IN Soviet time A five-point system for assessing students' knowledge was developed. The criteria are clearly defined in special provision brought to the attention of students, parents and, of course, teachers. And at the present stage of development educational system Russia needed to modernize it. Let's take a closer look at this system.
Features of the modern grading system
The task of the teacher is to develop in schoolchildren the desire for self-education, to create in students the need to acquire knowledge and acquire skills of mental activity. But to evaluate such student activity, a 5-point system is not enough. Therefore, the problem of finding new evaluation criteria is currently particularly relevant.
There are several reasons for this:
- First of all, the five-point grading system is not suitable for determining the level of general cultural skills and special knowledge. And without them, a full-fledged adaptation of school graduates to the realities of society is impossible.
- In addition, there is an active development information systems, the possibility of individual growth in the development of which is also difficult to assess at 5 points.
Graduate Requirements
From the walls educational institutions real creators should come out, capable of taking responsibility, able to solve practical and theoretical problems of varying degrees of complexity. And the classic five-point system at school has long been outdated, since it is not compatible with the requirements of the new federal standards that have been introduced at the primary and secondary levels of schooling.

What determines the effectiveness of training
Conclusion
We repeat that the five-point assessment system, the criteria for which were developed in Soviet times, has lost its relevance and is recognized by leading teachers as untenable, unsuitable for new students. educational standards. It is necessary to modernize it, use new criteria for analysis personal growth schoolchildren and their educational achievements.
Only in the case of bringing the marking scale in line with the basic pedagogical principles, we can talk about taking into account the individuality of each child. Among the priorities that should be taken into account when modernizing the assessment system, we single out the use of a multi-level gradation of grades, due to which the educational achievements of schoolchildren will be adequately assessed.
Many countries have already abandoned the five-point rating system, recognizing such an option as untenable for the modern one. At present, the issue of changing it in Russia is also being decided. So, according to the Federal State Educational Standard primary school traditional points have already been removed so that the guys can develop, improve themselves without experiencing psychological discomfort.
To date, the main task facing the country's universities is to improve the quality of education. One of the key areas in its solution is the need to move to new standards. In accordance with them, a clear ratio of the number of hours for independent and classroom work is established. This, in turn, required a revision and the creation of new forms of control. One of the innovations was the point-rating system for assessing students' knowledge. Let's consider it in more detail.
Purpose
The essence of the point-rating system is to determine the success and quality of mastering the discipline through certain indicators. The labor intensity of a particular subject and the entire program as a whole is measured in credit units. The rating is a certain numerical value, which is expressed in a multi-point system. It integrally characterizes the progress of students and their participation in research work within any given discipline. The point-rating system is considered as the most important part of the quality control of the educational work of the Institute.
Advantages

Significance for educators
- Plan in detail the educational process in a particular discipline and stimulate the constant activity of students.
- Timely adjust the program in accordance with the results of control measures.
- Objectively determine the final grades in the disciplines, taking into account systematic activities.
- Provide gradation of indicators in comparison with traditional forms of control.
Significance for learners

Selection of criteria
- Implementation of the program in terms of practical, lecture, laboratory classes.
- Performance of extracurricular and classroom written and other works.
The timing and number of control activities, as well as the number of points allocated for each of them, are set by the lead teacher. The teacher responsible for the implementation of control must inform the students about the criteria for their certification at the first lesson.
Structure
The point-rating system involves the calculation of the results obtained by students for all types of learning activities. In particular, attendance at lectures, writing control works, performing typical calculations, etc. So, for example, overall result at the Department of Chemistry can consist of the following indicators:

Additional elements
The point-rating system provides for the introduction of fines and rewards for students. Teachers inform about these additional elements at the first lesson. Penalties are provided for violations of the requirements for the preparation and execution of abstracts, untimely submitted standard calculations, laboratory works etc. At the end of the course, the teacher can reward students by adding additional points to the number of points scored.
