About the procedure for writing off bad debts at the expense of reserves, as well as debts not covered by reserves, BUKH.1C was told by 1C experts.
Accounts receivable is the sum of all debts owed to the organization by other legal entities and individuals. Accordingly, the organization's debtors are its debtors. Accounts receivable can be recognized as reliable (for example, if it is secured by a pledge, surety, bank guarantee), doubtful and hopeless (unrealistic to collect).
When debts of counterparties are recognized as uncollectible
An uncollectible receivable is an amount that an organization cannot recover from its counterparties for certain reasons. For the purposes of income taxation, bad debts (debts that are uncollectible) are recognized as debts if at least one of the conditions listed in paragraph 2 of Article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is met:
1. The established limitation period has expired. In the general case, this period is three years (clause 1, article 196 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The limitation period begins to run from the moment when the person found out or should have found out about the violation of his right (Article 200 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The limitation period is interrupted if the debtor performs actions indicating the recognition of the debt (Article 203 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). After a break, the limitation period begins to run again, but it cannot exceed ten years (clause 2, article 196 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, accounts receivable may not be recognized as uncollectible for quite a long time.
2. The obligation of the debtor is terminated due to the impossibility of its execution on the basis of an act of a state body or the liquidation of an organization.
3. There is a decision of the bailiff-performer on the completion of enforcement proceedings, confirming the impossibility of collecting debts. In this case, the executive document must be returned to the recoverer on the following grounds:
- it is impossible to establish the location of the debtor, his property or obtain information about the availability of funds and other valuables belonging to him;
- the debtor has no property that can be foreclosed.
If there are several grounds for recognizing receivables as uncollectible (for example, the expiration of the limitation period and the liquidation of the debtor organization), then the debt is recognized as uncollectible in the tax (reporting) period in which the first ground for recognizing the debt as uncollectible took place (letter Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 22, 2011 No. 03-03-06 / 1/373).
In the Regulation on accounting and reporting in the Russian Federation, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n (hereinafter referred to as the Regulation), only accounts receivable with an expired limitation period are explicitly named as debts uncollectible (clause 77 of the Regulation).
However, in practice, the criteria for recognizing debts as uncollectible, which are named in paragraph 2 of Article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, are also applied for accounting purposes.

How to write off bad debts...
... in accounting
Accounts receivable recognized as uncollectible (unrealistic to collect) are written off for each obligation on the basis of an inventory, written justification and an order (instruction) of the head of the organization (clause 77 of the Regulations). If in the period preceding the reporting period, the amounts of such debts were not reserved in the manner prescribed by paragraph 70 of the Regulations, then they are attributed to the financial results of a commercial organization or to an increase in expenses of a non-profit organization (paragraph 77 of the Regulations, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 14.01.2015 No. 07-01-06/188). note that, according to the Regulations, since 2011, the formation of a reserve for doubtful debts is the responsibility of the organization.
It should be borne in mind that writing off a debt at a loss due to the insolvency of the debtor is not a cancellation of the debt. This debt should be reflected off the balance sheet within five years from the date of writing off to monitor the possibility of its collection in the event of a change in the property status of the debtor (paragraph 2, clause 77 of the Regulations).
The amount of debt written off is accounted for on off-balance sheet account 007 “Debt of insolvent debtors written off at a loss”. If the debtor makes payment on a previously written off debt, it should be reflected in other income of the organization (clauses 4, 7 of PBU 9/99 “Income of the organization”, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06.05.1999 No. 32n).
We remind you that balances on account 63 “Reserves for doubtful debts” are not shown in the balance sheet, and the amount of receivables for which a reserve is formed is reflected minus the amount of the reserve. At the same time, retained earnings are reduced by the same amount (Chart of Accounts for Accounting for the Financial and Economic Activities of Organizations and Instructions for its Application, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n, clause 35 PBU 4/99 "Accounting Statements of the Organization", approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 6, 1999 No. 43n). In the statement of financial results, deductions to reserves for doubtful debts are reflected in other expenses (clause 11 of PBU 10/99 "Expenses of the organization", approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06.05.1999 No. 33n). Thus, the write-off of debts at the expense of the reserve does not affect the financial statements.
... in tax accounting
Amounts of receivables for which the limitation period has expired or whose collection is impossible are recognized as uncollectible and are written off in full, including VAT (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 24, 2013 No. 03-03-06/1/29315, dated June 11, 2013 No. 03 -03-06/1/21726).
The taxpayer may create reserves for doubtful debts in the manner prescribed by Article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Pay attention that only accounts receivable of the counterparty related to the sale of goods, performance of work, provision of services can be recognized as doubtful debt for the purposes of forming reserves in tax accounting. The amounts of deductions to reserves for doubtful debts are included in non-operating expenses on the last day of the reporting (tax) period and, accordingly, reduce the tax base of this period (clause 7, clause 1, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 3 of article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ).
If the taxpayer has decided to create a reserve for doubtful debts, then the write-off of bad debts is carried out at the expense of the amount of the created reserve (clause 4, article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If such a reserve was not created, or the amounts of bad debts are not covered by the reserve, then they are included in non-operating expenses (clause 2, clause 2, article 265, clause 5, article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, debts, the occurrence of which is not related to the sale of goods (works, services), can also be recognized as bad debts, for example:
- the amount of the advance payment transferred to the supplier on account of the forthcoming delivery of goods (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 04.09.2015 No. 03-03-06/2/51088);
- the amount of the debt under the loan agreement (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 16, 2015 No. 03-03-06/3/40956, dated April 24, 2015 No. 03-03-06/1/23763).
How should a taxpayer write off this kind of debt? The Decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation No. 4580/14 dated June 17, 2014 sets out the position according to which a bad debt that arose not in connection with the sale of goods (works, services) cannot participate in the formation of a reserve for doubtful debts (clause 1, article 266 Tax Code of the Russian Federation), therefore, it cannot be written off at the expense of the reserve. Such a debt may be taken into account as part of non-operating expenses when calculating the income tax base in accordance with subparagraph 2 of paragraph 2 of Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The date of recognition of non-operating expenses in tax accounting is established by paragraph 7 of Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Bad debts for which the limitation period has expired are taken into account in their composition on the last day of the reporting period in which the limitation period expires (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 6, 2015 No. No. 03-03-06/1/38).
If the amounts of reserves accrued in accounting and tax accounting differ, then there are differences in the assessment of income and expenses recorded on account 91 “Other income and expenses” and, as a result, profits and losses recorded on account 99 “Profits and losses” . In accordance with the Regulation on accounting "Accounting for income tax settlements", approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 19, 2002 No. 114n (hereinafter referred to as PBU 18/02), these differences are permanent. Permanent differences recorded on account 99 are taken into account when calculating income tax for the relevant period: a permanent tax liability (TLT) or a permanent tax asset (TLT) is recognized.
In the income tax return (approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 19, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected]) losses from writing off bad debts are reflected in Appendix No. 2 to Sheet 02:
- on line 302 "the amount of bad debts, and if the taxpayer has decided to create a reserve for doubtful debts, the amount of bad debts not covered from the reserve";
- in the total amount on line 300 "Losses equated to non-operating expenses - total".

