Financial plan is a comprehensive plan of functioning and development in value (monetary) terms. In the financial plan, the efficiency and financial results production, investment and financial activities firms.
The financial plan reflects the final results of production economic activity. It covers inventory items, financial flows of all structural divisions, their relationship and interdependence.
Financial plan is the final synthesizing and reflecting in value terms the results of the company's activities. Information base for compiling financial plan is mainly accounting documentation. First of all, these are applications for balance.
In the financial plan of the company, enterprises are reflected:- income and receipts of funds;
- expenses and deductions Money;
- credit relationships;
- relationship with the budget.
The results of calculations of the said income and expenses are summarized in the form "Balance of income and expenses". Financial planning documents also include the company's balance sheet.
Enterprise balance
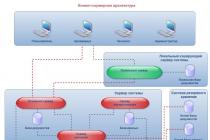
Enterprise balance- this is a summary table indicating the sources of capital and the means of its placement. The balance sheet serves as the basis for the first stage of financial planning - the analysis of financial indicators. In this case, the internal balance is usually used, i.e. balance reflecting the true financial position firms for internal use. Especially for publication, an external balance sheet is drawn up, usually aimed at underestimating the size of profits in order to reduce taxation amounts and create reserve capital and for other reasons. For better financial planning in firms, a plan of financial flows of the enterprise.
The income part reflects income from ordinary activities, operating income (various receipts, profit from joint activities etc.), and extraordinary income (income arising as a consequence of extraordinary circumstances of economic activity). Expenses are reflected in the same items as income.
Enterprise budget
An integral part of the short-term and long term planning is budgeting.
Any action plan must be accompanied by a budget (expenditure and income estimates), which is quantitative implementation of the plan, characterizing income and expenses for a specific period and determining the need for resources to achieve the goals set by the plan.
Can be compiled for: firms, enterprises, divisions.
The budget far exceeds the plan in terms of rigor and commitment. A budget only makes sense when it is put into practice. a simple estimate of income and expenses would be of no value.
The enterprise as a whole develops a general or main budget, which considers future profits in terms of value, cash flows and supporting plans. Core Budget is a financially quantified expression of marketing and production plans providing operational and financial management.
Types of financial plans
Strategic plans are plans for the general development of the business and long-term structure organizations. IN financial aspect strategic plans define the most important financial indicators and proportions of reproduction, characterize investment strategies and opportunities for reinvestment and accumulation. Such plans define the scope and structure financial resources necessary to maintain the enterprise as a business unit.
In its most general form, a strategic financial plan is a document containing the following sections:
1. Investment policy of the enterprise:
- fixed asset financing policy;
- policy of financing intangible assets;
- policy in the field of long-term financial investments.
2. Working capital management:
- cash management;
- management of receivables (credit policy of the enterprise);
- Inventory Management.
3. Dividend Policy enterprises.
4. Financial projections:
- enterprise income forecast;
- cost forecast;
- general need for capital;
- cash budget.
5. Accounting policy enterprises.
6. Management control system.
Current plans are developed on the basis of strategic ones by detailing them. If strategic plan gives indicative list financial resources, their volume and directions of use, then within the framework of the current planning, each type of investment is mutually agreed with the sources of their financing, the effectiveness of each source of financing is studied, financial assessment the main activities of the enterprise and ways to generate income.
Operational plans are short term tactical plans directly related to the achievement (production plan, plan for the purchase of raw materials and materials, etc.). Operational plans are included as an integral part of the annual or quarterly total budget of the enterprise.
To take into account possible factors of uncertainty and the risk associated with it, it is recommended to prepare several options for financial plans: pessimistic, optimistic and most probable.
operational plan
Operational financial plans are a cash flow management tool.
Financing of planned activities should be carried out at the expense of incoming funds. This requires day-to-day effective control over the formation of financial resources. In order to control the receipt of financial proceeds to the settlement account and the expenditure of cash financial resources, the organization needs to promptly financial planning, which complements the current one. When drawing up an operational financial plan, it is necessary to use objective information about the trends in economic development in the field of activity of the organization, inflation, possible changes in technology and the organization of the production process.