Transfer to academic marks
It is carried out on a special scale. It may include the following limits:

Another variant
The total number of points also depends on the level of labor intensity of the discipline (on the size of the loan). The point-rating system can be represented in the following form:

Point-rating system: pros and cons
The positive aspects of this form of control are obvious. First of all, active presence at seminars, participation in conferences will not go unnoticed. For this activity, the student will be awarded points. In addition, a student who scores a certain number of points will be taken into account, can receive an automatic credit in the discipline. Attendance at the lectures themselves will also be taken into account. The disadvantages of the point-rating system are as follows:

Conclusion
The key place in the point-rating system is control. It provides for end-to-end certification in all disciplines within the curriculum. As a result, the student is given rating score, which, in turn, depends on the degree of preparedness. The advantage of using this form of control is to ensure its information transparency and openness. This allows students to compare their results with those of their peers. Monitoring and evaluation of educational achievements acts as the most important element of the educational process. They must be carried out systematically throughout the semester and throughout the year. To do this, the ratings of students in the group and on the course in specific disciplines are formed, intra-semester and final indicators for a certain period are displayed.
Company management performance indicators are high economic indicators, stable position in the market, competitiveness, stability. They also include specific indicators: employee performance, low staff turnover, staff satisfaction and loyalty, discipline and the absence of conflicts. Unfortunately, one net salary is not able to provide this; it also does not have the proper stimulating effect on employees. That is why all sorts of point systems of incentives have arisen - bonuses, the main task of which is to motivate employees, inspire them, officially speaking, to further labor achievements. best suited to the aforementioned purposes.
As the name implies, when using such a scoring system of incentives, staff receive assessments, or points, for their work. They show what abilities professional growth of each employee and other qualities: organization, responsibility, diligence, ability to plan work time, work in a team, etc. According to the points scored, the employee is awarded a bonus.
Trainings and evaluation of managers are conducted by Aleksey Shirokopoyas, an expert in the development of managerial competencies. -consultant. Chief Editor magazine.
8-926-210-84-19. [email protected]
When scoring a staff incentive system, one should take into account the key point: setting goals, planning work and summing up the results are tied to the performance of tasks that can be assigned to an individual employee, department and organization as a whole.
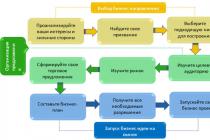
The project to develop and implement a new point system for incentives and remuneration (its model is schematically shown in the figure) requires not only the participation of HR department specialists, but also the support of the company's management and functional services and hence their interest. For the successful completion of the project, it is necessary to form working group capable of taking into account all the features of the organization's activities. So, when creating a scoring system for stimulating personnel, management should take into account the overall strategy, plans, policies of the enterprise, etc. Accordingly, the heads of departments form specific tasks for departments and employees, requirements for the quality of work and timely execution of internal regulations. The personnel service determines norms, standards and monitors the level of remuneration in its segment market economy. It is important that the work associated with the job responsibilities is discussed, and not the employees themselves. For the objectivity of the distribution of incentive payments in the company, a balance commission is created, the composition of which is elected by a simple majority of votes at general meeting labor collective for a period of one year.
Drawing
Model of the points system for staff incentives
When developing performance indicators for each business process, it is necessary to adhere to the following rules to avoid conflicts:
- Clear requirements for the evaluation of positions should be formed.
- The set of indicators should contain the required number of indicators to ensure full-fledged management of the business process.
- Each indicator must be measurable.
- The point system for stimulating personnel should be flexible, i.e. vary depending on the functionality of the unit.
- The stimulus fund in the division should be formed on the basis of the achievement of the company's strategic goals, and not on the basis of figures for the past period.
- The total amount of incentive payments cannot exceed the size of the "stimulus" fund.
To assess the results achieved by the employee, the degree of performance official duties, the quality of the labor expended, the employer must ensure control and accounting of the work performed. It is important that the immediate supervisor expresses his opinion on the quality of the employee’s work, thanks for Good work, gave constructive criticism if, for some indicators, the results were below the planned values. For each of the evaluation criteria, a scale (2-, 5-, 10-point, etc.) should be developed, which describes clear characteristics for each of the points. For example, "0" is set in the following cases:
- the work (corresponding item) is not submitted within the established deadlines;
- mistakes were made in the submitted documents (quality);
- deviation from the standard (quality);
- justified claims from management.
The points received are recorded in special evaluation forms, so that, summing up, the commission for the distribution of incentive payments (balance commission) can determine the specific amount of the bonus. Since tasks such as compiling professiograms, vacation schedules, training plans, career ladders and / or creating a list personnel reserve, can be one-time, therefore, the names of works and evaluation indicators for them are formed as necessary. Moreover, any employee of the company has the right to familiarize himself with the assessment of his own professional activity and in case of disagreement, file an application for appeal, which makes this point system of incentives and rewards fair.
