and through its interregional territorial offices (MTU), as well as Russian services standardization.
The structure of the State Standard includes:
- - Central Interregional territorial administration(location central office territorial authority- Moscow city);
- - North-Western Interregional Territorial Administration (location of the central office of the territorial body - St. Petersburg);
- - Southern Interregional Territorial Administration (location of the central office of the territorial authority - Rostov-on-Don);
- - Privolzhsky Interregional Territorial Administration (location of the central office of the territorial body - Nizhny Novgorod);
- - Ural Interregional Territorial Administration (location of the central office of the territorial body - Yekaterinburg);
- - Siberian Interregional Territorial Administration (location of the central office of the territorial body - Novosibirsk);
- - Far Eastern Interregional Territorial Administration (location of the central office of the territorial authority - Khabarovsk).
MTU carry out technical supervision both in the field of technical regulation and in the field of ensuring the uniformity of measurements.
In the field of technical regulation, MTUs supervise compliance with the requirements technical regulations and mandatory requirements of national standards.
Standardization Services- specially created organizations and divisions for carrying out work on standardization at certain levels of government - state, industry, enterprises (organizations).
Russian standardization services - research institutes of Rosstandart and technical committees for standardization.
To research institutes Rosstandart, for example, includes the All-Russian Research Institute for Normalization in Mechanical Engineering (FGUP "VNIINMASH") - the leading institute in the development of scientific and methodological foundations national system of standardization, unification and aggregation in mechanical engineering; All-Russian Research Institute of Certification (FGUP VNIIS) is the leading institute in the development of theoretical and methodological foundations of technical regulation and confirmation of conformity of products and services, etc.
Technical committees for standardization (TC) are created on the basis of organizations specializing in certain types of products (services) and having the highest scientific and technical potential in this area. The main function of the TC is the development of standards. There are currently 354 TCs registered.
As mentioned above, any standard is a product of the agreed opinion of all parties (users) interested in this document. The task of the Technical Committee (hereinafter - TC) is to provide a "round table" of participants in the development of the draft standard, to present on an equal footing the opinions of manufacturers, consumers, public organizations. Therefore, these TCs include representatives of developers, manufacturers, suppliers, consumers (customers) of products, consumer societies (unions) and other interested enterprises and organizations, as well as leading scientists and experts in a particular field. According to the Federal Law on technical regulation, TC members can be legal entities: commercial and non-profit organizations(JSC Gazprom, JSC Russian Railways, etc.). TCs are responsible for the quality and timing of the draft standards they develop in accordance with the current legislation and concluded contracts for these works.
For example, we indicate the structure and composition of some TCs.
In TC 389 "Property Valuation" there are subcommittees (PC): PC 1 " General principles and terminology"; PC 2 "Evaluation of real estate"; PC 3 "Evaluation of movable property"; PC 4 "Evaluation of an operating enterprise"; PC 5 "Evaluation of intangible benefits".
By order of the State Standard (dated August 13, 2010 No. 3019), a new TC was created - "Protection of the temper of consumers based on product control at the stages of circulation and during the provision of services." The TC secretariat is entrusted to the Russian Consumer Institute.
To organize and coordinate work on standardization in the sectors of the national economy in necessary cases create subdivisions (services) of standardization of ministries (and other bodies government controlled) and parent standardization organizations from among organizations with high scientific and technical potential in the relevant fields of science and technology.
The heads of enterprises are directly responsible for the organization and the state of the standardization work performed at these enterprises. Enterprises create, if necessary, standardization services (department, laboratory, bureau) that perform research, development and other standardization work.
Standardization activities are carried out in accordance with the Federal Law "On Technical Regulation".
Standardization- activities to establish rules and characteristics for the purpose of their voluntary multiple use, aimed at achieving order in the areas of production and circulation of products and increasing the competitiveness of products, works or services.
