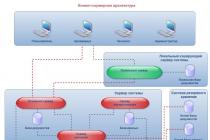
Social inequality-- form social differentiation where individual individuals social groups strata, classes are at different levels of the vertical social hierarchy and have unequal life chances and opportunities to meet needs.
Any society is always structured on many grounds - national, social class, demographic, settlement, etc. Structuring, that is, the belonging of people to certain social, professional, socio-demographic groups, can give rise to social inequality. Even natural genetic or physical differences between people can be the basis for the formation of unequal relationships. But the main thing in society is those differences, those objective factors that give rise to the social inequality of people. Inequality is an enduring fact of every society. Ralf Dahrendorf wrote: “Even in a prosperous society, the unequal position of people remains an important enduring phenomenon ... Of course, these differences are no longer based on direct violence and legislative norms on which the system of privileges was kept in a caste or estate society. However, apart from the coarser divisions of property and income, prestige and power, our society is characterized by many rank differences - so subtle and at the same time so deeply rooted that claims of the disappearance of all forms of inequality as a result of leveling processes can be perceived as at least skeptical.
Social differences are those that are generated by social factors: division of labor, way of life, social roles performed by individuals or social groups.
The essence of social inequality lies in the unequal access of different categories of the population to social benefits, such as money, power and prestige.
The problem of social inequality:
1. Significance of social classes
Belonging to a particular social class influences the behavior and thinking of people to a much greater extent than other aspects. social life, it determines their life chances.
First, in order to survive, the representatives of the upper strata of society need to spend a smaller share of available resources than the representatives of the lower social classes.
Secondly, representatives of the upper classes no longer have wealth. Their children are more likely to study at prestigious educational institutions and, most likely, will show better results than children of parents occupying a lower social position.
Thirdly, wealthy people average duration active life is higher than that of the poor.
Fourth, people with higher incomes experience greater satisfaction from life than people who are less well off, since belonging to a certain social class affects the lifestyle - the amount and nature of consumption of goods and services. Summarizing, we can say that social class a person determines almost all spheres of his life.
2. Social inequality.
Inequality and poverty are concepts closely related to social stratification. Inequality characterizes the uneven distribution of society's scarce resources - money, power, education, and prestige - between different strata, or strata of the population. The main measure of inequality is the number of liquid values. This function is usually performed by money. If inequality is presented in the form of a scale, then on one of its poles there will be those who own the largest (rich), and on the other - the smallest (poor) amount of goods. Thus, poverty is the economic and socio-cultural condition of people who have a minimum amount of liquid values and limited access to social benefits.
If inequality characterizes society as a whole, then poverty concerns only part of the population. Depending on how high the level of economic development of the country is, poverty covers a significant or insignificant part of the population. Sociologists call the scale of poverty the proportion of a country's population (usually expressed as a percentage) living near the official line, or threshold, of poverty.
Below the poor in the social hierarchy are the poor and the destitute. In Russia, poor, poor and exploited peasants were classified as poor. Poverty was called extreme poverty. A beggar was a person who lived on alms, collecting alms. But not everyone living in absolute poverty should be called beggars. The poor live either on earnings or on pensions and benefits, but they do not beg. It is more correct to refer to the poor as that category of those living in poverty who earn their living by regular begging.
Ways to solve social inequality
social inequality society class
The main ways of conducting social policy are:
- 1. protection of living standards by introducing various forms of compensation for price increases and indexation;
- 2. providing assistance to the poorest families;
- 3. issuance of assistance in case of unemployment;
- 4. policy enforcement social insurance, setting the minimum wages for employees;
- 5. development of education, health protection, environment mainly at the expense of the state;
- 6. conducting an active policy aimed at ensuring qualifications.
And the development of our planet in the global sense of the word? Interesting thoughts on this subject were expressed by a well-known physicist from the UK, Mr. Stephen Hawking. In his opinion, the most dangerous time period for our entire planet has now come. In his publication, which was recently published in the popular The Guardian, the scientist drew public attention to the ever-growing gap between social elites, including prominent politicians, financiers and ordinary people. This generalized term refers to the working and so-called middle class. The ubiquitous robotization reinforces the lack of practical need for human resources. To increase their profits, the elites are no longer so important simple people. This leads to internal contradiction and potential conflict between different social groups in our society. The Internet and technological tools that speed up processes social inequality allow a small group of people to extract super profits, creating a minimum of real jobs. On the one hand, this is a natural progress, which has always been considered positive. However, the fact that it is socially destructive in its essence is undeniable.