Expert opinion on the point system for staff incentives
Valery Chemekov,
candidate of psychological sciences, one of the leading specialists and practitioners in grading,
assessment and development of personnel in Russia and the CIS, professional trainer and coach, author of a number of articles
in personnel periodicals
The author's approach to assessing the contribution of staff and determining the amount of bonuses has a right to exist. After all, KPI technologies are well known and widely used, based on objective, and most importantly, measurable criteria: sales volumes, financial indicators, timing, etc. We know that such indicators are applicable to the layer of employees who directly influence them - to "white collars", top managers. And what to do with the assessment of the work of those who are “distant” from the economic and operational processes of the company? For example, back office workers do not have SMART tasks, and, unlike the work of managers, the contribution of “clerks” (for example, accountants, personnel officers, etc.) is difficult to evaluate using objective criteria. But how to determine the degree to which they perform routine functions? The methodology proposed in the article makes it possible to evaluate the quality of the performance of official duties and the amount of labor expended.
Of course, such an assessment is subjective, since it is based on expert opinion, but its objectivity is ensured by the work of a whole team - the balance commission. In addition, the author rightly notes that the success of such a technology depends on the involvement of the manager: his participation not only in assessment activities, but also in setting goals and daily monitoring of the employee. Thus, the methodology encourages managers to be interested in the management process and take a more responsible approach to assessing the work of subordinates. It is also valuable that the employee knows for what he was awarded or not awarded points, i.e. receives feedback about your work.
At the same time, the reader would like to see what is the mechanism (criteria) for scoring, and how the maximum number of points per unit is determined. It is also clear that not all evaluation criteria have the same time perspective. So, planning tasks and projects - “compiling professiograms”, “scheduling vacations”, “drafting training plans”, “forming a list of personnel reserve” and “planning career ladders” - may not be set every week or even every month, but, for example, quarterly, and then remuneration according to these criteria can also be quarterly.
The author pointed to several objects of assessment, the main one being the degree of performance of official duties, as well as the quantity and quality of labor. If we assume that the degree of fulfillment of duties and the amount of labor expended are one and the same, and this is precisely what is measured using the methodology, then the assessment of the quality of labor remains beyond its scope. But the criterion of labor quality is very relevant for workers for whom this tool is intended.
In Art. 135 Labor Code The Russian Federation states: “Point systems of remuneration, including the size of tariff rates, salaries (official salaries), additional payments and allowances of a compensatory nature, including for work in conditions that deviate from normal, point systems of additional payments and allowances of a stimulating nature and bonus systems are established by collective contracts, agreements, local regulations in accordance with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms”.
Therefore, this scoring system for staff incentives is described in detail in the relevant local document (see the sample in the Appendix). The regulation on the point system for staff incentives consists of the following sections:
- General provisions.
- The procedure for establishing incentive payments.
- The procedure for deprivation of incentive payments.
- The activities of the commission for the distribution of incentive payments.
- Final provisions.
Evaluation forms for each business process are a tabular form with columns: job title, job title, evaluation criterion, scores (planned and actual). Incentive payments are distributed by the balance commission, which compiles a summary table of employee performance based on the results of the month. The sum of points for each employee is calculated, then all points for each business process are summed up. The value of one point (i.e., the amount of incentive payments for each employee) is determined by dividing the amount of incentive payments for the unit by the total number of points for the unit (by the number of its employees). It can be visualized as a formula:
Where S stim. employee - incentive payments for each employee, amount in rubles;
- S stimul. – incentive payments per subdivision, amount in rubles;
- B points - the maximum number of points for the unit;
- K employee score - the number of points scored by the employee.
Let's consider an example of using a scoring system for staff incentives
Fund for incentive payments for the personnel department - 60,000 rubles.
Number of department: 3 people.
The rating scale is 2-point (for simplicity): 0 - not done, 1 - done without any complaints.
The maximum number of points for each position in each unit must be equal; in this case it is 14 points.
Head of Human Resources (1) scored 12 points.
HR manager (2) scored 10 points.
HR Specialist (3) scored 13 points.
The maximum number of points for the unit: 14 × 3 = 42 points.
As a result, using the above formula, we get the amount that constitutes an incentive increase to the employee's official salary:
- S stimul. employee (1) = 60,000: 42 × 12 = 17,143 rubles.
