Consider the theoretical foundations on which to rely when organizing the accounting of materials at the stage of receipt. We will also get acquainted with the accounting records of the facts of the economic life of the enterprise, that is, with the postings as a result of solving situational problems. Let's learn how to keep records of the receipt of materials using account 10 Materials.
There are three things to consider when submitting materials:
- With sub-account selection. The sub-account is determined by the type of incoming materials;
- To evaluate the received values, that is, to understand at what cost, in accordance with the norms of accounting legislation, they should be registered, clause 5 of PBU 5/01 offers 2 ways;
- The selected method is fixed in the Accounting Policy.
Legislation operates with the concept of "actual cost". In short, this is what it cost the company to acquire or receive materials.
Important! Materials are accepted for accounting at actual cost. This rule always applies!
The legislation provides 2 options for reflecting the actual cost:
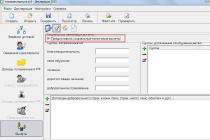
- The first reflection option - the actual cost is formed on account 10. The sub-account is determined by the type of materials received. Schematically, this can be represented as follows:
- The second reflection option - the actual cost is formed on account 15. Schematically, it looks like this:

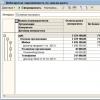
In this case, for incoming goods and materials, the company will use 3 accounts:
- Account 10 "Materials";
- Account 15 "Procurement and acquisition of material assets";
- Account 16 "Deviation in the value of material assets."
In addition, you will need to open sub-accounts for account 15 with names similar to the sub-accounts that make up synthetic account 10. This option sounds like “Materials are accounted for at accounting (planned) prices using accounts 15 “Procurement and acquisition of material assets” and 16 “Deviation in cost material values." Open sub-accounts to account 15 will sound similar to sub-accounts of account 10. For example, sub-account 15.1 “Procurement and purchase of raw materials and materials”.
The choice of the method of reflecting the actual cost is fixed in the Accounting Policy.
What is recognized as the actual cost
It is important to correctly reflect the actual cost. Depending on the method of receipt, the actual cost will be formed in different ways:

In practice, the arrival of materials at the warehouse has two scenarios:

Within the framework of this article, we will consider only admission based on documents.
Postings for typical acquisition and goods receipt situations
Example 1
Consider purchasing materials for a fee. Accounting policy option: the actual cost of materials is formed on account 10:
The company purchased the raw materials necessary for the production of products. The cost of raw materials according to the supplier's documents is 118,000 rubles, including VAT of 18,000 rubles. The cost of delivery according to the documents of the transport company is 12,500 rubles, excluding VAT. The storekeeper credited this raw material to the warehouse. The invoices of the supplier and the transport company have been paid.
Additional information: the company does not belong to the category of small, applies the general taxation regime. According to the accounting policy, the actual cost of materials is formed on account 10 "Materials".
Solution. From the summary table above, we see that according to the norms of accounting legislation, the actual cost of materials purchased for a fee is the sum of the organization's actual costs for the acquisition, excluding VAT and other reimbursable taxes, that is, the actual cost of such materials includes: the contract price of the supplier and other costs directly related to the acquisition of materials (transportation, procurement costs for bringing materials to a state in which they are suitable for use for the purposes envisaged by the organization).
Get 267 1C video lessons for free:
In our example, the actual cost of raw materials purchased for a fee is the sum of the supplier's price and shipping costs. Based on the type of materials, we use subaccount 10.01 "Raw materials and materials".
We form accounting entries for the receipt of materials at the warehouse:
| Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. | Facts of economic life |
| 10.01 | 60.01 | 100 000 | |
| 19.03 | 60.01 | 18 000 | |
| 68.02 | 19.03 | 18 000 | |
| 10.01 | 60.01 | 12 500 | |
| 60.01 | 51 | 118 000 | |
| 60.01 | 51 | 12 500 |
Example 2
We will study the acquisition of materials for a fee. Accounting policy option: the actual cost of materials is formed on account 15 using account 16, that is, on account 10, materials are accounted for at planned and estimated prices.