Increasing number of poor people
Let's try to figure this out together. Let's analyze practical examples how the common people's rejection of the trends of the modern structure of world society is already clearly manifested. Take at least as a basis the results of the last presidential elections in the United States of America. This country can be considered a good example, because. Western "democrats" popularize this model and often aggressively impose it on other peoples. But is everything all right there? The discussed results of the presidential elections actually surprised the American elites. They really have something to think about. Why did Trump win? Let's leave aside the explanations of the "democrats" that he left on jokes and racism. As statistics show, his victory was ensured by precisely those regions in which the working and middle class predominate, and which, accordingly, feel the most inequality in society. If you look at American financial statistics, over the past five decades, the average wage has increased by only $1. It went from $19 to $20 an hour. In other words, taking into account inflationary processes, the overall growth in labor productivity and widespread technological effectiveness did nothing to increase the wealth of the middle class. Moreover, since the 21st century, another trend has become more pronounced: the number of poor US citizens has increased significantly and the middle class has decreased in number. The number of those who have an income of more than $100,000 per year and were previously considered a slightly above average class has also become much smaller. Against this background, there was a reduction in American jobs. They "emigrated" to Southeast Asia, Mexico, South America. At the same time, for example, immigration from Mexico still increased. This only intensified the real competition in the intra-American market for vacancies for workers and employees.
America is one of the most corrupt countries
Further more. The financial crisis of 2008 exacerbated the negative picture in society. But, first of all, it was not banks and financial tycoons who suffered, but ordinary people. Some of them were left without houses, because. unable to make mortgage payments. The American elites bailed out the multinationals and banks, but they did so at the expense of the taxpayers. However, few thought about the latter. It is noteworthy that in 2010 the American Supreme Court a little-known decision was made with the name Citizens United. Briefly speaking, it established the updated rules of the political game in the American "democratic" state. What was it expressed in? Banks and large corporations were given the opportunity to participate with an unlimited number of banknotes in US election campaigns at all levels. American elites love to criticize third countries for corruption. However, in America itself, for more than 5 years, real corruption has been completely legalized. Long gone are the days when politicians who raised funds for their fair campaign through infusions of voters ended up defending their interests later. Today they are forced to serve rich "donors", without whose money there would be no victories. A similar picture is observed in the island of Great Britain. There exist specific features Britons, but in general Brexit can also be considered a clear indication of social inequality and that the populace is not satisfied with the current state of affairs.
Social discontent will grow
Considering that socio-economic and political problems, briefly analyzed on the example of the United States and Britain, can automatically spread to most other countries of the world, it becomes clear that the alienation between politicians, financial and industrial magnates and the people is growing more and more every year, which means that discontent in society will also grow. Thus, the reflections of the British physicist are absolutely logical and more relevant than ever for our time. The eternal question remains: what to do. There is no single answer. So far, there is only an understanding that the world is on the verge of change. Barriers must be removed, not created, both within countries and at the interstate level. And remember about eternal values, understanding that capital and resources should serve everyone, not the chosen ones.
Aspects of inequality
Inequality in human society is one of the topical objects of sociological research. Its reasons also lie in several main aspects.
Inequality initially implies different opportunities and unequal access to available social and material goods. Among these benefits are the following:
- Income - represents a certain amount of money that a person receives per unit of time. Often, income is directly wages that are paid for the labor produced by a person and the physical or mental strength expended. In addition to labor, it can also be the ownership of property that “works”. Thus, the lower the income of a person, the lower he is in the hierarchy of society;
- Education is a complex of knowledge, skills and abilities acquired by a person during his stay in educational institutions. The level of education is measured by the number of years of education. They can range from 9 years (junior high school). For example, a professor may have more than 20 years of education behind him, respectively, he will be much higher in level than a person who has completed 9 classes;
- Power - the ability of an individual to impose his worldview, point of view on the wider population, regardless of their desire. The level of power is measured by the number of people to whom it extends;
- Prestige is a position in society and its assessment, which has developed on the basis of public opinion.