- S stimul. employee (2) \u003d 60,000: 42 × 10 \u003d 14,286 rubles.
- S stimul. employee (3) = 60,000: 42 × 13 = 18,571 rubles.
Total for the division (personnel department): 50,000 rubles.
Further, these amounts for each employee are indicated in the minutes, which are signed by all members of the balance commission who were present at the meeting. Payments to employees are made on the basis of the order of the head of the company.
If we compare the scoring system of staff incentives with the currently popular KPI's system (from the English Key Performance Indicators), then the key differences between these systems are as follows:
- in the point system of staff incentives, the number of indicators is not limited to a few (usually 3-5) key indicators efficiency;
- the point system of staff incentives is based on performance indicators, and not on abstract KPIs;
- the accrual of points does not depend on employees occupying high positions or having a large economic or financial impact on the performance of the company, since points are awarded not for achieving goals, but for performing functions. Therefore, the results of the "clerks" of the back office do not depend much on the results of the "white collars" who earn money.
The use of a point system for staff incentives to assess the performance and motivate staff, despite the complexity and high requirements for the qualifications of employees conducting the assessment, while correct application contributes to the creation of an atmosphere of justice in the interaction between the manager and subordinates, stimulates the growth of responsibility and independence, increases employee satisfaction with the work performed and their commitment to their organization and unit. Evaluating the staff in this way, the manager can increase the efficiency of the enterprise and successfully manage it, because the introduction of this scoring system for staff incentives allows you to move from evaluation tools to a personnel management system.
Thus, is great way increasing the efficiency of corporate work.
I studied the official documents and is ready to explain what each mark is for.
First level (low): 1-2 points
Recognizing, recognizing and distinguishing concepts are requirements for the lowest marks.Yes, yes, no zero knowledge.
Second level (satisfactory): 3-4 points
Marks 3 and 4 are given to students who present educational material from memory, that is, a memorized theory is enough for satisfactory scores.
Third level (intermediate): 5-6 points
To get 5 or 6 points, the educational material must not only be reproduced, but understood. Plus, be able to describe and analyze actions with objects of study.
Fourth level (sufficient): 7-8 points
A student who claims to be of a sufficient level easily applies knowledge in practice and gives his own examples, similar to those given in the textbook. On the basis of a generalized algorithm, it also solves new learning problems. Another requirement is the ability to understand the essence of the objects being studied and perform actions with clearly defined rules.
Fifth level (high): 9-10 points
Applicants for "9" and "10" apply knowledge in unfamiliar, non-standard situations. And to solve qualitatively new problems. They independently describe, explain and transform the objects of study.
Is it worth it to equal the annual mark in the subject during the delivery of the CT? Before the introduction, this indicator did not coincide with the real test results. With the introduction of the new technique, this difference was leveled. And now you can roughly count on the result of the CT, equal to the annual score in the school subject, multiplied by 10.
If the material was useful to you, do not forget to put "I like" in our social networks
Pay systems
The system of remuneration within the meaning of art. 135 of the Labor Code is a set of rules defined by the employer in accordance with the norms labor law and regulating 3 aspects:
- the method of correlation of labor and remuneration of employees, on the basis of which the procedure for calculating wages is built;
- form (salary or tariff rate) and size (a specific amount or "fork") of the main part of the salary;
- compensation payments in the form of allowances and additional payments and incentive payments in the same forms or in the form of bonuses and other payments in terms of establishing the conditions, amount and procedure for calculation.
In a narrow sense, the system of payment is understood as a method of correlation of the measure of labor and the amount of remuneration of employees.
The most commonly used calculation systems are associated with 2 main forms of salary:
|
Salary form |
Calculation system |
The procedure for calculating salaries |
|
|
Piecework, when the payment is charged for the result labor activity: number of works performed, services rendered. |
Direct piecework |
Price for work, service × number of work performed, services rendered |
|
|
Piecework premium |
Price for work, service × number of work performed, services rendered + bonus |
||
|
piece-progressive |
Price for work, service × number of work performed, services rendered within the norm + increased price × number of works in excess of the norm |
||
|
piece-regressive |
Price for work, service × number of work performed, services rendered. For overfulfillment of the plan, prices do not increase. |
||
|
Indirect piecework |
The salary of an auxiliary employee depends on the salary of the main employees |
||
|
chord |
Payment for the volume (complex) of work |
||
|
Time-based, when the employee's pay depends on the hours worked. |
simple time-based |
Pay rate × working hours |
|
|
Salary × working hours |
|||
|
Time-bonus |
Pay rate × working hours + bonus |
||
|
Salary × hours worked + bonus |
There are less common systems:
- tariff (Article 143 of the Labor Code);
- non-traditional methods, including tariff-free, rating, etc.;
- wage systems for civil servants (Article 144 of the Labor Code).