The company purchased the raw materials necessary for the production of products. The cost of raw materials according to the supplier's documents is 118,000 rubles, including VAT of 18,000 rubles. The cost of delivery according to the documents of the transport company is 12,500 rubles, excluding VAT. The accounting cost (planned and estimated) of the incoming raw materials is 107,500 rubles. The storekeeper credited this raw material to the warehouse. The invoices of the supplier and the transport company have been paid.
Additional Information. The company does not belong to the category of small, applies the general taxation regime. The company is newly formed, it has been operating for the first month and raw materials worth 50,000 rubles have been released for production.
Solution. For the solution, it will be necessary to determine the average percentage of deviations of the actual cost from the planned and estimated cost and the amount of deviations to be written off from account 16. Let's consider the nuances of working with accounts 15 and 16 upon receipt of materials.
In the debit of account 15, on the basis of settlement documents (invoices, invoices, acts), the cost of materials, delivery costs, procurement and expenses for bringing materials to a state in which they are suitable for use for the purposes provided for by the organization are recorded. With this option, materials are credited to account 10 at the planned and estimated price (forecasted) and only when the materials get to the warehouse, they arrive by posting on the debit of account 10 and credit of account 15 - in an amount equal to the planned and estimated price of materials. Planned and estimated prices are fixed by an internal document of the company.
When the company uses the registered materials or transfers them to production or sells, the difference accumulated on account 16 between the actual cost and the target price must be written off to costs. To do this, make the wiring:
- Dt 20 (23, 25, 26, 29, 44 ...) Kt 16 - the accumulated positive difference between the actual cost and the estimated price is written off.
To determine what amount of the difference on account 16 to include in the costs, it is necessary to calculate the average percentage of deviations. It is determined by a complex formula and this is not for beginners. But to understand the essence, let's assume that the company is new, then, based on the results of the first month of work, the accountant will take two indicators:
- The amount of deviations for materials received during the month;
- The cost of materials received per month (in planned and estimated prices).
We divide the first indicator by the second and find out the average percentage. We multiply the average percentage of deviations by the accounting cost of the materials written off.
Let's determine the average percentage of deviations in our example:
- Average deviation percentage: 5,000 / 107,500 = 4.65;
- If the accounting value of the materials to be written off is 50,000 rubles. multiply by 4.65%, we get the amount of deviations to be written off to costs in the amount of 2,325 rubles.
Now there is everything you need according to the methodology of working with a score of 15 and 16 upon receipt of materials. We form accounting entries:
| Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. | Facts of economic life |
| 15.01 | 60.01 | 100 000 | The receipt of raw materials is reflected on the basis of settlement documents |
| 19.03 | 60.01 | 18 000 | Input VAT from the cost of raw materials is taken into account |
| 68.2 | 19.03 | 18 000 | VAT deduction accepted, conditions under Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation met |
| 15.01 | 60.01 | 12 500 | Delivery costs are included in the actual cost of raw materials |
| 10.01 | 15.01 | 107 500 | Raw materials are credited to the warehouse at the planned settlement price |
| 16 | 15.01 | 5 000 | Reflected the excess of the actual cost over the book price |
| 60.01 | 51 | 118 000 | Payment made to the supplier of raw materials |
| 60.01 | 51 | 12 500 | Payment made to the transport company |
| 20 | 10.01 | 5 0000 | Raw material transferred to production |
| D20 | K16 | 2 325 | The accumulated positive difference between the actual cost and the planned price is written off |
Example 3. Receipt of materials on account of a contribution to the authorized capital.
The actual cost of materials contributed as a contribution to the authorized capital of the company is determined based on the monetary value agreed with the founders, unless otherwise provided by law.
If the expenses are taken by the receiving party, then the actual cost of materials increases by the amount of expenses incurred (clause 65 of the Guidelines for accounting for inventories).