Causes of social inequality
For a long time, many researchers have wondered whether a society can exist in principle if there is no inequality or hierarchy in it. In order to answer this question, it is necessary to understand the causes of social inequality.
Different approaches interpret this phenomenon and its causes in different ways. Let's analyze the most influential and famous.
Remark 1
Functionalism explains the phenomenon of inequality in terms of diversity social functions. These functions are inherent in different layers, classes and communities.
Functioning, development public relations are possible only if there is a division of labour. In this situation, each social group carries out the solution of tasks that are vital for the entire society. Some are engaged in the creation and production of material goods, while the activities of others are aimed at creating spiritual values. We also need a control layer that will control the activities of the first two - hence the third follows.
For the successful functioning of society, a combination of all three of the above types is simply necessary. human activity. Some are the most important, and some are the least. Thus, on the basis of function hierarchies, a hierarchy of classes and layers that perform them is formed.
Status explanation of social inequality. It is based on observations of the actions and behavior of specific individuals. As we understand, every person who occupies a certain place in society automatically acquires his status. Hence the opinion that social inequality is, first of all, inequality of statuses. It follows both from the ability of individuals to fulfill a certain role, and from the possibilities that allow a person to achieve a certain position in society.
In order for an individual to perform a particular social role, he needs to have certain skills, abilities and qualities (to be competent, sociable, to have the appropriate knowledge and skills to be a teacher, engineer). Opportunities that allow a person to achieve a particular position in society are, for example, in the ownership of property, capital, origin from a well-known and wealthy family, belonging to a high class or political forces.
An Economic Perspective on the Causes of Social Inequality. In accordance with this daughter of view, the main cause of social inequality lies in the unequal attitude to property, the distribution of material wealth. This approach manifested itself most clearly under Marxism, when it was the emergence of private property that led to social stratification society and the formation of antagonistic classes.
Problems of social inequality
Social inequality is a very common phenomenon, and therefore, like many other manifestations in society, it faces a number of problems.
First, the problems of inequality arise simultaneously in two of the most developed areas of society: in public and economic sphere.
When we talk about the problems of inequality in the public sphere, it is worth mentioning the following manifestations of instability:
- Uncertainty in one's future, as well as in the stability of the position in which the individual is now;
- Suspension of production due to dissatisfaction on the part of various segments of the population, which leads to a lack of production for the rest;
- The growth of social tension, which can lead to such consequences as unrest, social conflicts;
- The absence of real social elevators that will allow you to move up the social ladder both from the bottom up and vice versa - from the top down;
- Psychological pressure due to the feeling of unpredictability of the future, the lack of clear forecasts for further development.
In the economic sphere, the problems of social inequality are expressed as follows: an increase in government spending on the production of certain goods or services, a partially unfair distribution of income (not those who really work and use their physical strength receive, but those who invest more cash), respectively, another significant problem comes from here - unequal access to resources.
Remark 2
The peculiarity of the problem of inequality of access to resources lies in the fact that it is both a cause and a consequence of modern social inequality.
Social inequality - it's kind social division in which individual members of a society or group are at different levels of the social ladder (hierarchy) and have unequal opportunities, rights and obligations.
Main indicators of inequality:
- different levels of access to resources, both physical and moral (for example, women in Ancient Greece who were not allowed to the Olympic Games);
- various working conditions.
Causes of social inequality.
The French sociologist Émile Durkheim deduced two causes of social inequality:
- The need to encourage the best in their field, that is, those who bring great benefits to society.
- Different levels of personal qualities and talent in people.
Robert Michels put forward another reason: the protection of the privileges of power. When the size of the community exceeds a certain number of people, they put forward a leader, or a whole group, and give him more authority than everyone else.
Criteria of social inequality.
Key inequality criteria Max Weber stated:
- Wealth (difference in income).
- Prestige (the difference in honor and respect).
- Power (difference in the number of subordinates).
Hierarchy of inequality.