Standardization in Russia carried out in order to:
- increasing the level of safety of life or health of citizens, property of individuals or legal entities, state or municipal property, environmental safety, safety of life or health of animals and plants and promotion of compliance with the requirements of technical regulations;
- ensuring scientific and technological progress;
- technical and information compatibility;
- interchangeability of products;
- increasing the competitiveness of products, works and services;
- rational use of resources;
- increasing the level of safety of facilities, taking into account the risk of natural and man-made emergencies;
- comparability of the results of research (tests) and measurements, technical and economic-statistical data.
TO documents in the field of standardization relate:
- national standards;
- standardization rules, norms and recommendations in the field of standardization;
- classifications applied in accordance with the established procedure, all-Russian classifiers of technical, economic and social information;
- organization standards.
National body of the Russian Federation for standardization:
- approves national standards;
- adopts a program for the development of national standards;
- organizes the examination of draft national standards;
- ensures the compliance of the national standardization system with the interests of the national economy, the state of the material and technical base and scientific and technological progress;
- takes into account national standards, standardization rules, norms and recommendations in this area and ensures their availability to interested parties;
- creates technical committees for standardization and coordinates their activities;
- organizes the publication of national standards and their distribution;
- participates in accordance with the charters of international organizations in the development international standards and ensures that the interests of the Russian Federation are taken into account when they are adopted;
- approves the image of the sign of compliance with national standards;
- represents the Russian Federation in international organizations carrying out activities in the field of standardization.
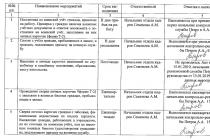
Any person can be a developer of a national standard. Notification of the development of a national standard is sent to the national standardization body and published in information system general use in electronic digital form and in printed edition federal executive body for technical regulation. The developer of the national standard must ensure that the draft national standard is available to all interested parties for review.
The developer finalizes the draft national standard, taking into account the received writing comments stakeholders, conducts a public discussion of the draft national standard and compiles a list of comments received in writing from interested parties with a summary of the content of these comments and the results of their discussion. The period of public discussion of the draft standard cannot be less than two months.
The notice of the completion of the public discussion of the draft national standard must be published in the printed edition of the federal executive body for technical regulation and in the public information system. The draft national standard is submitted by the developer to the technical committee for standardization, which organizes the examination this project. Taking into account the results of the examination, the technical committee prepares a reasoned opinion on the approval or rejection of the draft national standard.
The national standardization body, on the basis of documents submitted by the technical committee for standardization, makes a decision to approve or reject the national standard. The notification of the approval of the national standard is subject to publication in the printed edition of the federal executive body for technical regulation and in the public information system.
The Russian Federation has a State Standardization System (SSS), which includes all this moment standards, standards bodies and organizations.
GOST R - state standards in force on the territory of the Russian Federation.
OST - industry standards that apply to the area that is the industry of production a certain kind products.
STP - enterprise standards.
STO - standards of scientific, technical, engineering societies and other public associations.
State standards are developed for products, works and services intersectoral production or applications, as well as specific products of major national economic importance.
Requirements established by state standards to ensure the safety of products, works and services for the environment, life, health and property, to ensure technical and information compatibility, interchangeability of products, uniformity of methods for their control and uniformity of labeling, are mandatory government bodies management and subjects economic activity.
Compliance of products with these requirements is confirmed by mandatory product certification.
Other requirements of state standards for products, works and services are mandatory for business entities if they are confirmed by an agreement or technical documentation product manufacturer. Compliance of products with these requirements can be confirmed by voluntary product certification.
Compliance of products with the requirements of state standards can be certified by marking the products with the sign of conformity with state standards.
Business entities that have received licenses for labeling products with a mark of conformity, as well as the products themselves marked with this mark, are included in State Register products and services marked with the sign of compliance with state standards.
State standards are adopted by the State Standard of the Russian Federation, and in the field of construction and industry building materials - State Committee RF for Architecture and Construction (Gosstroy RF).
The requirements established in state standards can be both mandatory and recommendatory. This is one of the fundamental differences between standardization in Russia and standardization in the Soviet Union, where all the requirements of state standards were mandatory.