Let's say 08/30/2016. the founder contributed materials to the account of the contribution to the authorized capital of the enterprise, which were estimated by the founders in the amount of 10,000 rubles. For the delivery of materials, the organization paid the transport company 2,950 rubles, including VAT 450 rubles. The transferring party provided an acceptance certificate and an invoice.
Additional Information. The company is formed in the form of LLC, applies the general taxation regime - OSNO. The company is a small business. Type of materials - production inventory. In her accounting policy, she recorded the following:
- Accounting is carried out at actual cost with reflection in accounting on account 10.
- Transport and procurement costs are included in the actual cost on account 10.
Example solution. The transferring party used the so-called VAT recovery mechanism. Being a VAT payer, in connection with the disposal of materials, the VAT company restored and provided an invoice. Thus, the transferring party increased its obligations to the budget. Why is that?
The fact is that earlier, when these materials were purchased, the organization used the VAT deduction by making the posting Dt 68.02 (VAT) Kt 19, but the materials were no longer used by the transferring party in activities subject to VAT. In such cases, the transferring party in its accounting is obliged to make a reverse entry Dt 19 Kt 68.02 (VAT) - this is called the VAT recovery mechanism.
Since the transferring party transferred materials with VAT, having previously shown an increase in obligations to the budget in terms of VAT, the receiving company is obliged to register the submitted VAT on the basis of the invoice.
The enterprise is classified as small, but in the Accounting Policy, according to the conditions of the example, a simplified method for assessing the initial cost is not fixed. There is such a right in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of May 16, 2016 No. No. 64n. But even if this were recorded, the company would not be able to attribute the delivery costs to expenses, since this innovation according to PBU 5/01 applies only to purchased materials for a fee. In the presented example, goods and materials were received without payment.
We form accounting entries for the receipt of materials on account of the contribution to the authorized capital:
| Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. | Facts of economic life |
| 10.09 | 75 | 10 000 | Receipt of materials under the memorandum of association in the assessment agreed by the founders |
| 10.09 | 60.01 | 2 500 | Clarification of the actual cost of materials for the amount of delivery (clause 65 of the Guidelines for accounting for inventories) |
| 19.03 | 60.01 | 450 | The presented VAT on transport services is taken into account on the invoice |
| 68.02 | 19.03 | 450 | VAT is accepted for deduction when all the conditions under clause 2 of article 171, clause 1 of article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are met |
| 19.03 | 83 | 1 800 | Accepted for VAT accounting from materials received as a contribution on the basis of clause 3 of article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
Bottom line: the actual cost of materials was formed on account 10.09 in the amount of 12,500 rubles.
Documentation of receipt of materials
All facts of the economic life of the organization as a legal entity must be documented.
The requirements of accounting legislation for documents are determined by the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. No. 402-FZ (as amended on May 23, 2016) "On Accounting". Article 9 of this law establishes a list of 7 mandatory details of an accounting document.
Forms and forms of documents used at the enterprise must be approved as part of the Accounting Policy for accounting purposes.
The table shows typical forms that can be used to develop your documents on their basis upon receipt of materials:
| Document | Explanations |
| Power of attorney to receive goods and materials (form M-2 and M-2a) | Issued upon receipt of inventory items by a trustee |
| Receipt order (form M-4) | It is filled in upon receipt of materials at the warehouse of the enterprise in the absence of discrepancies in quantity and quality claims |
| The act of acceptance of materials M-7 | It is filled in in case of discrepancies between the quantity indicated in the documents and the actual availability, as well as in case of inadequate quality of materials; This act is also drawn up to formalize the acceptance of materials received without documents (non-invoiced deliveries) |
| Advance report | Attached to it are documents confirming the fact of payment for purchased goods and materials, receipts for PKO of other organizations, checks of CCP |
| Accounting reference and others | To confirm settlements for specific transactions and other movements of materials on off-balance sheet and balance accounts that were not found in the above lines |
The enterprise has the right to develop its own forms of documents or use standard ones. It is not allowed to accept for accounting documents that document facts of economic life that did not take place.