Write-off of bad receivables in "1C: Accounting 8"
Let's consider how "1C: Accounting 8" (rev. 3.0) reflects operations to write off bad receivables.
Example 1
Calculation inventory
To check the amounts of receivables, as well as to compare the reserves for doubtful debts accrued in accounting and tax accounting, we will use the report Subconto analysis(chapter Reports).
In the command panel of this report, you need to set the period for generating the report, and from the presented list of subconto types, select the value Treaties. In the settings panel (button Show settings) on the tab Indicators set the flags BU (accounting data) And NU (tax accounting data).
Bookmark Selection you can set the selection for a specific contract with the debtor.
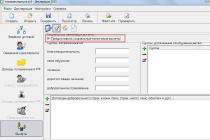
The generated report allows you to analyze the data of accounting and tax accounting for the selected agreement at the time of the expiration of the limitation period with details on the accounts (Fig. 1).

Rice. 1. Analysis of subconto under an agreement with the debtor
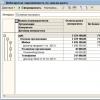
Before performing an operation to write off a bad debt, it is necessary to draw up an inventory of settlements. The document is used for this in the program. Act of inventory of settlements, accessed via the hyperlink of the same name from the sections Sales And Purchases.
Fill based on accounting data Accounts receivable(Fig. 2) is filled in with the balances of accounts receivable as of the date of the inventory as follows:
Table 1
|
Field |
Data |
|
"Contractor" |
Names of debtors |
|
"Settlement account" |
Accounts with accounts receivable |
|
Amount of accounts receivable |
|
|
"Confirmed" |
The amount for which there is documentary evidence. By default, all debt is considered confirmed |
|
"Not confirmed" |
An amount for which there is no documentary evidence. This field is filled in manually |
|
“Incl. statute of limitations expired" |
The amount of overdue receivables for which the limitation period has expired. This field is filled in manually |