The concept of a point system for calculating salaries
In the tariff-free procedure, the contribution of employees to the overall activity is assessed. One of the varieties of the tariff-free system is the method of point payment calculation.
The point order also assumes a direct dependence of the salary of the worker on his participation in general activities. The main unit for determining the scope of participation is the score. Points are assigned to workers for compliance with a number of characteristics. According to Art. 132 of the Labor Code for differentiation it is allowed to use the following criteria:
- qualification of the employee;
- the complexity of the work;
- the amount of labor;
- quality of work activity.
The qualifications of the worker are assessed on the basis of work experience and professional knowledge received as a result of special education.
It is more difficult to assess the amount of work performed, its complexity and the quality of an employee's work activity using general indicators. It is advisable for the employer to independently establish such criteria, and it will be more useful to use not one, but a group of criteria.
For example, in general terms, the amount of labor of an educator can be assessed by the totality of hours worked in the accounting period, and seamstresses - by the number of things made.
The quality of work must also be assessed in conjunction with the performance of the organization. For example, the quality of a seamstress's work can be assessed by the absence or minimum amount of marriage. The work of an office worker positive feedback customers, including those related to compliance with the rules of polite treatment (see the letter of the Ministry of Labor “On establishing the duty of polite treatment of customers for employees ...” dated September 16, 2016 No. 14-2 / B-888).
Similarly, criteria are established for assessing the complexity of the work.
Point, bonus and rating systems - varieties of points or independent ways of calculating salaries?
Wage systems are enough to confuse the names. To eliminate confusion, we denote the features of several other number systems:
- Bonus.
Is independent. The method of calculation includes the addition of salary and allowances as a percentage of profit. The salary is usually fixed within the tariff scale, and the percentage of the allowance is also specifically determined. Payment in fact is "floating" and depends on the profit received by the organization. - Rating.
It is also independent and is based on the inclusion of each worker in the rating, compiled on the basis of 3 characteristics:- the level of education;
- experience;
- place in the structure of the organization.
Earnings are calculated by multiplying the predetermined price of one rating point by the number of points assigned to the employee.
- Point.
This is a distorted name for the point system of remuneration.
The composition of wages under the point system
In the letter "On the establishment equal pay... "of 27.04.2011 No. 1111-6-1 Rostrud explained that in order to comply with Art. 3 of the Labor Code on the prohibition of discrimination, it is recommended to establish the same salary for employees of the same positions. Compliance with Art. 132 TC at the same time provides different size over-tariff part of the payment. This means that the amount of bonuses, allowances and other additional payments may be tied to the qualifications of workers, the complexity of their work, the quantity and quality of labor activity, and therefore may vary.
Taking into account the explanation of Rostrud, when determining the composition of earnings, various situations are possible.
Situation No. 1. The organization has employees who fill positions of the same name.
In this case, the employer can act on the basis of 2 options:
- Ignore the instructions of Rostrud and introduce a payment that depends entirely on the points scored. However, there is a high risk that the worker will consider different wages as discrimination. This will lead to an argument.
- Act in accordance with the instructions of Rostrud. Then the payment will be equal to the total salary and allowances from the general salary fund, calculated according to a separate formula. At the same time, a mixture with the time-based or piece-rate-bonus method is obvious.
Situation #2. The organization is small, all workers fill different positions.
In this case, the employer can safely use the point-based pay formula.
Payment Calculation Formula
The salary of employees when using the point method is calculated by the formula:
Salary = (employee points / total points of all employees) × total collective payroll.
The formula can be simplified if, overall, the total score and the organization's payroll income are stable. In this case, it is appropriate to define average price points as a ratio of income to the total number of points scored by workers. Then the formula becomes simpler:
Salary = employee points × average point value.
Interesting: since the point system is a kind of tariff-free system, the calculation formulas are similar. When calculating earnings by the tariff-free method, the following procedure is used:
Don't know your rights?
Salary \u003d percentage of labor participation × total salary fund of the team.