Operational financial planning includes:
- preparation and execution of the payment calendar;
- calculation of the need for a short-term loan;
- preparation of a cash register.
Legion Financial Group offers:
- * investment in business (from 10,000 rubles); - **participation in business projects through venture investments (investment of funds representing share capital, into promising fast-growing enterprises).
Plan number 1.
Investment for 1 month (no more than 100 thousand rubles) at 10%. When paying, withholding 3% of the total amount (insurance and banking commissions, tax deductions). Example: 10,000 rubles. + 10% = 11,000 rubles. - 3% \u003d 10670 rubles.
Plan number 2.
Investment for two months (no more than 500 thousand rubles) at 15% per month. After a month, 15% are transferred to the investor's account. After the 2nd month, the amount payable minus 7% (insurance and bank commissions, tax deductions) is transferred to the investor's account. The yield of the plan is 21.95%. Example: 10,000 rubles. - investments. Payment in a month 1500 rubles. Payment for the second month is: 10,000 rubles. + 15% = 11500 rubles. - 7% \u003d 10695 rubles. The total amount paid, taking into account the returned investments, is 12,195 rubles. * In case of early termination of the Agreement at the initiative of the Lender within a period exceeding one month from the date of its conclusion, the Loan Amount minus 10 (ten)% of the investment amount is paid to him. In this case, the amount is transferred within 30 days!
Plan number 3.
Investment for three months (no more than 1 million rubles) at 20% per month. Interest payments are made monthly. After the 3rd month, the amount payable minus 10% (insurance and bank commissions, tax deductions) is transferred to the investor's account. The yield of the plan is 48%. Example: 10,000 rubles. - investments. Monthly payment in the amount of 2000 rubles. Payment for the third month is: 10,000 rubles. + 20% = 12,000 rubles. - 10% = 10800 rubles. The total amount paid, taking into account the returned investment, is 14,800 rubles. * In case of early termination of the Agreement at the initiative of the Lender within a period exceeding one month from the date of its conclusion, he is paid the Loan Amount minus 15 (fifteen)% of the investment amount. In this case, the amount is transferred within 30 days!
Plan number 4.
Investment for six months (without limitation of amounts) at 22% per month. Interest payments are made monthly. After the 6th month, the amount payable minus 15% (insurance and bank commissions, tax deductions) is transferred to the investor's account. The yield of the plan is 113.7%. Example: 10,000 rubles. - investments. Monthly payment of 22% = 2200 rubles. Payment for the sixth month is: 10,000 rubles. + 22% = 12200 rubles. - 15% \u003d 10370 rubles. The total amount paid, taking into account the returned investment, is 21,370 rubles. * In case of early termination of the Agreement at the initiative of the Lender within a period exceeding one month from the date of its conclusion, he is paid the Loan Amount minus 20 (twenty)% of the investment amount. In this case, the amount is transferred within 30 days!
*In order to avoid double taxation, relationships with Investors are built on the basis of loan agreements with interest.
**Business projects with venture investment will be presented on the Legion Financial Group website:FG "LEGION"
Advantages:
1. The activities of the companies of the Legion financial group are legitimate, based on the provisions of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the legislation governing the activities of Companies with limited liability, consumer societies, as well as the national legislation of Switzerland and the UK.
2. Contracts are concluded with legal entity therefore, in accordance with the law, their execution is mandatory.
3. The reliability of transactions with investment amounts is guaranteed by the participation of the Swiss company Aecon Consulting AG in the project, insurance of the consolidated investment funds placed on the account with the Credit Suisse bank, as well as a bank guarantee of their return to the beneficiary's accounts.
4. The timeliness of interest payments and the return of investment amounts is additionally ensured by a permanently open credit line in a partner bank.
5. success investment investments is confirmed by the legality of the assets, the flawless operation of the trading platform and high level professionalism of traders.