Mandatory requirements are subject to strict observance by all government bodies and business entities without exception. The customer and the contractor are obliged to include in the contract conditions on the conformity of the subject matter of the contract mandatory requirements state standards. The Law of the Russian Federation "On Standardization" and GOST R 1.0-92 include the following as mandatory:
requirements contained in the standard and providing
- 1. safety of a product, service, process for human health, the environment, property, as well as industrial safety and sanitary standards;
- 2. technical and information compatibility and interchangeability of products;
- 3. unity of control methods and unity of marking.
- 4. any requirements that are established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Industry standards(industry standards) are established for products of industry production or application, as well as for specific products assigned to the relevant department (ministry). OSTs are obligatory for all enterprises and organizations of this industry, as well as enterprises of other industries that use these products. Industry standards set Additional requirements, absent in GOSTs, which are necessary for the development, production and operation of products of intersectoral application. OSTs are developed for individual consumer goods, as well as for raw materials and semi-finished products used in the industry.
Enterprise standards are developed and approved by enterprises independently in order to improve the organization and management of production, technological processes, technological equipment.
The requirements of the STP are mandatory for compliance with other economic entities, if it is stipulated by the contract.
The standards of scientific, technical, engineering societies and other public associations are developed and adopted by these associations for the dynamic dissemination and use of research and development results obtained in various fields of knowledge. Business entities determine the need to apply these standards on their own.
Depending on the features of the object of standardization and the requirements for it, standards can be divided into the following types:
- Fundamental standards;
- standards for products and services;
- standards for processes;
- · standards for control methods (tests, measurements, analysis).
The fundamental standards establish general organizational and methodological provisions for a certain area of activity, as well as general technical requirements, norms and rules that ensure mutual understanding, technical unity and interconnection various areas science, technology and production in the processes of creation and use of products, environmental protection, safety of products, processes and services for life, health of people and property and other general technical requirements.
The objects of standardization here are terms and definitions, designations, General requirements and norms, methods, dimensional and parametric series according to the main characteristics, general consumer characteristics of products during their manufacture, supply and operation.
This type also includes standards for product quality management systems, which are organizational and methodological normative documents. GOSTs establish general requirements for the development, organization and operation of such systems. STP determine the special conditions of the enterprise, the features of the product and the technology of its manufacture, the organization of production and its management.
Standards for products (services) establish requirements for groups of homogeneous products (services) or for specific products (services).
These standards contain norms and requirements for the parameters of a particular product, depending on its type and purpose (for strength, heat resistance, reliability, safety, etc.), data on the shape and dimensions finished products or individual parts and parts, the chemical composition of materials, the range of grades, design features and the main dimensions of a certain group of products in order to unify them and ensure interchangeability.
Process standards establish the basic requirements for methods (methods, techniques, modes, norms) for performing various types of work in technological processes development, manufacture, storage, transportation, operation, repair and disposal of products.
Among other things, these standards establish requirements for labeling goods in order to inform the buyer about their features, requirements for packaging, transportation and storage conditions that ensure the preservation of the quality of the goods.
Standards for control methods establish methods (methods, techniques, modes, etc.) for testing, measuring, analyzing products during their creation, certification and use.
These standards regulate the methodology for determining the indicators of product properties. They specify the rules and methods for sampling, preparing them for testing and conducting tests, and the rules for processing test results. All this helps to ensure the objectivity and comparability of test results.
On a territorial basis, all standards can be divided into the following categories:
International standard - a standard adopted by an international organization for standardization. These are ISO non-governmental organizations ( international organization standardization) and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission). Therefore, the status of standards adopted for use in ISO and IEC member countries is voluntary.
Regional standard - a standard adopted by an international regional organization for standardization. For example, within the European Economic Union(EEC) there are intergovernmental organizations CEN (European Committee for Standardization), CENELEC (European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization), ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute). The standards developed under their leadership and approved by them have a mandatory status for the member countries of the EEC.
National Standard - A standard adopted by a national standards body. These are, for example, the state standards of Ukraine (DSU), Germany (DIN), Russian Federation (GOST R).
These categories of standards are commonly used in international practice. The standard is distributed within the competence of the standardization body. In Russia, the competent authorities in the field of standardization are GOSSTANDART of Russia and Gosstroy of Russia.