Rice. 2. Act of inventory of settlements
Tabular part on the tab Accounts payable filled in the same way as filling a bookmark Accounts receivable. Under the terms of Example 1, there are no accounts payable.
Bookmark Settlement accounts displays a list of accounts for accounting for settlements with counterparties for which an inventory of settlements is performed.
By default, the specified list includes the following accounts:
- 60 "Settlements with suppliers and contractors";
- 62 "Settlements with buyers and customers";
- 66 "Settlements on short-term credits and loans";
- 67 "Settlements on long-term credits and loans";
- 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”, including accounts 76.07 “Lease settlements”, 76.27 “Lease settlements (in currency)” and 76.37 “Lease settlements (in USD)”;
- 58 "Financial investments".
The user can manage the list of accounts by adding other accounts or deactivating the accounts offered by the program.
Bookmark Taking inventory in the appropriate fields, you should indicate the timing of the inventory, the details of the basis document, as well as the reason for the inventory of calculations.
Bookmark Inventory commission you need to fill in the list of commission members by selecting them from the directory Individuals.
The chairman of the commission is indicated with a flag in the field Chairman.
Document Act of inventory of settlements does not generate postings, but allows you to generate the following printed forms of documents (button Seal):
- Inventory Order (INV-22);
- Settlement Inventory Act (INV-17).
Write off the buyer's debt
Under the terms of Example 1, the amount of accrued reserves in accounting and tax accounting differs.
In accounting, a bad debt in the amount of 150,000.00 rubles. will be fully written off at the expense of the reserve. In tax accounting, only 100,000.00 rubles will be written off from the reserve, and the remaining part of the debt in the amount of 50,000.00 rubles, not covered by the reserve, will be included in non-operating expenses.
A standard program document can be used to write off bad debt against reserves. Debt Adjustment(Fig. 3). This document is available from both Sales, and from the section Purchases.
Document header Debt Adjustment must be filled in by selecting the following values from the proposed lists:
table 2
The document is filled in automatically by clicking the button Fill ->Fill in balances for mutual settlements based on accounting data. Tabular part on the tab Buyer's debt (accounts receivable) is filled in with the balances of mutual settlements as of the date of adjustment as follows:
Table 3
|
Field |
Data |
|
"Settlement Amount" |
Total debt (150,000.00 rubles) |
|
The amount of debt write-off in accounting. By default, this amount corresponds to the total debt |
|
|
"Sum NU" |
Amount of write-off of debt in tax accounting. By default, this amount also corresponds to the total debt. Since we will write off the debt with this document at the expense of the reserve, it is necessary to manually correct the amount in the "Amount of NU" field (100,000.00 rubles) |
|
"Account Account" |
Account on which the debt was formed (62.01) |
Bookmark Withdrawal account you need to specify the account where the doubtful receivables will be assigned (63 “Reserves for doubtful debts”), as well as the details of the agreement with the counterparty and the settlement document for which the doubtful receivables were formed (see Fig. 3).

Rice. 3. Write-off of bad receivables against provisions
After posting the document, an accounting entry will be generated:
Debit 63 Credit 62.01 - for the amount of debt written off at the expense of the reserve formed in accounting (150,000.00 rubles).
For the purposes of tax accounting for income tax, amounts are entered into special resources of the accounting register:
The amount of NU Dt 63 and the amount of NU Kt 62.01 - for the amount of debt written off at the expense of the reserve formed in tax accounting (100,000.00 rubles). The amount of PR Dt 63 and the amount of PR Kt 62.01 - for a permanent difference, the amount of which is 50,000.00 rubles.
For income tax purposes, the remaining part of the bad debt is written off to non-operating expenses using the document Operation(chapter Operations-> Accounting-> Operations entered manually). In the form of a document to create a new transaction, click the button Add and enter the amounts in the special resources of the accounting register (in this case, the field Sum must remain empty):
Amount NU Dt 91.02 and Amount NU Kt 62.01 - for the amount of written-off debt not covered by the reserve (50,000.00 rubles). The amount of PR Dt 91.02 and the Amount of PR Kt 62.01 - for a negative constant difference (-50,000.00 rubles). When performing the scheduled operation Calculation of income tax for March, which is included in the processing of the Closing of the month, this permanent difference leads to the recognition of a permanent tax asset in the amount of 10,000.00 rubles.
Pay attention that in order to correctly complete the income tax return, it is important to correctly select the item of other income and expenses - Write-off of receivables (accounts payable). Then, when automatically completing the income tax return for the 1st quarter of 2017, losses from writing off bad debts in the amount of 50,000.00 rubles. will be reflected on line 302 of Appendix No. 2 to Sheet 02, as well as in the total amount on line 300 of Appendix No. 2 to Sheet 02.
To make sure that bad debts have been written off in accounting and tax accounting, you can generate a balance sheet for account 62 for March 2017, having previously made the appropriate settings on the Indicators tab. The balance sheet, formed on account 63 for March 2017, will show the absence of reserves for doubtful debts.
To account for the written-off debt in order to monitor the possibility of its collection (in accordance with paragraph 2 of clause 77 of the Regulations), we will also use the document Operation.
In the document form, to create a new transaction, you need to click the button Add and enter an entry for the amount of 150,000.00 rubles. on the debit of the off-balance account 007 indicating the relevant analytics (subconto Counterparties And Treaties).
Repayment of written-off debt
Let's add the condition of Example 1 and see how the program "1C: Accounting 8" edition 3.0 reflects the repayment by the buyer of a debt that was legally written off earlier as bad.
Example 2
To register the debt repayment by the buyer, you need to create a document Receipt to the current account with the type of operation Payment from the buyer. It is convenient to create a document based on a document Implementation (act, invoice), then the main details will be filled in automatically. Since the debt has already been written off in the accounting system, the funds received from the buyer are automatically determined as an advance payment. After posting the document, an accounting entry will be generated:
Debit 51 Credit 62.02 - for the amount of funds received from the buyer (150,000.00 rubles).
For the purposes of tax accounting for income tax, the amount is fixed in the resource Amount NU Kt 62.02.
The amount of the repaid debt must be included in the organization's other income, and also written off from the off-balance sheet account 007. These operations can be reflected in one document Operation(see Fig. 4).

Rice. 4. Inclusion of repaid debts in income