Successful business development largely depends on adequate planning. This is especially true for enterprises that are new market players. It is important for their founders, firstly, to competently occupy their niche, secondly, to form a sustainable business model, and thirdly, to ensure the investment attractiveness of the company, as well as high credit ratings. All these problems can be solved by competent planning. How is the financial plan prepared? What is the nature of this source?
Main components of a financial plan
A financial plan is a set of documents. In general, it consists of:
Forecast on sales volumes;
Balance of revenue and expenses;
Schedule of estimated profitability;
Accounting balance.
Of course, in the methodology of individual enterprises, the principles for the formation of the corresponding source may differ significantly from this scheme. But it is widespread among Russian businesses. Let us consider the specifics of each of the noted components of the financial plan in more detail.
Sales forecast
This document involves, in essence, the study of the market segment in which the company operates and the subsequent determination of the size of its share, which, most likely, the company will be able to occupy. As a rule, the financial plan in this part is drawn up for several years in advance - for example, for 3 years. At the same time, the expected growth for the first year can be calculated on a monthly basis (since in this case, forecasts based on a study of current factors are likely to be very close to reality).
Estimated Profit Graph
The financial plan is largely related to forecasts. If the relevant sales document is intended to help shape revenue expectations, then the source under consideration is directly related to profit. That is, when it is calculated, forecasts for costs are also made.
Balance of revenue and expenses
This document is important from the point of view that the leaders of the company need to know which expenses and at what point in time will assume a return within the framework of current activities, and which will pay for themselves over time. Another function of the balance of revenue and expenses is to estimate the amount of costs necessary to achieve the required turnover (for example, sufficient in terms of the company's current obligations - credit, management, etc.). As a rule, the document in question is supplemented by a table that reflects the ratio of costs and income.

There is an official name for the corresponding component of the financial plan - "Profit and Loss Statement". He is part of financial statements, which the company must provide in government bodies Therefore, its formation is mandatory for many businesses. At the same time, the corresponding document is the most important in terms of drawing up a financial plan. It contains valuable and informative information that reflects the effectiveness of the company's business model.
Of course, the development of a company's financial plan may involve the formation of a balance of revenue and expenses in forms that differ significantly from the "Profit and Loss Statement". It can be more detailed or, conversely, less complex. However, the official form of the Profit and Loss Statement is considered by many entrepreneurs to be quite logical and informative, and therefore is widely used in business.
Balance sheet
This document, like the previous one, belongs to the official category. The enterprise must form it not only as part of the financial plan, but also as a necessary element of reporting provided to the Federal Tax Service. At the same time, the balance sheet is an important element of forecasting. Based on the figures that it reflects, management can analyze how effectively the company worked in the reporting period, and adjust the business development strategy if necessary. The balance sheet is one of the most detailed documents characterizing the activities of the enterprise. Through it, financial accounting is carried out. The chart of accounts of the balance sheet is an obligatory component of the activities of specialists of the relevant departments of the company dealing with monetary issues.
The document in question, as a rule, is created by enterprises without any special differences from the official form approved by the laws of the Russian Federation (although, as in the case of the profit and loss balance, the company has the right to determine its own criteria for the formation of the corresponding source). The legislator of the Russian Federation, therefore, has developed a fairly well-thought-out, logical and informative structure of the balance sheet, and companies are willing to use it not only in fulfilling reporting obligations, but also in the process of creating internal corporate financial plans.
It can be noted that the use of forms approved by the state is mandatory for budget institutions. So, every year, the relevant organizations, as a rule, are given the task of submitting a plan of financial and economic activity to a higher authority. It can be considered as an analogue of the corresponding document for private enterprises. Moreover, many businesses form a financial and economic plan based on the structure of the noted source developed by the state. But if reporting procedures do not require it, a private enterprise has the right to create documents according to its own concept.
So, the creation of a financial plan for the development of a corporation involves, first of all, the formation of four key sources. What is the best order to develop them? Let's try to create a step-by-step instruction that reflects the algorithm recommended by market experts for creating a financial plan.