There are two types of hierarchy, which are usually represented as geometric shapes: pyramid(a bunch of oligarchs and great amount the poor, and the poorer, the greater their number) and rhombus(few oligarchs, few poor and the bulk of the middle class). A rhombus is preferable to a pyramid in terms of the stability of the social system. Roughly speaking, in a diamond-shaped version satisfied with life the middle peasants will not allow a handful of poor peasants to stage a revolution and civil war. You don't have to go far for an example. In Ukraine, the middle class was far from being the majority, and disgruntled residents of poor western and central villages overthrew the government in the country. As a result, the pyramid turned over, but remained a pyramid. There are already other oligarchs at the top, and at the bottom there is still a large part of the country's population.
Solving the problem of social inequality.
It is natural that social inequality is perceived as social injustice, especially by those who are in the hierarchy of social division at the lowest level. IN modern society the issue of social inequality is in the introduction of the bodies of social policy. Their responsibilities include:
- Introduction of various compensations for socially unprotected segments of the population.
- Help poor families.
- Benefit for the unemployed.
- Determining the minimum wage.
- Social insurance.
- Development of education.
- Healthcare.
- Ecological problems .
- Raising the qualifications of workers.
Even a superficial look at the people around us gives reason to talk about their dissimilarity. People are different by gender, age, temperament, height, hair color, intelligence level and many other features. Nature endowed one with musical abilities, the other with strength, the third with beauty, and prepared the fate of a weak invalid for someone. Differences between people, due to their physiological and mental characteristics, are called natural.
All societies famous stories, were organized in such a way that some social groups always had a privileged position over others, which was expressed in an unequal distribution of social benefits and powers. In other words, social inequality is inherent in all societies without exception. Even the ancient philosopher Plato argued that any city, no matter how small it may be, is actually divided into two halves - one for the poor, the other for the rich, and they are at enmity with each other.
Natural differences are far from harmless, they can become the basis for the emergence of unequal relationships between individuals. The strong force the weak, the cunning triumph over the simpletons. Inequality resulting from natural differences is the first form of inequality, in one form or another manifested in some species of animals. However, in in human society, the main thing is social inequality, inextricably linked with social differences, social differentiation.
Inequality between people exists in every society. This is quite natural and logical, given that people differ in their abilities, interests, life preferences, value orientations, etc. In every society there are poor and rich, educated and uneducated, enterprising and unenterprising, those with power and those without it. In this regard, the problem of the origin of social inequality, attitudes towards it and ways to eliminate it has always aroused increased interest among researchers, politicians and society, which consider social inequality as an injustice.
In the absence of social inequality, individuals would lose the incentive to engage in complex and laborious, dangerous or uninteresting activities, to improve their skills. With the help of inequality in income and prestige, society encourages individuals to engage in necessary, but difficult and unpleasant professions, encourages more educated and talented people, and so on.
Social inequality- a form of differentiation in which individual individuals, social groups, strata, classes are at different levels of the vertical social hierarchy and have unequal life chances and opportunities to meet needs.
In its most general form, inequality means that people live in conditions in which they have unequal access to limited resources of material and spiritual consumption.
Social inequality is perceived and experienced by many people (primarily the unemployed, economic migrants, those who are at or below the poverty line) as a manifestation of injustice. Social inequality, property stratification of society, as a rule, lead to an increase in social tension in society.
The main principles of social policy implementation are:
1. protection of living standards by introducing various forms of compensation for price increases and indexation;
2. providing assistance to the poorest families;
3. issuance of assistance in case of unemployment;
4. ensuring social insurance policy, establishing a minimum wage for employees;
5. development of education, protection of health, the environment, mainly at the expense of the state;
6. conducting an active policy aimed at ensuring qualifications.
Social those are called differences, which generated by social factors: way of life (urban and rural population), division of labor (mental and physical labor), social roles (father, doctor, politician), etc., which leads to differences in the degree of ownership of property, income received, power, achievement of social status, prestige, education.
Various levels social development are basis for social inequality, the emergence of rich and poor, the stratification of society, its stratification (a stratum is a layer that includes people with the same income, power, education, prestige).
Income- the amount of cash receipts received by a person per unit of time. It may be labor, or it may be the possession of property that “works”.
Education- a complex of knowledge obtained in educational institutions. Its level is measured by the number of years of study. Say, incomplete secondary school - 9 years. The professor has more than 20 years of education behind him.