An example of calculating payment by a point system
Consider the examples of the head of the organization and his assistant payroll using the point method. To determine their earnings, you must proceed in the following order:
- determine the number of points earned by employees in accordance with the points table;
- determine the total number of points scored by all employees of the company;
- determine the amount of the organization's income aimed at paying wages;
- calculate payment.
The scoring table adopted in the company for the assistant manager is as follows:
|
Evaluation criterion |
Worker |
|||||
|
Quality of work |
Assistant Manager |
Organizational support for the activities of the head |
Lack of manager's work schedule |
Drawing up a work schedule |
Drawing up and tracking the relevance of the work schedule |
|
|
Technical support for the activities of the head |
Delays in the preparation of documentation |
Timely preparation of documentation, periodic support at meetings |
Timely preparation of documentation, accompanying the head at all meetings |
|||
|
Supervisor |
Organization of the activities of the company's employees |
Lack of direct instructions, subordinates are guided in their activities by job descriptions |
Assigning tasks to superiors structural divisions firms |
Setting individual tasks taking into account the professional skills of employees |
||
|
Development of strategic objectives |
Lack of planning for the future of the company |
Planning for the next six months |
Planning 3 years ahead |
|||
|
Number of work |
Work time |
0.5 bets |
0.75 stakes |
Full time work |
||
|
Qualification |
||||||
|
Education |
Specialized secondary |
Higher professional |
Higher professional, as well as professional development courses |
|||
This month, the assistant scored 17 points, the leader - 25 points.
If the total points of all employees is 100, and the payroll is 100,000, then the salary for an assistant will be 17 / 100 × 100,000 = 17,000, for the manager - 25 / 100 × 100,000 = 25,000.
Introduction by the employer of the points system
The transition to a point system or its initial establishment is carried out in accordance with the instructions of the Labor Code according to the following algorithm:
- The head of the organization or another person with the necessary powers, in pursuance of Art. 135 of the Labor Code decides on the introduction or transition to a point system. At the same time, the circle of persons who are entrusted with the development of a draft local act is determined.
- An employee or a group of employees, in pursuance of the decision, develops a draft act.
- The project in accordance with Art. 135 of the Labor Code is transferred to the representative body, which must, on the basis of Art. 372 of the Labor Code to issue a reasoned opinion on the submitted draft no later than 5 days later. The countdown starts from the day the draft is received by the representative body.
If a trade union or representative issues a negative opinion about the project, then the employer's representative is required to hold consultations within 3 days in order to resolve the contradictions. If, in this case, a mutually acceptable solution is not found, the project may be submitted for approval, but the representative body has the right to appeal against it.
If the organization does not have a trade union or other similar body and there is no employee representative, then proceed to the next step.
- When switching to a point system in accordance with Art. 72 of the Labor Code, the representative of the employer obtains the written consent of the employees.
Consent is not required if:
- the system is introduced into the organization as the first;
- the transition is caused by a change in technological or organizational conditions labor, and the further application of the old order is impossible (Article 74 of the Labor Code).
- The head of the organization or another person with the necessary authority approves the local act.
- The employer, in accordance with Art. 22 of the Labor Code introduces all workers to the new act.
Advantages and disadvantages of the point system
Considering the essence of the scoring method and the order of its introduction in the company, it is possible to single out the main positive and negative features that take place when using it. The advantages include the following:
- such a system is suitable for assessing labor devoid of specific indicators (for example, the number of goods produced), i.e., for assessing the performance of accounting staff, personnel services, secretariat, etc.;
- as criteria, it is possible to establish precisely those factors that are decisive for the successful activity of the employer. For example, in more large organization the criterion may be the volume and timeliness of the documentation being drawn up, and in a small one - the correctness of the design.
Among the minuses can be identified:
- "floating" amount of salary;
- complexity of use: for each period of payroll, it is necessary to re-evaluate the work of each employee;
- the emergence of a threat of conflicts between employees on the basis of establishing certain criteria as determining the number of points.
Let's summarize. The point system is suitable for organizations with a small team. It involves the calculation of earnings based on the correlation of the number of points scored by the employee and the total number achieved by all workers. The resulting ratio is multiplied by the total size wages, and the final figure is the income of an individual employee. The point system, also known as the point system, differs from the rating and bonus calculation procedures. The introduction of a point system in an organization is carried out in general order taking into account the views of representatives of the interests of workers, and in some cases - the workers themselves.