Step-by-step instructions for drawing up a financial plan: main steps
Many experts in the field corporate governance consider it right, at the same time, to start work not with the formation of any of the noted documents, but with another source - a funding strategy. It thus precedes the creation of any of the four components of the plan noted above, which in question.

The next stage, within which a financial plan can be drawn up, is the development of a sales forecast. The fact is that the calculation of revenue is a procedure based on information that is more accessible in most cases than an analysis of possible costs. As a rule, a new enterprise enters an already existing market segment, the dynamics of demand in which is generally known to all players. From here you can calculate what sales volumes can be in relation to certain terms.
Once you have your sales forecast, it's time to work on the estimated profitability chart. Thus, the organization's management will have to work to identify, in turn, the likely dynamics of the organization's costs in relation to a particular period.
Having at your disposal revenue and profit forecasts, as well as actual figures reflecting commercial activities, you can form a balance sheet that takes into account relevant indicators. This document is more statistical, it records financial transactions that have already been completed. A similar function is performed by the balance sheet. Most often, it is formed simultaneously with the document in which profits and losses are recorded - largely because both of them together form, as we noted above, the financial statements that the enterprise must submit to government agencies.
Stages of drawing up a financial plan
So, the preparation of a financial plan can be carried out within the following main stages:
1. Defining a funding strategy.
2. Formation of revenue forecasts.
3. Determining the dynamics of costs.
4. Fixing the results of the company's activities in the balance of revenue and costs ("Profit and Loss Statement"), as well as in the balance sheet.

Of course, the marked structure of the formation of the source in question may be different. Thus, it is logical to assume that the financial plan of an organization that has just entered the market will not initially contain data on profits and losses, as well as a balance sheet. Relevant components will be added to it later.
It may well be that the balance, reflecting revenues and costs, will be supplemented not only by statistical, but also by forecast data. An organization's financial plan may suggest such a need if, again, the firm is just entering the market, and investors have a need to obtain as much detail as possible about its business model.
What information should be reflected in the marked sources - documents that form the financial plan of the organization? Let's consider the aspect concerning its content.
What should a financial plan include? As we noted above, it can consist of four key sources. They are also complemented by a funding strategy. Let us consider the content of the plan in relation to the sources, the essence of which we have considered above.
The financial plan of the enterprise is recommended to start with a strategy for acquiring and distributing the necessary capital. What should be included in this document? Its recommended structure assumes the presence of the following main sections in it:
Determining sources of revenue;
Formation of the spectrum of necessary expenses;
Identification of channels for attracting additional capital (through loans, investments);
Formation of key principles of interaction with the state (selection and justification of the organizational and legal form, taxation regime).
The revenue forecast involves the preparation of a document that will reflect:
Identification of key profit channels (for example, the sale of specific types of goods that are in the highest demand);
Identification of factors affecting sales dynamics (season, currency fluctuations, regulators' policy);
Formation of a forecast for revenue in relation to certain periods (month, quarter, year and other periods).
The graph showing the dynamics of expenses suggests a very similar structure:
Identification of key cost items (for example, wages, raw materials, transport services);
Identification of factors affecting costs;
Formation of forecasts for expenses.
In turn, the balance of revenue and costs, as well as financial statements have enough complex structure(if they are based on forms approved by the state). The purpose of these documents is to identify how effective the current business model of the organization is, to determine how profitable the company is in a particular billing period.
It is possible that the management of the enterprise decides to use official forms income statement and balance sheet. In this case, to fill them out, you will need access to the records of the movement of capital in the company, to the postings. So, it will be necessary to examine the chart of accounts of the financial and economic activities of the company. The data for filling in the marked forms is mainly taken from there. The chart of accounts of financial activities must, of course, be correctly drawn up. This is guaranteed by its standardization - at the level of federal legal acts.
What to look for when drawing up a financial plan?
So, we have studied what a financial plan of an enterprise is and in accordance with what algorithms it can be developed. Let us now consider the key nuances that are useful to pay attention to when compiling the components of this source.
The first thing to note is that the financial plan is one of many documents that are drawn up in order to optimize the organization's development model. It can complement other sources. Most often, it is an integral component, and at the same time a very important, larger document - a business plan. Its main function in this case is to form an idea among the founders of the organization, investors or creditors about the prospects for commercial activities. specific enterprise. The financial activity plan, as we noted above, will include data on revenue, costs, as well as statistical data reflecting them. All this information is needed by business founders and their partners.
The main thing is to reflect in the document what will be the main factors affecting the receipt and distribution of capital, how to recognize them in a timely manner and adapt the business model of the enterprise to possible changes. The plan of the financial and economic activity of the company allows you to determine the so-called "break-even point" of the company - the moment from which the revenue consistently exceeds the costs (in another interpretation - when the return of the established part of the investment is made).

Forecasting income and expenses is usually formed for several years - most often for 3 years. As we noted above, in the first year, you can distribute the corresponding indicators monthly. In the structure of income and expenses, those that are characterized by high stability or, conversely, volatility can be additionally distinguished. For example, with regard to the costs of the first type, it could be rent in accordance with the contract. Volatile spending can be associated with the import of goods from abroad. Their value may change due to changes in the exchange rate of the ruble in the foreign exchange market.
When drawing up a financial plan, one should pay closer attention, according to some researchers, not to the production aspect, but to the marketing one. A company can develop a completely unique, technological product, but the company's business model will be ineffective due to an insufficiently capacious sales market for the corresponding product at the prices that are included in the business plan as guaranteeing the profitability of the enterprise. The solution of the corresponding problem may involve not only financial analysis, but also the use, as an option, of sociological methods - surveys, communication with potential consumers on the Internet in order to identify their buying sentiment, demand potential.
In principle, when drawing up an algorithm for obtaining and distributing capital, one should not neglect promotion costs that are not directly related to production costs. It may well turn out that in order to occupy the necessary niche in the market, the enterprise will need to invest heavily in advertising - so that more target consumers know about the brand.

When drawing up financial plans, it is necessary to act in conditions of access to relevant sources of legislation. Need to stay up to date with the latest news legal sphere. The legislator can quite significantly change, relatively speaking, the tax rate. The task of the company's management is to find out about this in time and make the necessary adjustments to the financial plan.
Also, you should not plan savings on staff salaries. Initially, it is recommended that, if possible, it is recommended to lay in the budget of the company, firstly, the size of the staff, which is larger than may be required, based on profitability criteria, in order to increase if necessary overall performance enterprises in short time, and secondly, a sufficiently high value labor compensation. The organization must be attractive to the best specialists of the market segment in which it operates.
Who should develop the financial plan?
Who develops the organization's financial plans? In practice, it can be both ordinary specialists with the necessary competencies and managers. It is quite possible that the development of the corresponding plan will be outsourced. Which of the noted mechanisms for compiling an algorithm for obtaining and distributing capital is the most effective?
Eat a large number of points of view on this. Some researchers believe that the long-term part of the plan should be trusted to those employees who have access to strategic information. For example, this may be information about the specifics of the company's loans. Most likely, such employees will be people from among the top managers of the enterprise. In turn, the monthly periods of financial plans, perhaps, can best be worked out by specialists who understand in detail the specifics of specific production sites. They will not need to know information of a strategic nature. But their competence in terms of detailing business processes will probably be even higher than that of the company's management.

What is better - when the financial plan of the institution is developed by full-time specialists, or a scheme in which the solution of the corresponding task is outsourced? It depends on many factors. Many enterprises do not trust outsourcing schemes too much due to the use of secret technologies, drawings, and materials in production. Those firms that see their competitive advantage not in unique developments, but in an effective business model, in many cases they willingly agree to such cooperation mechanisms. Thus, competent, experienced specialists are involved in the preparation of business plans - albeit freelance ones. So, if these are accountants, then they, in particular, will always be able to properly take into account the chart of accounts of financial and economic activities, with which an unprepared specialist may have problems.